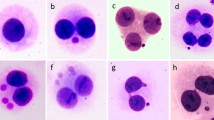
Abstract
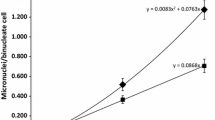
Ionizing radiation can induce a wide range of DNA damage that leads to chromosomal aberrations. Some of those aberrations (dicentrics and micronuclei) are applied in biodosimetry. Biological dosimetry assumes similar radiosensitivity of each donor, but it does not exclude inter-individual variations in radiation susceptibility. Therefore, for biological reasons, it is always challenging to investigate inter-individual variability in response to radiation. For mechanistic reasons, it is also interesting to investigate the correlation between dicentric and micronuclei formation in response to radiation. In this experiment, irradiated blood specimens from 14 healthy male and female donors have been used to evaluate inter-individual variability in response to the genotoxic effects of X-ray radiation, as well as the dose–response relationship and test sensitivity using two endpoints (dicentrics and micronuclei). The results showed similar patterns of cytogenetic biomarker distribution between donors, but differences in the response of some donors at some doses. Data also showed that responses of male donors were better detected using the dicentric test, while for females, micronucleus frequencies were higher in response to the same dose of radiation. No influence of smoking status or age on specific responses was observed. Group variability in response to radiation was evaluated using coefficient of variation for each group of individuals irradiated with the same doses; as the dose increases, group variability becomes substantially lower. Despite sporadic inter-individual variability, trend of radiation-induced changes was similar. Produced calibration curves for both types of damage revealed dicentrics as genetic damage more typical for radiation than micronuclei.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsbury EA, Bakhanova E, Barquinero JF, Brai M, Chumak V, Correcher V et al (2011) Review of retrospective dosimetry techniques for external ionising radiation exposures. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 147(4):573–592
Antunes AC, Martins V, Cardoso J, Santos L, Monteiro Gil O (2014) The cytokinesis-blocked micronucleus assay: dose estimation and inter-individual differences in the response to γ radiation. Mutat Res 760:17–22
Bolegenova NK, Bekmanov BO, Djansugurova LB, Bersimbaev RI, Salama SA, Au WW (2009) Genetic polymorphisms and expression of minisatellite mutations in a 3 generation population around the Semipalatinsk nuclear explosion test site, Kazakhstan. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212(2009):654–660
Bonassi S, Fenech M, Lando C, Lin Y, Ceppi M, Chang WP et al (2001) Human MicroNucleus project: international database comparison for results with the cytokinesis block micronucleus assay in human lymphocytes: I. Effect of laboratory protocol, scoring criteria, and host factors on the frequency of micronuclei. Environ Mol Mutagen 37:31–45
Bonassi S, Neri M, Lando C et al (2003) Effect of smoking habit on the frequency of micronuclei in human lymphocytes: results from the Human MicroNucleus project. Mutat Res 543:155–166
Bonassi S, Ugolini D, Kirsch-Volders M, Stromberg U, Vermeulen R, Tucker D (2005) Human population studies with cytogenetic biomarkers: review of the literature and future prospective. Environ Mol Mutagen 45:258–270
Ceppi M, Gallo F, Bonassi S (2011) Study design and statistical analysis of data in human population studies with the micronucleus assay. Mutagenesis 26:247–252
Di Giorgio M, Sardi M, Busto E, Vallerga M, Taja M, Mairal L (2010) Assessment of individual radiosensitivity in human lymphocytes using micronucleus and microgel electrophoresis “Comet” assays. In: Proceedings of third European IRPA congress June 14 − 18, Helsinki, Finland
Fenech M (1993) The cytokinesis-block micronucleus technique and its application to genotoxicity studies in human populations. Environ Health Perspect Suppl 101:101–107
Fenech M (2007) Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Protocol. Nat Protoc 2:1084–1104
Fenech M, Bonassi S (2011) The effect of age, gender, diet and lifestyle on DNA damage measured using micronucleus frequency in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mutagenesis 26:43–49
Fenech M, Morley AA (1986) Cytokinesis-block micronucleus method in human lymphocytes: effect of in vivo ageing and low-dose x-irradiation. Mutat Res 161:193–198
