Abstract
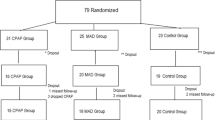
The objective of this study was to assess treatment outcomes and compliance according to obesity among groups of patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) receiving different treatments. A total of 297 patients with OSA treated between 2006 and 2009 underwent pre- and post-treatment polysomnography. One hundred and fifty-one patients were treated with continuous airway positive pressure (CPAP), 76 with mandible advancement device (MAD), and 70 with oropharyngeal surgery. All patients were classified according to obesity. Treatment success rate and compliance of CPAP were analyzed according to obesity. For each treatment modality, the overall treatment success rate was not significantly different between obese and non-obese patients. However, the oxygen desaturation index was different in patients who were treated with MAD and surgery. Additionally, obese patients with severe OSA showed an unfavorable response to CPAP treatment. For CPAP compliance, obese patients showed a tendency to be highly compliant with CPAP treatment at 12 months than non-obese patients. This study showed that obesity might be a factor in determining the success or failure of treatment. Additionally, obesity may be a predictive factor to determine CPAP compliance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parish JM, Somers VK (2004) Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Mayo Clin Proc 79(8):1036–1046
Duran J, Esnaola S, Rubio R, Iztueta Á (2001) Obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea and related clinical features in a population-based sample of subjects aged 30 to 70 yr. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163(3):685–689
Resta O, Foschino-Barbaro M, Legari G, Talamo S, Bonfitto P, Paulumbo A, Minenna A, Giorgino R, De Pergola G (2001) Sleep-related breathing disorders, loud snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness in obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(5):669–675
Fritscher LG, Mottin CC, Canani S, Chatkin JM (2007) Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome: the impact of bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 17(1):95–99
Wolk R, Somers V (2006) Obesity‐related cardiovascular disease: implications of obstructive sleep apnea. Diabetes Obes Metab 8(3):250–260
Shelton KE, Woodson H, Gay S, Suratt PM (1993) Pharyngeal fat in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 148(2):462–466
Lee CH, Mo JH, Choi IJ, Lee HJ, Seo BS, Kim DY, Yun PY, Yoon IY, Won Lee H, Kim JW (2009) The mandibular advancement device and patient selection in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(5):439–444
Friedman M, Soans R, Joseph N, Kakodkar S, Friedman J (2009) The effect of multilevel upper airway surgery on continuous positive airway pressure therapy in obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 119(1):193–196
Choi K, Lee J, Park H, Baik S, Choi D, Kim S (2001) Relationship between sleep duration and the metabolic syndrome: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Int J Obes 32(7):1091–1097
Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ Jr, Friedman N, Malhotra A, Patil SP, Ramar K, Rogers R, Schwab RJ, Weaver EM, Weinstein MD; Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2009) Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J Clin Sleep Med 5(3):263–276
Kribbs NB, Pack AI, Kline LR, Smith PL, Schwartz AR, Schubert NM, Redline S, Henry JN, Getsy JE, Dinges DF (1993) Objective measurement of patterns of nasal CPAP use by patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 147(4):887–895
Young T, Peppard PE, Taheri S (2005) Excess weight and sleep-disordered breathing. J Appl Physiol 99(4):1592–1599
Li C, Ford ES, Zhao G, Croft JB, Balluz LS, Mokdad AH (2010) Prevalence of self-reported clinically diagnosed sleep apnea according to obesity status in men and women: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005–2006. Prev Med 51(1):18–23
Kaditis AG, Alexopoulos EI, Hatzi F, Karadonta I, Chaidas K, Gourgoulianis K, Zintzaras E, Syrogiannopoulos GA (2008) Adiposity in relation to age as predictor of severity of sleep apnea in children with snoring. Sleep Breath 12(1):25–31
Tauman R, Gozal D (2006) Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea in children. Paediatr Respir Rev 7(4):247–259
Redline S, Tishler PV, Schluchter M, Aylor J, Clark K, Graham G (1999) Risk factors for sleep-disordered breathing in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159(5):1527–1532
Welch KC, Foster GD, Ritter CT, Wadden TA, Arens R, Maislin G, Schwab RJ (2002) A novel volumetric magnetic resonance imaging paradigm to study upper airway anatomy. Sleep 25(5):532–542
Isono S (2012) Obesity and obstructive sleep apnoea: mechanisms for increased collapsibility of the passive pharyngeal airway. Respirology 17(1):32–42
Phillips BG, Hisel TM, Kato M et al (1999) Recent weight gain in patients with newly diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea. J Hypertens 17(9):1297–1300
Phillips BG, Kato M, Narkiewicz K, Choe I, Somers VK (2000) Increases in leptin levels, sympathetic drive, and weight gain in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279(1):H234–H237
Romero-Corral A, Caples SM, Lopez-Jimenez F, Somers VK (2010) Interactions between obesity and obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 137(3):711–719
Greenburg DL, Lettieri CJ, Eliasson AH (2009) Effects of surgical weight loss on measures of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Am J Med 122(6):535–542
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J (2000) Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA 284(23):3015–3021
Redline S, Storfer-Isser A, Rosen CL, Johnson NL, Kirchner HL, Emancipator J, Kibler AM (2007) Association between metabolic syndrome and sleep-disordered breathing in adolescents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176(4):401–408
Chin K, Shimizu K, Nakamura T, Narai N, Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Mishima M, Nakamura T, Nakao K, Ohi M (1999) Changes in intra-abdominal visceral fat and serum leptin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome following nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Circulation 100(7):706–712
Spiegel K, Tasali E, Penev P, Van Cauter E (2004) Brief communication: sleep curtailment in healthy young men is associated with decreased leptin levels, elevated ghrelin levels, and increased hunger and appetite. Ann Intern Med 141(11):846–850
Lam B, Sam K, Mok WY et al (2007) Randomised study of three non-surgical treatments in mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 62(4):354–359
Chiner E, Signes-Costa J, Arriero JM, Marco J, Fuentes I, Sergado A (1999) Nocturnal oximetry for the diagnosis of the sleep apnoea hypopnoea syndrome: a method to reduce the number of polysomnographies? Thorax 54(11):968–971
Trenell MI, Ward JA, Yee BJ et al (2007) Influence of constant positive airway pressure therapy on lipid storage, muscle metabolism and insulin action in obese patients with severe obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab 9(5):679–687
Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Vicente E, Agusti AG (2005) Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: an observational study. Lancet 365(9464):1046–1053
Vgontzas AN, Papanicolaou DA, Bixler EO, Hopper K, Lotsikas A, Lin HM, Kales A, Chrousos GP (2000) Sleep apnea and daytime sleepiness and fatigue: relation to visceral obesity, insulin resistance, and hypercytokinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(3):1151–1158
Walker-Engström ML, Ringqvist I, Vestling O, Wilhelmsson B, Tegelberg Å (2003) A prospective randomized study comparing two different degrees of mandibular advancement with a dental appliance in treatment of severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 7(3):119–130
Carrera M, Barbe F, Sauleda J, Tomás M, Gómez C, Santos C, Agustí AG (2004) Effects of obesity upon genioglossus structure and function in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 23(3):425–429
Weaver TE, Grunstein RR (2008) Adherence to continuous positive airway pressure therapy: the challenge to effective treatment. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5(2):173–178
Conflict of interest
All authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Kim, MS., Lee, JE. et al. Treatment outcomes and compliance according to obesity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2885–2890 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2397-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2397-0