Abstract
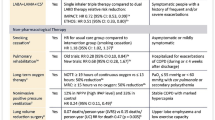
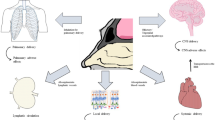
Therapeutic liposomal powders (i.e., lipospheres and proliposomes) for dry powder inhalation aerosol delivery, formulated with phospholipids similar to endogenous lung surfactant, offer unique opportunities in pulmonary nanomedicine while offering controlled release and enhanced stability. Many pulmonary diseases such as lung cancer, tuberculosis (TB), cystic fibrosis (CF), bacterial and fungal lung infections, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) could greatly benefit from this type of pulmonary nanomedicine approach that can be delivered in a targeted manner by dry powder inhalers (DPIs). These delivery systems may require smaller doses for efficacy, exhibit reduced toxicity, fewer side effects, controlled drug release over a prolonged time period, and increased formulation stability as inhaled powders. This state-of-the-art review presents these novel aspects in depth.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mansour HM, Rhee YS, Wu X (2009) Nanomedicine in pulmonary delivery. Int J Nanomedicine 4:299–319
Desai TR, Wong JP, Hancock REW, Finlay WH (2002) A novel approach to the pulmonary delivery of liposomes in dry powder form to eliminate the deleterious effects of milling. J Pharm Sci 91(2):482–491
Patton JS, Byron PR (2007) Inhaling medicines: delivering drugs to the body through the lungs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(1):67–74
Hickey AJ, Mansour HM (2009) Chapter 5: delivery of drugs by the pulmonary route. In: Florence AT, Siepmann J (eds) Modern pharmaceutics, vol 2, 5th edn. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 191–219
Hickey AJ, Mansour HM (2008) Chapter 43: formulation challenges of powders for the delivery of small molecular weight molecules as aerosols. In: Rathbone MJ, Hadgraft J, Roberts MS, Lane M (eds) Modified-release drug delivery technology, vol 2, 2nd edn. Informa Healthcare, New York, pp 573–602
Evora C, Soriano I, Rogers RA, Shakesheff KN, Hanes J, Langer R (1998) Relating the phagocytosis of microparticles by alveolar macrophages to surface chemistry: the effect of 1,2-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. J Control Release 51(2–3):143–152
Wu X, Mansour HM (2011) Nanopharmaceuticals II: application of nanoparticles and nanocarrier systems in pharmaceutics and nanomedicine. Int J Nanotechnol 8(1/2):115–145
Rhee YS, Mansour HM (2011) Nanopharmaceuticals I: nanocarrier systems in drug delivery. Int J Nanotechnol 8(1/2):84–114
Mansour HM, Rhee YS, Park CW, DeLuca PP (2011) Chapter 9: lipid nanoparticulate drug delivery and nanomedicine. In: Moghis A (ed) Lipids in nanotechnology, 1st edn. American Oil Chemists Society (AOCS) Press, Chicago, pp 221–268
Zhang J, Wu L, Chan HK, Watanabe W (2011) Formation, characterization, and fate of inhaled drug nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(6):441–455
Bi R, Zhang N (2007) Liposomes as a carrier for pulmonary delivery of peptides and proteins. J Biomed Nanotechnol 3(4):332–341
Dandekar P, Venkataraman C, Mehra A (2010) Pulmonary targeting of nanoparticle drug matrices. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 23(6):343–353
Hajos F, Stark B, Hensler S, Prassl R, Mosgoeller W (2008) Inhalable liposomal formulation for vasoactive intestinal peptide. Int J Pharm 357(1–2):286–294
Lu D, Hickey AJ (2005) Liposomal dry powders as aerosols for pulmonary delivery of proteins. AAPS PharmSciTech 6(4):E641–E648
Bailey MM, Berkland CJ (2009) Nanoparticle formulations in pulmonary drug delivery. Med Res Rev 29(1):196–212
Pison U, Welte T, Giersig M, Groneberg DA (2006) Nanomedicine for respiratory diseases. Eur J Pharmacol 533(1–3):341–350
Kurmi BD, Kayat J, Gajbhiye V, Tekade RK, Jain NK (2010) Micro- and nanocarrier-mediated lung targeting. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(7):781–794
