Abstract
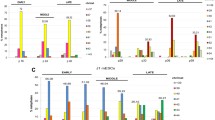
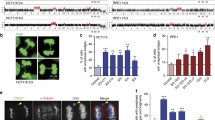
To examine chromosome instability in the absence of telomerase, we established mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) lines from late generation mTR−/− and wild-type animals and examined metaphases using telomere fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and spectral karyotyping (SKY). In early passages, mTR−/− G6 cell lines showed more chromosome ends with no telomere signal, more chromosome end-to-end fusions and greater radiosensitivity than wild-type lines. At later passages, however, the rate of genomic instability in the wild-type MEFs increased to a level similar or higher than seen in the mTR−/− G6 cell lines. This high degree of instability in wild-type MEF lines suggests that post-crisis MEFs should not be considered genetically defined cell lines. Surprisingly, the increased radiosensitivity seen in early passage mTR−/− G6 cultures was lost after crisis. Both post-crisis mTR−/− G6 MEFs and wild-type MEFs showed loss of p53 and γ-H2AX phosphorylation in response to irradiation, indicating a loss of DNA damage checkpoints.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blasco MA, Lee H-W, Hande PM, Samper E, Lansdorp PM, DePinho RA, Greider CW (1997) Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell 91:25–34
Cahill DP, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Lengauer C (1999) Genetic instability and darwinian selection in tumours. Trends Cell Biol 9:M57–M60
Chang S, Khoo CM, Naylor ML, Maser RS, DePinho RA (2003) Telomere-based crisis: functional differences between telomerase activation and ALT in tumor progression. Genes Dev 17:88–100
Chin L, Artandi S, Shen Q, Tam S, Lee S-L, Gottlieb G, Greider CW, DePinho RA (1999) p53 deficiency rescues the adverse effects of telomere loss in vivo and cooperates with telomere dysfunction to accelerate carcinogenesis. Cell 97:527–538
Dunham MA, Neumann AA, Fasching CL, Reddel RR (2000) Telomere maintenance by recombination in human cells. Nat Genet 26:447–450
Espejel S, Blasco MA (2002) Identification of telomere-dependent “senescence-like” arrest in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 276:242–248
Goytisolo FA, Samper E, Martin-Caballero J, Finnon P, Herrera E, Flores JM, Bouffler SD, Blasco MA (2000) Short telomeres result in organismal hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation in mammals. J Exp Med 192:1625–1636
Greider CW (1996) Telomere length regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 65:337–365
Greider CW (2000) Cellular responses to telomere shortening: cellular senescence as a tumor suppressor mechanism. Harvey Lect 96:33–50
Hande MP, Samper E, Lansdorp P, Blasco MA (1999) Telomere length dynamics and chromosomal instability in cells derived from telomerase null mice. J Cell Biol 144:589–601
Harrington L, Robinson MO (2002) Telomere dysfunction: multiple paths to the same end. Oncogene 21:592–597
Harvey DM, Levine AJ (1991) p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo fibroblasts. Genes Dev 5:2375–2385
Hemann MT, Hackett J, IJpma A, Greider CW (2000) Telomere length, telomere binding proteins and DNA damage signaling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol LXV:275–279
Hemann MT, Rudolph KL, Strong MA, DePinho RA, Chin L, Greider CW (2001a) Telomere dysfunction triggers developmentally regulated germ cell apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 12:2023–2030
Hemann MT, Strong MA, Hao LY, Greider CW (2001b) The shortest telomere, not average telomere length, is critical for cell viability and chromosome stability. Cell 107:67–77
Henson JD, Neumann AA, Yeager TR, Reddel RR (2002) Alternative lengthening of telomeres in mammalian cells. Oncogene 21:598–610
IJpma A, Greider CW (2003) Short telomeres induce a DNA damage response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 14:987–1001
Kamijo T, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Quelle DE, Downing JR, Ashmun RA, Grosveld G, Sherr CJ (1997) Tumor suppression at the mouse INK4a locus mediated by the alternative reading frame product p19ARF. Cell 91:649–659
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Dai Y, Hardy S, de Lange T (1999) p53- and ATM-dependent apoptosis induced by telomeres lacking TRF2. Science 283:1321–1325
de Lange T (2002) Protection of mammalian telomeres. Oncogene 21:532–540
Lansdorp PM, Verwoerd NP, van de Rijke FM, Dragowska V, Little M-T, Dirks RW, Raap AK, Tanke HJ (1996) Heterogeneity in telomere length of human chromosomes. Hum Mol Genet 5:685–691
Lee H-W, Blasco MA, Gottlieb GJ, Horner JW, Greider CW, DePinho RA (1998) Essential role of mouse telomerase in highly proliferative organs. Nature 392:569–574
Liyanage M, Coleman A, du Manoir S, Veldman T, McCormack S, Dickson RB, Barlow C, Wynshaw-Boris A, Janz S, Wienberg J, Ferguson-Smith MA, Schrock E, Ried T (1996) Multicolour spectral karyotyping of mouse chromosomes. Nat Genet 14:312–315
Lundblad V, Blackburn EH (1993) An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1-senescence. Cell 73:347–360
McClintock B (1941) The stability of broken ends of chromosomes in Zea mays. Genetics 26:234–282
Peltomaki P, de la Chapelle A (1997) Mutations predisposing to hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Adv Cancer Res 71:93–119
Sherr CJ, DePinho RA (2000) Cellular senescence: mitotic clock or culture shock? Cell 102:407–410
van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T (1998) TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions. Cell 92:401–413
Todaro GJ, Green H (1963) Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol 17:299–313
Varley H, Pickett HA, Foxon JL, Reddel RR, Royle NJ (2002) Molecular characterization of inter-telomere and intra-telomere mutations in human ALT cells. Nat Genet 30:301–305
Wong KK, Chang S, Weiler SR, Ganesan S, Chaudhuri J, Zhu C, Artandi SE, Rudolph KL, Gottlieb GJ, Chin L, Alt FW, DePinho RA (2000) Telomere dysfunction impairs DNA repair and enhances sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Nat Genet 26:85–88
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Michael Hemann, Forrest Spencer and members of the Greider laboratory for critical reading of the manuscript, Margaret Strong for technical support and Dr. Steve Elledge for providing the Chk2 antibody. This work was supported by NIH grant CA16519 to C.W.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Ishikawa
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, LY., Greider, C.W. Genomic instability in both wild-type and telomerase null MEFs. Chromosoma 113, 62–68 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0291-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0291-7