Fenech M, Neville S, Rinaldi J (1994) Sex is important variable affecting spontaneous micronucleus frequency in cytokinesis-blocked lymphocytes. Mutat Res 313:203–207
Fenech M, Holland N, Zeiger E, Chang WP, Burgaz S, Thomas P et al (2011) The HUMN and HUMNxL international collaboration projects on human micronucleus assays in lymphocytes and buccal cells-past, present and future. Mutagenesis 26:239–245
Ginsberg G, Angle K, Guyton K, Sonawane B (2011) Polymorphism in the DNA repair enzyme XRCC1: utility of current database and implications for human health risk assessment. Mutat Res 727:1–15
IAEA, WHO (2011) EPR-biodosimetry cytogenetic dosimetry: applications in preparedness for and response to radiation emergencies. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna International Centre, Vienna
INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY (1986) Biological dosimetry: chromosomal aberration analysis for dose assessment. Technical reports series No. 260, IAEA, Vienna
INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY (2001) Cytogenetic analysis for radiation dose assessment. International atomic agency technical report series 405. IAEA, Vienna
Kocisova J, Sram RJ (1990) Mutagenicity studies on paracetamol on human volunteers. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus method. Mutat Res 244:27–30
Maki-Paakinen J, Walles S, Osterman-Golkr S, Norrpa H (1991) Single-strand breaks, chromosome aberrations, sister chromatid exchanges and micronuclei in lymphocytes of workers exposed to styrene during the production of reinforced plastics. Environ Mol Mutagen 17:27–31
Migliore L, Parrini M, Sbrana I, Biagini C, Battaglia A, Loprieno N (1991) Micronucleated lymphocytes in people occupationally exposed to potential environmental contaminants: the age effect. Mutat Res 256:13–20
Mutlu-Türkoğlu Ü, Ilhan E, Öztecan S, Kuru A, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2003) Age-related increases in plasma malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl levels and lymphocyte DNA damage in elderly subjects. Clin Biochem 36:397–400
Nefic H, Handzic I (2013) The effect of age, sex, and lifestyle factors on micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes of the Bosnian population. Mutat Res 753:1–11
Parshad R, Sanford KK (2001) Radiation induced chromatid breaks and deficient DNA repair in cancer predisposition. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 37:87–96
Paul SF, Venkatachalam P, Jeevanram RK (1997) Analysis of radiation dose response curve obtained with cytokinesis block micronucleus assay. Nucl Med Biol 25:413–416
Rodrigues AS, Oliveira NG, Monteiro Gil O, Léonard A, Rueff J (2005) Use of cytogenetic indicators in radiobiology. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 115:455–460
Silva-Barbosa I, Pereira-Magnata S, Amaral A, Sotero G, Cavalcanti Melo H (2005) Dose assessment by quantification of chromosome aberrations and micronuclei in peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients exposed to gamma radiation. Genet Mol Biol 28:452–457
Smart V, Curwen GB, Whitehouse CA, Edwards A, Tawn EJ (2003) Chromosomal radiosensitivity: a study of the chromosomal G2 assay in human blood lymphocytes indicating significant inter-individual variability. Mutat Res 528:105–110
Stephan G, Pressl S (1999) Chromosomal aberrations in peripheral lymphocytes from healthy subjects as detected in The first cell division. Mutat Res 446:231–237
Vencatachalam P, Pauu Solomon FD, Karthiyeka Prabhu B, Mohankumar Mary N, Gjendiran N, Jeevanram RK (2001) Estimation of dose in cancer patients treated with fractionated radiotherapy using translocations, dicentrics and micronuclei frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mutat Res 429:1–12
Wojcik A, Stephan G, Sommer S, Buraczewska I, Kuszewski T, Wieczorek A, Gózdz S (2003) Chromosomal aberrations and micronuclei in lymphocytes of breast cancer patients after an accident during radiotherapy with 8 MeV electrons. Radiat Res 160:677–683
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pajic, J., Rakic, B., Rovcanin, B. et al. Inter-individual variability in the response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to ionizing radiation: comparison of the dicentric and micronucleus assays. Radiat Environ Biophys 54, 317–325 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-015-0596-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-015-0596-3