Dailey LA, Jekel N, Fink L, Gessler T, Schmehl T, Wittmar M, Kissel T, Seeger W (2006) Investigation of the proinflammatory potential of biodegradable nanoparticle drug delivery systems in the lung. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 215(1):100–108
Perrie Y, Rades T (2010) Pharmaceutics—drug delivery and targeting. Pharmaceutical Press, London
Mansour HM, Zografi G (2007) The relationship between water vapor absorption and desorption by phospholipids and bilayer phase transitions. J Pharm Sci 96(2):377–396
Mansour HM, Damodaran S, Zografi G (2008) Characterization of the in situ structural and interfacial properties of the cationic hydrophobic heteropolypeptide, KL4, in lung surfactant bilayer and monolayer models at the air-water interface: implications for pulmonary surfactant delivery. Mol Pharm 5(5):681–695
Mansour HM, Wang DS, Chen CS, Zografi G (2001) Comparison of bilayer and monolayer properties of phospholipid systems containing dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol and dipalmitoylphosphatidylinositol. Langmuir 17(21):6622–6632
Mansour HM, Zografi G (2007) Relationships between equilibrium spreading pressure and phase equilibria of phospholipid bilayers and monolayers at the air–water interface. Langmuir 23(7):3809–3819
Changsan N, Chan HK, Separovic F, Srichana T (2009) Physicochemical characterization and stability of rifampicin liposome dry powder formulations for inhalation. J Pharm Sci 98(2):628–639
Darwis Y, Kellaway IW (2002) The lyophilisation and aerosolisation of liposomes for pulmonary drug administration. STP Pharma Sci 12(2):91–96
Gibbons AM, McElvaney NG, Cryan SA (2010) A dry powder formulation of liposome-encapsulated recombinant secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (rSLPI) for inhalation: preparation and characterisation. AAPS PharmSciTech 11(3):1411–1421
Gibbons AM, McElvaney NG, Taggart CC, Cryan SA (2009) Delivery of rSLPI in a liposomal carrier for inhalation provides protection against cathepsin L degradation. J Microencapsul 26(6):513–522
El-Ridy MS, Mostafa DM, Shehab A, Nasr EA, Abd El-Alim S (2007) Biological evaluation of pyrazinamide liposomes for treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Pharm 330(1–2):82–88
Wyde PR, Six HR, Wilson SZ, Gilbert BE, Knight V (1988) Activity against rhinoviruses, toxicity, and delivery in aerosol of enviroxime in liposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32(6):890–895
Goldbach P, Brochart H, Stamm A (1993) Spray-drying of liposomes for a pulmonary administration. 1. Chemical stability of phospholipids. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 19(19):2611–2622
Goldbach P, Brochart H, Stamm A (1993) Spray-drying of liposomes for a pulmonary administration. 2. Retention of encapsulated materials. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 19(19):2623–2636
Alves GP, Santana MHA (2004) Phospholipid dry powders produced by spray drying processing: structural, thermodynamic and physical properties. Powder Technol 145(2):139–148
Taylor KMG, Farr SJ (1993) Liposomes for drug delivery to the respiratory tract. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 19(1–2):123–142
Abu-Dahab R, Schafer UF, Lehr CM (2001) Lectin-functionalized liposomes for pulmonary drug delivery: effect of nebulization on stability and bioadhesion. Eur J Pharm Sci 14(1):37–46
Canonico AE, Plitman JD, Conary JT, Meyrick BO, Brigham KL (1994) No lung toxicity after repeated aerosol or intravenous delivery of plasmid–cationic liposome complexes. J Appl Physiol 77(1):415–419
Saari M, Vidgren MT, Koskinen MO, Turjanmaa VMH, Nieminen MM (1999) Pulmonary distribution and clearance of two beclomethasone liposome formulations in healthy volunteers. Int J Pharm 181(1):1–9
Thomas DA, Myers MA, Wichert B, Schreier H, Gonzalezrothi RJ (1991) Acute effects of liposome aerosol inhalation on pulmonary-function in healthy-human volunteers. Chest 99(5):1268–1270
Wijagkanalan W, Higuchi Y, Kawakami S, Teshima M, Sasaki H, Hashida M (2008) Enhanced anti-inflammation of inhaled dexamethasone palmitate using mannosylated liposomes in an endotoxin-induced lung inflammation model. Mol Pharmacol 74(5):1183–1192
