Abstract
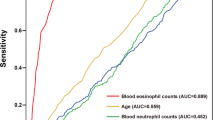
The surrogate markers for subclassifying eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS) and non-ECRS remain elusive. We herein performed a cross-sectional study to assess the clinical implication of clinical symptoms, CT findings, blood eosinophil (EOS) examination based on histological examination of tissue eosinophilia in 105 adult CRS patients (including 72 with nasal polyps and 33 without nasal polyps) in southern China. We found the mean score of smell loss was significantly higher in ECRS subgroup than those in non-ECRS subgroup (p < 0.05), whereas the average ethmoid osteitis index in non-ECRS subgroup was significantly higher than that in ECRS subgroup (p < 0.05). Moreover, we found both the mean blood EOS number and ratio were significantly higher in ECRS subgroup than those in non-ECRS subgroup (p < 0.05). By applying receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, we found blood EOS number had a sensitivity of 84.9 % and specificity of 84.4 % [area under the curve (AUC): 0.873] at the cutoff level of 0.16 × 109/L, and blood EOS ratio had a sensitivity of 89.0 % and specificity of 84.4 % (AUC: 0.863) at the cutoff level of 2.05 % in this cohort. Our findings indicated that smell loss score, ethmoid osteitis index and blood EOS number and ratio may be used for the differential diagnosis of ECRS as the surrogate markers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilos DL (2011) Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and medical management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:693–707
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P, Georgalas C, Goossens H, Harvey R, Hellings P, Hopkins C, Jones N, Joos G, Kalogjera L, Kern B, Kowalski M, Price D, Riechelmann H, Schlosser R, Senior B, Thomas M, Toskala E, Voegels R, de Wang Y, Wormald PJ (2012) EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 50:1–12
Marple BF, Stankiewicz JA, Baroody FM, Chow JM, Conley DB, Corey JP, Ferguson BJ, Kern RC, Lusk RP, Naclerio RM, Orlandi RR, Parker MJ, American Academy of Otolaryngic Allergy Working Group on Chronic Rhinosinusitis (2009) Diagnosis and management of chronic rhinosinusitis in adults. Postgrad Med 121:121–139
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, Bachert C, Baraniuk J, Baroody FM, Benninger MS, Brook I, Chowdhury BA, Druce HM, Durham S, Ferguson B, Gwaltney JM, Kaliner M, Kennedy DW, Lund V, Naclerio R, Pawankar R, Piccirillo JF, Rohane P, Simon R, Slavin RG, Togias A, Wald ER, Zinreich SJ, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI), American Academy of Otolaryngic Allergy (AAOA), American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS), American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), American Rhinologic Society (ARS) (2004) Rhinosinusitis: establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114(6 Suppl):155–212
Van Crombruggen K, Zhang N, Gevaert P, Tomassen P, Bachert C (2011) Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis: inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:728–732
Katotomichelakis M, Tantilipikorn P, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, Feng L, Van Zele T, Muangsomboon S, Jareonchasri P, Bunnag C, Danielides V, Cuvelier CA, Hellings PW, Bachert C, Zhang N (2013) Inflammatory patterns in upper airway disease in the same geographical area may change over time. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27:354–360
Kim JW, Hong SL, Kim YK, Lee CH, Min YG, Rhee CS (2007) Histological and immunological features of non-eosinophilic nasal polyps. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:925–930
Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, Wang DY, Desrosiers M, Liu Z (2009) Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:478–484 (pp 484.e1–2)
Snidvongs K, Lam M, Sacks R, Earls P, Kalish L, Phillips PS, Pratt E, Harvey RJ (2012) Structured histopathology profiling of chronic rhinosinusitis in routine practice. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2:376–385
Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, Schleimer RP, Ledford D (2013) Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131:1479–1490
Kountakis SE, Arango P, Bradley D, Wade ZK, Borish L (2004) Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 114:1895–1905
Lee JT, Kennedy DW, Palmer JN, Feldman M, Chiu AG (2006) The incidence of concurrent osteitis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a clinicopathological study. Am J Rhinol 20:278–282
Kim SJ, Lee KH, Kim SW, Cho JS, Park YK, Shin SY (2013) Changes in histological features of nasal polyps in a Korean population over a 17-year period. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 149:431–437
Ishitoya J, Sakuma Y, Tsukuda M (2010) Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan. Allergol Int 59:239–245
Chin D, Harvey RJ (2013) Nasal polyposis: an inflammatory condition requiring effective anti-inflammatory treatment. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21:23–30
Sakuma Y, Ishitoya J, Komatsu M, Shiono O, Hirama M, Yamashita Y, Kaneko T, Morita S, Tsukuda M (2011) New clinical diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 38:583–588
Snidvongs K, McLachlan R, Chin D, Pratt E, Sacks R, Earls P, Harvey RJ (2012) Osteitic bone: a surrogate marker of eosinophilia in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 50:299–305
Hsu J, Peters AT (2011) Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Am J Rhinol Allergy 25:285–290
Payne SC, Borish L, Steinke JW (2011) QueryGenetics and phenotyping in chronic sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:710–720
Hu Y, Cao PP, Liang GT, Cui YH, Liu Z (2012) Diagnostic significance of blood eosinophil count in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chinese adults. Laryngoscope 122:498–503
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 81070771, 81070772, 81271054) and a grant from the Ministry of Hygiene (No. 201202005) and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-10-0851).
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Zuo and J. Guo have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, K., Guo, J., Chen, F. et al. Clinical characteristics and surrogate markers of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Southern China. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 2461–2468 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2910-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2910-0