Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to evaluate vitamin D nutritional status and its relation with ionic calcium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), maternal anthropometry and perinatal outcomes in pregnant women who previously underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery.
Methods
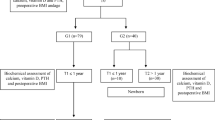
In a clinic specialized in obesity control located in the city of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), the following information were collected for adult women who underwent RYGB before pregnancy: serum concentrations of vitamin D [25(OH)D], calcium and PTH per gestational trimester and data on maternal anthropometry, gestational intercurrences and perinatal outcomes.
Results
The present study included 46 post-RYGB pregnant women. The prevalence of pregnant women with deficiency (≤20 ng/mL) or insufficiency (≥21 and 29 ng/mL) of vitamin D was above 70 % in all trimesters. The prevalence of calcium deficiency was 15.2 % in the first and in the second trimesters and 20 % in the third trimester, while the prevalence of excess PTH was 19.6, 30.4 and 32.6 % in the first, the second and the third trimesters, respectively. In the second and the third trimesters, a significant difference was observed between concentrations of 25(OH)D, and a negative correlation was observed between concentrations of calcium and PTH. Association of 25(OH)D with urinary tract infection (UTI) was found, but there was no association with calcium, PTH, maternal anthropometry, type of delivery and weight and gestational age at birth
Conclusions
The post-RYGB pregnant women showed an elevated serum inadequacy (deficiency or insufficiency) of 25(OH)D during pregnancy. Maternal vitamin D status showed no association with maternal variables, except UTI, and the neonatal variables analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomes GS, Rosa MA, Faria HRM (2009) Perfil nutricional dos pacientes de pós-operatório de cirurgia bariátrica. Nutrir Gerais 3(5):462–476
Facchiano E, Iannelli A, Santulli P, Mandelbrot L, Msika S (2012) Pregnancy after laparoscopic bariatric surgery: comparative study of adjustable gastric banding and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 8(4):429–433
WHO (World Health Organization) (2013) World Health Statistics. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2013/en/. Accessed 10 Feb 2014
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (2010) Pesquisa de Orçamentos Familiares 2008–2009. Available at: http://www.ibge.gov.br. Accessed 30 Nov 2013
Sociedade Brasileira de Cirurgia Bariátrica e Metabólica (2007) Mapeamento obesidade. Available at: http://www.sbcb.org.br/obesidade.asp?menu=4. Accessed 30 Oct 2013
Nomura RM, Dias MC, Igai AM, Liao AW, Miyadahira S, Zugaib M (2010) Avaliação da vitalidade fetal e resultados perinatais em gestações após gastroplastia com derivação em Y de Roux. Rev Assoc Med Bras 56(6):670–674
Lima JG, Nóbrega LHC, Mesquita JB, Nóbrega MLC, Medeiros AC, Maranhão TMO, Azevedo GD (2006) Gestação após gastroplastia para tratamento de obesidade mórbida: série de casos e revisão da literatura. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 28(2):107–111
Schuch NJ, Garcia VC, Martini LA (2009) Vitamina D e doenças endocrinometabólicas. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 53(5):625–633
Leffelaar ER, Vrijkotte TG, van Eijsden M (2010) Maternal early pregnancy vitamin D status in relation to fetal and neonatal growth: results of the multi-ethnic Amsterdam Born Children and their Development cohort. Br J Nutr 104(1):108–117
Sørensen IM, Joner G, Jenum PA, Eskild A, Torjesen PA, Stene LC (2012) Maternal serum levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of type 1 diabetes in the offspring. Diabetes 61(1):175–178
Erkkola M, Kaila M, Nwaru BI, Kronberg-Kippilä C, Ahonen S, Nevalainen J, Veijola R, Pekkanen J, Ilonen J, Simell O, Knip M, Virtanen SM (2009) Maternal vitamin D intake during pregnancy is inversely associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis in 5-year-old children. Clin Exp Allergy 39(6):875–882