Albasarah YY, Somavarapu S, Stapleton P, Taylor KMG (2010) Chitosan-coated antifungal formulations for nebulisation. J Pharm Pharmacol 62(7):821–828
Patton JS, Fishburn CS, Weers JG (2004) The lungs as a portal of entry for systemic drug delivery. Proc Am Thorac Soc 1(4):338–344
Chimote G, Banerjee R (2009) Evaluation of antitubercular drug-loaded surfactants as inhalable drug-delivery systems for pulmonary tuberculosis. J Biomed Mater Res A 89A(2):281–292
Barker SA, Taylor KMG, Short MD (1994) The deposition and clearance of liposome-entrapped Tc-99m-DTPA in the human respiratory tract. Int J Pharm 102(1–3):159–165
Myers MA, Thomas DA, Straub L, Soucy DW, Niven RW, Kaltenbach M, Hood CI, Schreier H, Gonzalezrothi RJ (1993) Pulmonary effects of chronic exposure to liposome aerosols in mice. Exp Lung Res 19(1):1–19
Misra A, Jinturkar K, Patel D, Lalani J, Chougule M (2009) Recent advances in liposomal dry powder formulations: preparation and evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 6(1):71–89
El-Gendy N, Gorman EM, Munson EJ, Berkland C (2009) Budesonide nanoparticle agglomerates as dry powder aerosols with rapid dissolution. J Pharm Sci 98(8):2731–2746
Naikwade SR, Bajaj AN, Gurav P, Gatne MM, Singh Soni P (2009) Development of budesonide microparticles using spray-drying technology for pulmonary administration: design, characterization, in vitro evaluation, and in vivo efficacy study. AAPS PharmSciTech 10(3):993–1012
Joshi M, Misra AN (2001) Pulmonary disposition of budesonide from liposomal dry powder inhaler. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 23(10):531–536
Saari SM, Vidgren MT, Herrala J, Turjanma VMH, Koskinen MO, Nieminen MM (2002) Possibilities of formoterol to enhance the peripheral lung deposition of the inhaled liposome corticosteroids. Respir Med 96(12):999–1005
Sharafkhaneh A, Mattewal AS, Abraham VM, Dronavalli G, Hanania NA (2010) Budesonide/formoterol combination in COPD: a US perspective. Int J Chron Obstr Pulm Dis 5:357–366
Saari SM, Vidgren MT, Koskinen MO, Turjanmaa VM, Waldrep JC, Nieminen MM (1998) Regional lung deposition and clearance of 99mTc-labeled beclomethasone-DLPC liposomes in mild and severe asthma. Chest 113(6):1573–1579
Huang WH, Yang ZJ, Wu H, Wong YF, Zhao ZZ, Liu L (2010) Development of liposomal salbutamol sulfate dry powder inhaler formulation. Biol Pharm Bull 33(3):512–517
Joshi M, Misra A (2001) Dry powder inhalation of liposomal ketotifen fumarate: formulation and characterization. Int J Pharm 223(1–2):15–27
Joshi M, Misra A (2003) Disposition kinetics of ketotifen from liposomal dry powder for inhalation in rat lung. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30(3):153–156
Park CW, Hayes DJ, Mansour HM (2011) Pulmonary inhalation aerosols for targeted antibiotics drug delivery. Eur Pharm Rev 16(1):32–36
Gilbert BE (1996) Liposomal aerosols in the management of pulmonary infections. J Aerosol Med 9(1):111–122
Zaru M, Sinico C, De Logu A, Caddeo C, Lai F, Manca ML, Fadda AM (2009) Rifampicin-loaded liposomes for the passive targeting to alveolar macrophages: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Liposome Res 19(1):68–76
Vyas SP, Kannan ME, Jain S, Mishra V, Singh P (2004) Design of liposomal aerosols for improved delivery of rifampicin to alveolar macrophages. Int J Pharm 269(1):37–49
Vyas SP, Khatri K (2007) Liposome-based drug delivery to alveolar macrophages. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 4(2):95–99
Vyas SP, Quraishi S, Gupta S, Jaganathan KS (2005) Aerosolized liposome-based delivery of amphotericin B to alveolar macrophages. Int J Pharm 296(1–2):12–25
Corcoran TE, Venkataramanan R, Mihelc KM, Marcinkowski AL, Ou J, McCook BM, Weber L, Carey ME, Paterson DL, Pilewski JM, McCurry KR, Husain S (2006) Aerosol deposition of lipid complex amphotericin-B (Abelcet) in lung transplant recipients. Am J Transpl 6(11):2765–2773
