Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to compare the clinical outcomes of surgical management by one-stage posterior debridement, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and instrumentation and combined posterior and anterior approaches for lumbar spinal tuberculosis, and determine the clinical effectiveness of the posterior only surgical treatment for lumbar spinal TB at the same time.
Methods
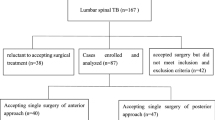
Thirty-seven patients who suffered lumbar tuberculosis were treated by two different surgical procedures in our center from May 2004 to June 2012. All the cases were divided into two groups: 19 cases in Group A underwent one-stage posterior debridement, TLIF and instrumentation, and 18 cases in Group B underwent posterior instrumentation, anterior debridement and bone graft in a single-stage procedure. The operation time, blood loss, lumbar kyphotic angle, recovery of neurological function and fusion time were, respectively, compared between Group A and Group B.
Results
The average follow-up period for Group A was 46.6 ± 16.7 months, and for Group B, 47.5 ± 15.0 months. It was obvious that the average operative duration and blood loss of Group A was less than those of Group B. Lumbar tuberculosis was completely cured and the grafted bones were fused in 10 months in all patients. There was no persistence or recurrence of infection and no differences in the radiological results in both groups. The kyphosis was significantly corrected after surgical management. The average pretreatment ESR was 60.7 ± 22.5 mm/h, which became normal (9.0 ± 2.8 mm/h) within 3 months in all patients.
Conclusions
Surgical management by one-stage posterior debridement, TLIF and instrumentation for lumbar tuberculosis is feasible and effective. This approach obtained better clinical outcomes than combined posterior and anterior surgeries.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moon MS, Moon YW, Moon JL et al (2002) Conservative treatment of tuberculosis of the lumbar and lower lumbar spine. Clin Orthop 398:40–49
Moon MS (2006) Development in the management of tuberculosis of the spine. Curr Orthop 20:132–140
Moon MS (2007) Tuberculosis of spine: contemporary thoughts on current issues and perspective views. Curr Orthop 27:364–379
Zhang HQ, Wang YX, Guo CF et al (2011) One-stage posterior focus debridement, fusion, and instrumentation in the surgical treatment of cervicothoracic spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis in children: a preliminary report. Childs Nerv Syst 27:735–742
Talu U, Gogus A, Ozturk C et al (2006) The role of posterior instrumentation and fusion after anterior radical debridement and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: experience of 127 cases. J Spinal Disord Tech 19:554–559
Hodgson AR, Stock FE (1960) Anterior spine fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine: The operative findings and results of treatment in the first 100 cases. J Bone Jt Surg Am 42:295–310
Fukuta S, Miyamoto K, Masuda T et al (2003) Two-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for pyogenic and tuberculotic spondylitis. Spine 28:E302–E308
Hirakawa A, Miyamoto K, Takahiro M et al (2010) Surgical outcome of 2-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord Tech 23:133–138
Kim DJ, Yun YH, Moon SH et al (2004) Posterior instrumentation using compressive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine. Spine 29:275–279
Laheri VJ, Badhe NP, Dewnany GT (2001) Single stage decompression, anterior interbody fusion and posterior instrumentation for tuberculous kyphosis of the dorso-lumbar spine. Spinal Cord 39:429–436
Zhang HQ, Li JS, Guo CF et al (2012) Two-stage surgical management using posterior instrumentation, anterior debridement and allografting for tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine in children of elementary school age: minimum 3-year follow-up of 14 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(9):1273–1279
Harms J, Jeszenszky D, Stolze D et al (1997) True spondylolisthesis reduction and more segmental fusion in spondylolisthesis. In: The textbook of spinal surgery, 2nd edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 1337–1347
Zhang HQ, Lin MZ, Shen KY, Ge L, Li JS, Tang MX, Wu JH, Liu JY (2012) Surgical management for multilevel noncontiguous thoracic spinal tuberculosis by single-stage posterior transforaminal thoracic debridement, limited decompression, interbody fusion, and posterior instrumentation (modified TTIF). Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(6):751–757
Hirakawa A, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, Fukuta S, Hosoe H, Iinuma N, Iwai C, Nishimoto H, Shimizu K (2010) Surgical outcome of 2-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(2):133–138
Medical Research Council Working Party On Tuberculosis of the Spine (1982) A 10-year assessments of controlled trials comparing debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine in patients on standard chemotherapy in Hong-Kong. J Bone Jt Surg (Br) 64:393–398
Bhojraj S, Nene A (2002) Lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculous spondylodiscitis in adults. Redefining the indications for surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:530–534
Jain AK (2007) Tuberculosis of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 460:39–49
Tuli SM (2007) Tuberculosis of the spine: a historical review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 460:29–38
Zaveri GR, Mebta SS (2009) Surgical treatment of lumbar tuberculosis spondylodiscitis by transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and posterior instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:257–262
Fukuta S, Miyamoto K, Masuda T et al (2003) Two-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for pyogenic and tuberculotic spondylitis. Spine 28:E302–E308
Rajasekaran S, Soundarapandian S (1989) Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71A:1314–1323
Garst RJ (1992) Tuberculosis of the spine: a review of 236 operated cases in an undeveloped region from 1954–1964. J Spinal Disord 3:286–299
Lehmer S, Steffee A, Gaines R (1994) Treatment of L5–S1 spondyloptosis by staged L5 resection with reduction and fusion of L4 onto S1. Spine 19:1916–1925
Upadhyay SS, Saji MJ, Sell P et al (1996) The effect of age on the change in deformity after anterior debridement surgery for tuberculosis of the spine. Spine 21:2356–2362
Guven O, Kumano K, Talcin S et al (1994) A single stage posterior approach and rigid fixation for preventing kyphosis in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Spine 19:1039–1043
Mehta JS, Bhojraj SY (2001) Tuberculosis of the thoracic spine: a classification based on the selection of surgical strategies. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:859–863
Govender S, Kumar KP (2003) Cortical allografts in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop 27(4):244–248
Govender S, Parbhoo AH (1999) Support of the anterior column with allografts in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81(1):106–109
Govender S (2002) The outcome of allografts and anterior instrumentation in spinal tuberculosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 398:60–66
Jain AK (2010) Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(7):905–913
Ozdemir HM, Us AK, Ogun T (2003) The role of anterior spinal instrumentation and allograft fibula for the treatment of pott disease. Spine 28(5):474–479
Acknowledgments
This publication was funded in part by the Major Program of the Hunan Province Fu Rong Scholar Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Hq., Lin, Mz., Li, Js. et al. One-stage posterior debridement, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and instrumentation in treatment of lumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective case series. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133, 333–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1669-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-012-1669-2