Viljakainen HT, Saarnio E, Hytinantti T, Miettinen M, Surcel H, Mäkitie O, Andersson S, Laitinen K, Lamberg-Allardt C (2010) Maternal vitamin D status determines bone variables in the newborn. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(4):1749–1757
Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Chopra S, Agarwal N, Garg MK, Sharma B, Kanwar RS, Bhadra K, Singh S, Mani K, Puri S (2011) Vitamin D status in pregnant Indian women across trimesters and different seasons and its correlation with neonatal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Br J Nutr 106(9):1383–1389
Holmes VA, Barnes MS, Alexander HD, McFaul P, Wallace JM (2009) Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in pregnant women: a longitudinal study. Br J Nutr 102(6):876–881
Bodnar LM, Catov JM, Roberts JM, Simhan HN (2007) Prepregnancy obesity predicts poor vitamin d status in mothers and their neonates. J Nutr 137(11):2437–2442
WHO (World Health Organization) (1998) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of WHO consultation on obesity. Geneva: WHO
IOM (Institute of Medicine) (2009) Weight Gain during Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press
Dorsey JG (2010) Introduction to modern liquid chromatography. J Am ChemSoc 132:9220
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM, Endocrine Society (2011) Evaluation, treatment and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(7):1911–1930
Andriolo A, Moreira SR, Silva LA, Carvalho AB, Vieira JGH, Ghiringhello MT, Juliano Y (2004) Cálcio ionizado no soro: estimativa do intervalo de referência e condições de coleta. J Bras Patol Med Lab 40(2):85–89
Kao PC (1982) Parathyroid hormone assay. Mayo Clin Proc 57(9):596–597
Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. (2012) Atenção ao pré-natal de baixo risco. Brasília: Editora do Ministério da Saúde, 2012
Silva VRG (2009) Marcadores Pró-inflamatórios e de Estresse Oxidativo em Pacientes submetidos à Gastroplastia com Bypass em Y de Roux. Dissertation, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis
WHO (World Health Organization) (1995) Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry—report of a WHO Expert Committee. Geneva: WHO
Brasil. Ministério da Saúde (2005) Pré-natal e Puerpério: atenção qualificada e humanizada—manual técnico. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde, 2005
Pedreira CE, Pinto FA, Pereira SP, Costa ES (2011) Birth weight patterns by gestational age in Brazil. An Acad Bras Ciênc 83(2):619–625
Haliloglu B, Ilter E, Aksungar FB, Celik A, Coksuer H, Gunduz T, Yucel E, Ozekici U (2011) Bone turnover and maternal 25(OH) vitamin D3 levels during pregnancy and the postpartum period: should routine vitamin D supplementation be increased in pregnant women? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 158(1):24–27
González Navarro I, Pereira Cunill JL, Serrano Aguayo P, Morales Conde S, Martos Martínez JM, García Luna PP (2011) Resultados materno-fetales de la gestación tras cirugía bariátrica. Nutr Hosp 26(2):376–383
Aasheim ET, Björkman S, Søvik TT, Engström M, Hanvold SE, Mala T, Olbers T, Bøhmer T (2009) Vitamin status after bariatric surgery: a randomized study of gastric bypass and duodenal switch. Am J Clin Nutr 90(1):15–22
Lewis S, Lucas RM, Halliday J, Ponsonby AL (2010) Vitamin D deficiency and pregnancy: from preconception to birth. Mol Nutr Food Res 54(8):1092–1102
Need AG, O’Loughlin PD, Morris HA, Coates PS, Horowitz M, Nordin BE (2008) Vitamin D metabolites and calcium absorption in severe vitamin D deficiency. J Bone Miner Res 23(11):1859–1863
Shibata M, Suzuki A, Sekiya T, Sekiguchi S, Asano S, Udagawa Y, Itoh M (2011) High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in pregnant Japanese women with threatened premature delivery. J Bone Miner Metab 29(5):615–620
Andreassen MS, Ferraz LF, Jesus SNR, Piano A, Azevedo CH, Perez AIC (2012) Avaliação do binômio materno fetal após cirurgia bariátrica. BEPA 9(102):21–29
Guelinckx I, Devlieger R, Donceel P, Bel S, Pauwels S, Bogaerts A, Thijs I, Schurmans K, Deschilder P, Vansant G (2012) Lifestyle after bariatric surgery: a multicenter, prospective cohort study in pregnant women. Obes Surg 22(9):1456–1464