Allen SD, Sorensen KN, Nejdl MJ, Durrant C, Proffit RT (1994) Prophylactic efficacy of aerosolized liposomal (AmBisome) and non-liposomal (Fungizone) amphotericin B in murine pulmonary aspergillosis. J Antimicrob Chemother 34(6):1001–1013
Castagnola E, Moresco L, Cappelli B, Cuzzubbo D, Moroni C, Lanino E, Faraci M (2007) Nebulized liposomal amphotericin B and combined systemic antifungal therapy for the treatment of severe pulmonary aspergillosis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for a fatal mitochondrial disorder. J Chemother 19(3):339–342
Lowry CM, Marty FM, Vargas SO, Lee JT, Fiumara K, Deykin A, Baden LR (2007) Safety of aerosolized liposomal versus deoxycholate amphotericin B formulations for prevention of invasive fungal infections following lung transplantation: a retrospective study. Transpl Infect Dis 9(2):121–125
Slobbe L, Boersma E, Rijnders BJ (2008) Tolerability of prophylactic aerosolized liposomal amphotericin-B and impact on pulmonary function: data from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21(6):855–859
Rijnders BJ, Cornelissen JJ, Slobbe L, Becker MJ, Doorduijn JK, Hop WCJ, Ruijgrok EJ, Lowenberg B, Vulto A, Lugtenburg PJ, de Marie S (2008) Aerosolized liposomal amphotericin B for the prevention of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis during prolonged neutropenia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis 46(9):1401–1408
Takazono T, Izumikawa K, Mihara T, Kosai K, Saijo T, Imamura Y, Miyazaki T, Seki M, Kakeya H, Yamamoto Y, Yanagihara K, Kohno S (2009) Efficacy of combination antifungal therapy with intraperitoneally administered micafungin and aerosolized liposomal amphotericin b against murine invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(8):3508–3510
Shah SP, Misra A (2004) Development of liposomal amphotericin B dry powder inhaler formulation. Drug Deliv 11(4):247–253
DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM (2008) Pharmacotherapy: a pathophysiological approach, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill Medical, New York
Desjardins A, Chen T, Khalil H, Sayasith K, Lagace J (2002) Differential behaviour of fluid liposomes toward mammalian epithelial cells and bacteria: restriction of fusion to bacteria. J Drug Target 10(1):47–54
McLachlan G, Davidson DJ, Stevenson BJ, Dickinson P, Davidson-Smith H, Dorin JR, Porteous DJ (1995) Evaluation in vitro and in vivo of cationic liposome-expression construct complexes for cystic fibrosis gene therapy. Gene Ther 2(9):614–622
Tagalakis AD, McAnulty RJ, Devaney J, Bottoms SE, Wong JB, Elbs M, Writer MJ, Hailes HC, Tabor AB, O’Callaghan C, Jaffe A, Hart SL (2008) A receptor-targeted nanocomplex vector system optimized for respiratory gene transfer. Mol Ther 16(5):907–915
Okusanya OO, Bhavnani SM, Hammel J, Minic P, Dupont LJ, Forrest A, Mulder GJ, Mackinson C, Ambrose PG, Gupta R (2009) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of liposomal amikacin for inhalation in cystic fibrosis patients with chronic pseudomonal infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(9):3847–3854
Weers J, Metzheiser B, Taylor G, Warren S, Meers P, Perkins WR (2009) A gamma scintigraphy study to investigate lung deposition and clearance of inhaled amikacin-loaded liposomes in healthy male volunteers. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 22(2):131–138
Heijerman H, Westerman E, Conway S, Touw D, Doring G, Consensus Working Group (2009) Inhaled medication and inhalation devices for lung disease in patients with cystic fibrosis: a European consensus. J Cyst Fibros 8(5):295–315
Adi H, Young PM, Chan HK, Agus H, Traini D (2010) Co-spray-dried mannitol-ciprofloxacin dry powder inhaler formulation for cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Pharm Sci 40(3):239–247
Lacy CF, Armstrong LL, Goldman MP, Lance LL (2008) Drug information handbook, 17th edn. Lexi-Comp Inc., Hudson
Everard ML, Devadason SG, Sunderland VB, Le Souef PN (1995) An alternative aerosol delivery system for amiloride. Thorax 50(5):517–519
