Abstract
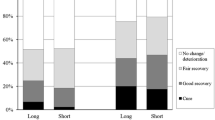
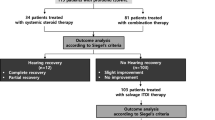
Profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is thought to have a poor prognosis, but few studies have focused on this condition. We aimed to assess the impact of patient factors, audiologic parameters, and salvage intratympanic steroid injection therapy on the prognosis of profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. The demographic, clinical, and audiologic data, degree of hearing recovery, and efficacy of intratympanic steroid injection therapy in 576 patients with profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (mean age 56.2 ± 14.9 years) who had been admitted at four tertiary referral centers between 2000 and 2011 were retrospectively reviewed. The mean hearing level at the initial presentation was 108.1 ± 9.5 dB. Many patients experienced vertigo (52.1 %) and tinnitus (77.4 %). At the 2-month follow-up, 172 (29.8 %) patients showed some degree of hearing recovery, but only 21 (3.6 %) patients recovered normal hearing. Further, the 116 patients who had received salvage intratympanic steroid injections showed a better audiologic outcome (improvement, 26.1 ± 24.3 vs. 15.7 ± 22.1 dB; P = 0.000) than those who had not (n = 429). In conclusion, a higher degree of hearing loss at the initial presentation indicates a poorer prognosis. Salvage intratympanic steroid injection therapy may improve the hearing of patients with profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss after the failure of systemic steroid therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME (1966) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 29:393–405
Byl FM (1984) Sudden hearing loss: eight years’ experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope 94:647–661
Mattox DE, Simmons FB (1977) Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86:463–480
Cole RR, Jahrsdoerfer RA (1988) Sudden hearing loss: an update. Am J Otol 9:211–215
Fuse T, Aoyagi M, Funakubo T, Sakakibara A, Yoshida S (2002) Short-term outcome and prognosis of acute low-tone sensorineural hearing loss by administration of steroid. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 64:6–10
Filipo R, Attanasio G, Russo FY, Viccaro M, Mancini P, Covelli E (2013) Intratympanic steroid therapy in moderate sudden hearing loss: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Laryngoscope 123:774–778
Paulo RL, Ana CKC (2006) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: etiopathogenic aspects. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 72:554–561
Saumil NM, Joe CA, Joseph BNJ (2005) Pathology and pathophysiology of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 26:151–160
Anne EC, Lorne SP (2007) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:573–581
Anita J, David F, Timothy D (2006) Treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 126:708–713
Ben IN, David U, Joseph A, Petah T (2004) Magnesium treatment for sudden hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 113:672–675
Corinne EH, Harvey NH, Samuel HS (2005) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective trial of patients failing steroid and antiviral treatment. Otol Neurotol 26:882–889
Weng SF, Chen YH, Hsu CJ, Tseng FY (2005) Clinical features of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients. Laryngoscope 115:1676–1680
Norma OP, Hugo VLR, Flávia AB, Oswaldo LMC, Ronaldo NT (2005) Clinical, etiological and progression factors of hearing in sudden deafness. Rev Bras Otorhinolaryngol 71:633–638
Toshifumi S, Toshihiko K (2006) Feeling of ear fullness in acute sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol 126:828–833
Shinichi I, Yoshinari T, Hidenori O, Ken I, Shotaro K, Toshihisa M (2005) Extent of lesions in idiopathic sudden hearing loss with vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:857–862
Ceylan A, Celenk F, Kemagoglu YK, Bayazit YA, Goksu N, Ozbilen S (2007) Impact of prognostic factors on recovery from sudden hearing loss. J Laryngol Otol 121:1035–1040
Chang NC, Ho KY, Kuo WR (2005) Audiometric patterns and prognosis in sudden sensorineural hearing loss in southern Taiwan. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:916–922
Kronenberg J, Almagor M, Bendet E, Kushnir D (1992) Vasoactive therapy versus placebo in the treatment of sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Laryngoscope 102:65–68
Siegel LG (1975) The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 8:467–473
Aydin M, Suleyman Y, Harun C, Ender I, Ender G, Levent D (2005) A study of prognostic factors in sudden hearing loss. Ear Nose Throat J 84:641–644
Xenellis J, Karapatsas I, Papadimitriou N, Nikolopoulos T, Maragoudakis P, Tzagkaroulakis M, Ferekidis E (2006) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: prognostic factors. J Laryngol Otol 120:718–724
Stefan KP, Michael B, Christoph M (2007) Comparison of pure-tone audiometry analysis in sudden hearing loss studies: lack of agreement for different outcome measures. Otol Neurotol 28:753–763
Shiraishi T, Kubo T, Okumura S (1993) Hearing recovery in sudden deafness patients using a modified defibrinogenation therapy. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 501:46–50
Moskowitz D, Lee KJ, Smith HW (1984) Steroid use in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 94:664–666
Grandis JR, Hirsch BE, Wagener MM (1993) Treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol 14:183–185
Hirano K, Ikeda K, Kawase T, Oshima T, Kekehata S, Takahashi S (1999) Prognosis of sudden deafness with special reference to risk factors of microvascular pathology. Auris Nasus Larynx 26:111–115
Laird N, Wilson WR (1983) Predicting recovery from idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol 4:161–165
Ohinata Y, Makimoto K, Kawakami M, Haginomori S, Araki M, Takahashi H (1994) Blood viscosity and plasma viscosity in patients with sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol 114:601–607
Pruszewicz A, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Smolinska K, Szyfter W (1983) Lipid levels in patients with sudden deafness of unknown aetiology. Audiology 22:63–72
Ulrich D, Aurbach G, Drobik C (1992) A prospective study of hyperlipidemia as a pathogenic factor in sudden hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 249:273–276
Sano H, Okamoto M, Shitara T, Hirayama M (1998) What kind of patients are suitable for evaluating the therapeutic effect of sudden deafness? Am J Otol 19:579–583
Mattox DE, Lyles CA (1989) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol 10:242–247
Mosnier I, Stepanian A, Baron G, Bodenez C, Robier A, Meyer B, Fraysse B, Bertholon P, Defay F, Ameziane N, Ferrary E, Sterkers O, de Prost D (2011) Cardiovascular and thromboembolic risk factors in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case-control study. Audiol Neurootol 16:55–66
Saeki N, Kitahara M (1994) Assessment of prognosis in sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 510:56–61
Danino J, Joachims HZ, Eliachar I, Podoshin L, Ben-David Y, Fradis M (1984) Tinnitus as a prognostic factor in sudden deafness. Am J Otolaryngol 5:394–396
Linssen O, Schultz-Coulon HJ (1997) Prognostic criteria in sudden deafness. HNO 45:22–29
Zadeh MH, Stopper IS, Spitzer JB (2003) Diagnosis and treatment of sudden-onset sensorineural hearing loss: a study of 51 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:92–98
Wilson WR (1986) The relationship of the herpesvirus family to sudden hearing loss: a prospective clinical study and literature review. Laryngoscope 96:870–877
Silverstein H, Choo D, Rosenberg SI, Kuhn J, Seidman M, Stein I (1996) Intratympanic steroid treatment of inner ear disease and tinnitus (preliminary report). Ear Nose Throat J 75:468–471
Filipo R, Covelli E, Balsamo G, Attanasio G (2010) Intratympanic prednisolone therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a new protocol. Acta Otolaryngol 130:1209–1213
Spear SA, Schwartz SR (2011) Intratympanic steroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145:534–543
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, YH., Chen, PR. & Wu, HP. Prognostic factors of profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 1423–1429 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2593-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2593-y