Kjær MM, Lauenborg J, Breum BM, Nilas L (2013) The risk of adverse pregnancy outcome after bariatric surgery: a nationwide register-based matched cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 208(6):464.e1–5
Melo ASO, Assunção PL, Gondim SSR, Carvalho DF, Amorim MMR, Benicio MHA, Cardoso MAA (2007) Estado nutricional materno, ganho de peso gestacional e peso ao nascer. Rev Bras Epidemiol 10(2):249–257
Magdaleno R Jr, Pereira BG, Chaim EA, Turato ER (2012) Pregnancy after bariatric surgery: a current view of maternal, obstetrical and perinatal challenges. Arch Gynecol Obstet 285(3):559–566
Di Carlo C, Iannotti G, Sparice S, Chiacchio MP, Greco E, Tommaselli GA, Nappi C (2014) The role of a personalized dietary intervention in managing gestational weight gain: a prospective, controlled study in a low-risk antenatal population. Arch Gynecol Obstet 289(4):765–770
Santulli P, Mandelbrot L, Facchiano E, Dussaux C, Ceccaldi PF, Ledoux S, Msika S (2010) Obstetrical neonatal outcomes of pregnancies following gastric bypass surgery: a retrospective cohort study in a French referral centre. Obes Surg 20(11):1501–1508
Lapolla A, Marangon M, Dalfrà MG, Segato G, De Luca M, Fedele D, Favretti F, Enzi G, Busetto L (2010) Pregnancy outcome in morbidly obese women before and after laparoscopic gastric banding. Obes Surg 20(9):1251–1257
Savvidou MD, Makgoba M, Castro PT, Akolekar R, Nicolaides KH (2012) First-trimester maternal serum vitamin D and mode of delivery. Br J Nutr 108(11):1972–1975
Fernández-Alonso AM, Dionis-Sánchez EC, Chedraui P, González-Salmerón MD, Pérez-López FR, Spanish Vitamin D and Women’s Health Research Group (2012) First-trimester maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 status and pregnancy outcome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 116(1):6–9
Merewood A, Mehta SD, Chen TC, Bauchner H, Holick MF (2009) Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Primary Cesarean Section. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(3):940–945
Bahadi A, El Kabbaj D, Elfazazi H, Abbi R, Hafidi MR, Hassani MM, Moussaoui R, Elouennass M, Dehayni M, Oualim Z (2010) Urinary tract infection in pregnancy. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 21(2):342–344
Nseir W, Taha M, Nemarny H, Mograbi J (2013) The association between serum levels of vitamin D and recurrent urinary tract infections in premenopausal women. Int J Infect Dis. 17(12):e1121–e1124
Lesko J, Peaceman A (2012) Pregnancy outcomes in women after bariatric surgery compared with obese and morbidly obese controls. Obstet Gynecol 119(3):547–554
Kominiarek MA (2011) Preparing for and managing a pregnancy after bariatric surgery. Semin Perinatol 35(6):356–361
Prentice A, Jarjou LMA, Goldberg GR, Bennett J, Cole TJ, Schoenmakers I (2009) Maternal plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and birthweight, growth and bone mineral accretion of Gambian infants. Acta Paediatr 98(8):1360–1362
Shand AW, Nassar N, Von Dadelszen P, Innis SM, Green TJ (2010) Maternal vitamin D status in pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes in a group at high risk for pre-eclampsia. BJOG 117(13):1593–1598
Farrant HJ, Krishnaveni GV, Hill JC, Boucher BJ, Fisher DJ, Noonan K, Osmond C, Veena SR, Fall CH (2009) Vitamin D insufficiency is common in Indian mothers but is not associated with gestational diabetes or variation in newborn size. Eur J ClinNutr 63(5):646–652
Bodnar LM, Zmuda JM, Cooper ME, Parrott MS, Roberts JM, Marazita ML, Simhan HN (2010) Maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with small-for-gestational age births in white women. J Nutr 140(5):999–1006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medeiros, M., Matos, A.C., Pereira, S.E. et al. Vitamin D and its relation with ionic calcium, parathyroid hormone, maternal and neonatal characteristics in pregnancy after roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Arch Gynecol Obstet 293, 539–547 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3861-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3861-4