Chougule MB, Padhi BK, Misra A (2006) Nano-liposomal dry powder inhaler of amiloride hydrochloride. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6(9–10):3001–3009
Chougule MB, Padhi BK, Misra AN (2008) Development of spray dried liposomal dry powder inhaler of Dapsone. AAPS PharmSciTech 9(1):47–53
Knoop C, Haverich A, Fischer S (2004) Immunosuppressive therapy after human lung transplantation. Eur Respir J 23(1):159–171
Chougule M, Padhi B, Misra A (2007) Nano-liposomal dry powder inhaler of tacrolimus: preparation, characterization, and pulmonary pharmacokinetics. Int J Nanomedicine 2(4):675–688
Waldrep JC, Scherer PW, Keyhani K, Knight V (1993) Cyclosporine-a liposome aerosol—particle-size and calculated respiratory deposition. Int J Pharm 97(1–3):205–212
Waldrep JC, Arppe J, Jansa KA, Vidgren M (1998) Experimental pulmonary delivery of cyclosporin A by liposome aerosol. Int J Pharm 160(2):239–249
Behr J, Zimmermann G, Baumgartner R, Leuchte H, Neurohr C, Brand P, Herpich C, Sommerer K, Seitz J, Menges G, Tillmanns S, Keller M, Munich Lung Transplant Group (2009) Lung deposition of a liposomal cyclosporine a inhalation solution in patients after lung transplantation. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 22(2):121–129
Waldrep JC, Arppe J, Jansa KA, Knight V (1997) High dose cyclosporin A and budesonide-liposome aerosols. Int J Pharm 152(1):27–36
Gilbert BE, Wilson SZ, Garcon NM, Wyde PR, Knight V (1993) Characterization and administration of cyclosporine liposomes as a small-particle aerosol. Transplantation 56(4):974–977
Koshkina NV, Golunski E, Roberts LE, Gilbert BE, Knight V (2004) Cyclosporin A aerosol improves the anticancer effect of paclitaxel aerosol in mice. J Aerosol Med 17(1):7–14
Ross HJ, Canada AL, Slater LM (1997) Cyclosporine A enhances paclitaxel toxicity against leukemia and respiratory epithelial cancers. Clin Cancer Res 3(1):57–62
Xu J, Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Tejada-Vera B (2007) Deaths: final data for 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep 58(19):1–135
Gautam A, Waldrep JC, Densmore CL, Koshkina N, Melton S, Roberts L, Gilbert B, Knight V (2002) Growth inhibition of established B16–F10 lung metastases by sequential aerosol delivery of p53 gene and 9-nitrocamptothecin. Gene Ther 9(5):353–357
Koshkina NV, Waldrep JC, Roberts LE, Golunski E, Melton S, Knight V (2001) Paclitaxel liposome aerosol treatment induces inhibition of pulmonary metastases in murine renal carcinoma model. Clin Cancer Res 7(10):3258–3262
Zou Y, Zong G, Ling YH, Perez-Soler R (2000) Development of cationic liposome formulations for intratracheal gene therapy of early lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 7(5):683–696
Kalantarian P, Najafabadi AR, Haririan I, Vatanara A, Yamini Y, Darabi M, Gilani K (2010) Preparation of 5-fluorouracil nanoparticles by supercritical antisolvents for pulmonary delivery. Int J Nanomedicine 5:763–770
Gagnadoux F, Hureaux J, Vecellio L, Urban T, Le Pape A, Valo I, Montharu J, Leblond V, Boisdron-Celle M, Lerondel S, Majoral C, Diot P, Racineux JL, Lemarie E (2008) Aerosolized chemotherapy. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 21(1):61–69
Weinstein JN, Leserman LD (1984) Liposomes as drug carriers in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther 24(2):207–233
Parthasarathy R, Gilbert B, Mehta K (1999) Aerosol delivery of liposomal all-trans-retinoic acid to the lungs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43(4):277–283
Carvalho TC, Carvalho SR, McConville JT (2011) Formulations for pulmonary administration of anticancer agents to treat lung malignancies. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 24(2):61–80
Zakharian TY, Seryshev A, Sitharaman B, Gilbert BE, Knight V, Wilson LJ (2005) A fullerene-paclitaxel chemotherapeutic: synthesis, characterization, and study of biological activity in tissue culture. J Am Chem Soc 127(36):12508–12509
Wittgen BP, Kunst PW, van der Born K, van Wijk AW, Perkins W, Pilkiewicz FG, Perez-Soler R, Nicholson S, Peters GJ, Postmus PE (2007) Phase I study of aerosolized SLIT cisplatin in the treatment of patients with carcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res 13(8):2414–2421
Debs RJ, Straubinger RM, Brunette EN, Lin JM, Lin EJ, Montgomery AB, Friend DS, Papahadjopoulos DP (1987) Selective enhancement of pentamidine uptake in the lung by aerosolization and delivery in liposomes. Am Rev Respir Dis 135(3):731–737
Koshkina NV, Kleinerman ES, Waldrep C, Jia SF, Worth LL, Gilbert BE, Knight V (2000) 9-Nitrocamptothecin liposome aerosol treatment of melanoma and osteosarcoma lung metastases in mice. Clin Cancer Res 6(7):2876–2880
Lawson KA, Anderson K, Snyder RM, Simmons-Menchaca M, Atkinson J, Sun LZ, Bandyopadhyay A, Knight V, Gilbert BE, Sanders BG, Kline K (2004) Novel vitamin E analogue and 9-nitro-camptothecin administered as liposome aerosols decrease syngeneic mouse mammary tumor burden and inhibit metastasis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54(5):421–431
Verschraegen CF, Gilbert BE, Loyer E, Huaringa A, Walsh G, Newman RA, Knight V (2004) Clinical evaluation of the delivery and safety of aerosolized liposomal 9-nitro-20(s)-camptothecin in patients with advanced pulmonary malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 10(7):2319–2326
Chen J, Ping QN, Guo JX, Chu XZ, Song MM (2006) Effect of phospholipid composition on characterization of liposomes containing 9-nitrocamptothecin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 32(6):719–726
Knight V, Koshkina NV, Waldrep JC, Giovanella BC, Gilbert BE (1999) Anticancer effect of 9-nitrocamptothecin liposome aerosol on human cancer xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44(3):177–186
Otterson GA, Villalona-Calero MA, Hicks W, Pan X, Ellerton JA, Gettinger SN, Murren JR (2010) Phase I/II study of inhaled doxorubicin combined with platinum-based therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(8):2466–2473
Azarmi S, Tao X, Chen H, Wang Z, Finlay WH, Lobenberg R, Roa WH (2006) Formulation and cytotoxicity of doxorubicin nanoparticles carried by dry powder aerosol particles. Int J Pharm 319(1–2):155–161
Latimer P, Menchaca M, Snyder RM, Yu WP, Gilbert BE, Sanders BG, Kline K (2009) Aerosol delivery of liposomal formulated paclitaxel and vitamin E analog reduces murine mammary tumor burden and metastases. Exp Biol Med 234(10):1244–1252
World Health Organization (2011) Global tuberculosis control. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2011/gtbr11_full.pdf. Accessed 10 Dec 2011
Muttil P, Kaur J, Kumar K, Yadav AB, Sharma R, Misra A (2007) Inhalable microparticles containing large payload of anti-tuberculosis drugs. Eur J Pharm Sci 32(2):140–150
Chimote G, Banerjee R (2010) In vitro evaluation of inhalable isoniazid-loaded surfactant liposomes as an adjunct therapy in pulmonary tuberculosis. J Biomed Mater Res B 94B(1):1–10
Sung JC, Padilla DJ, Garcia-Contreras L, Verberkmoes JL, Durbin D, Peloquin CA, Elbert KJ, Hickey AJ, Edwards DA (2009) Formulation and pharmacokinetics of self-assembled rifampicin nanoparticle systems for pulmonary delivery. Pharm Res 26(8):1847–1855
Sethuraman VV, Hickey AJ (2002) Powder properties and their influence on dry powder inhaler delivery of an antitubercular drug. AAPS PharmSciTech 3(4):E28
Changsan N, Nilkaeo A, Pungrassami P, Srichana T (2009) Monitoring safety of liposomes containing rifampicin on respiratory cell lines and in vitro efficacy against Mycobacterium bovis in alveolar macrophages. J Drug Target 17(10):751–762
American Cancer Society (2010) Cancer facts and figures 2010. http://www.cancer.org. Accessed 30 Nov 2010
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willis, L., Hayes, D. & Mansour, H.M. Therapeutic Liposomal Dry Powder Inhalation Aerosols for Targeted Lung Delivery. Lung 190, 251–262 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9360-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9360-x