Abstract
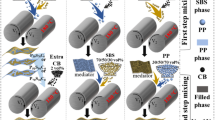
A carbon black (CB)/polypropylene (PP)/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composite with a segregated structure was fabricated by using binary polymer granules as matrices. In preparation, an ethanol-assisted dispersion method was employed to disperse CB particles on the surface of the two polymer granules. The segregated conductive network was then constructed by hot compaction based on the volume exclusion effect of the polymer matrices. The conductive composite shows an ultralow percolation threshold of 0.34 vol.%. In temperature-resistivity test, a double positive temperature coefficient (PTC) effect was observed. In addition, the negative temperature coefficient (NTC) effect was eliminated significantly. These interesting temperature-resistivity behaviors were ascribed to the introduction of the binary polymer matrices and the mobility limitation of CB particles located at the PP/UHMWPE interface. These characteristics were probed by in situ morphology observation in heating process. The present paper provides a novel route for preparing conductive composites with an ultralow percolation threshold, a wider PTC region, and a zero NTC effect.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai K, Xu XB, Li ZM (2007) Electrically conductive carbon black (CB) filled in situ microfibrillar poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/polyethylene (PE) composite with a selective CB distribution. Polymer 48:849–859
Dai K, Li ZM, Xu XB (2008) Electrically conductive in situ microfibrillar composite with a selective carbon black distribution: an unusual resistivity-temperature behavior upon cooling. Polymer 49:1037–1048
Zha JW, Li WK, Liao RJ, Bai JB, Dang ZM (2013) High performance hybrid carbon fillers/binary–polymer nanocomposites with remarkably enhanced positive temperature coefficient effect of resistance. J Mater Chem A 1:843–851
Dang ZM, Li WK, Xu HP (2009) Origin of remarkable positive temperature coefficient effect in the modified carbon black and carbon fiber cofilled polymer composites. J Appl Phys 106:024913
Bao SP, Liang GD, Tjong SC (2011) Effect of mechanical stretching on electrical conductivity and positive temperature coefficient characteristics of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon nanofiber composites prepared by non-solvent precipitation. Carbon 49:1758–1768
Deng H, Lin L, Ji MZ, Zhang SM, Yang MB, Fu Q (2014) Progress on the morphological control of conductive network in conductive polymer composites and the use as electroactive multifunctional materials. Prog Polym Sci 39:627–655
Luo YL, Wang GC, Zhang BY, Zhang ZP (1998) The influence of crystalline and aggregate structure on PTC characteristic of conductive polyethylene/carbon black composite. Eur Polym J 34:1221–1227
Isaji S, Bin YZ, Matsuo M (2009) Electrical conductivity and self-temperature-control heating properties of carbon nanotubes filled polyethylene films. Polymer 50:1046–1053
Heaney MB (1996) Resistance-expansion-temperature behavior of a disordered conductor-insulator composite. Appl Phys Lett 69:2602–2604
Azulay D, Eylon M, Eshkenazi O, Toker D, Balberg M, Shimoni N, Millo O, Balberg I (2003) Electrical-thermal switching in carbon-black-polymer composites as a local effect. Phys Rev Lett 90:236601
Duggal AR, Levinson LM (1997) High power switching behavior in electrically conductive polymer composite materials. Appl Phys Lett 71:1939–1941
Chan CM, Cheng CL, Yuen MMF (1997) Electrical properties of polymer composites prepared by sintering a mixture of carbon black and utra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder. Polym Eng Sci 37:1127–1136
Xi Y, Ishikawa H, Bin YZ, Matsuo M (2004) Positive temperature coefficient effect of LMWPE-UHMWPE blends filled with short carbon fibers. Carbon 42:1699–1706
Zhang C, Ma CA, Wang P, Sumita M (2005) Temperature dependence of electrical resistivity for carbon black filled ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene composites prepared by hot compaction. Carbon 43:2544–2553
Mironi-Harpaz I, Narkis M (2001) Electrical behavior and structure of polypropylene/ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/carbon black immiscible blends. J Appl Polym Sci 81:104–115
Mironi-Harpaz I, Narkis M (2001) Thermoelectric behavior (PTC) of carbon black-containing TPX/UHMWPE and TPX/XL-UHMWPE blends. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 39:1415–1428
Dai K, Zhang YC, Tang JH, Ji X, Li ZM (2012) Anomalous attenuation and structural origin of positive temperature coefficient (PTC) effect in a carbon black (CB)/poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/polyethylene (PE) electrically conductive microfibrillar polymer composite with a preferential CB distribution. J Appl Polym Sci 125:E561–E570
Di WH, Zhang G, Xu JQ, Peng Y, Wang XJ, Xie ZY (2003) Positive-temperature-coefficient/negative-temperature-coefficient effect of low-density polyethylene filled with a mixture of carbon black and carbon fiber. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 41:3094–3101
Bao Y, Xu L, Pang H, Yan DX, Chen C, Zhang WQ, Tang JH, Li ZM (2013) Preparation and properties of carbon black/polymer composites with segregated and double-percolated network structure. J Mater Sci 48:4892–4898
Pang H, Chen C, Bao Y, Chen J, Ji X, Lei J, Li ZM (2012) Electrically conductive carbon nanotube/ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composites with segregated and double percolated structure. Mater Lett 79:96–99
Pang H, Zhang YC, Chen T, Zeng BQ, Li ZM (2010) Tunable positive temperature coefficient of resistivity in an electrically conducting polymer/graphene composite. Appl Phys Lett 96:251907
Grunlan JC, Mehrabi AR, Bannon MV, Bahr JL (2004) Water-based single-walled-nanotube-filled polymer composite with an exceptionally low percolation threshold. Adv Mater 16:150–153
Pang H, Chen T, Zhang GM, Zeng BQ, Li ZM (2010) An electrically conducting polymer/graphene composite with a very low percolation threshold. Mater Lett 64:2226–2229
Ren PG, Di YY, Zhang Q, Li L, Pang H, Li ZM (2012) Composites of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene with graphene sheets and/or MWCNTs with segregated network structure: preparation and properties. Macromol Mater Eng 297:437–443
Gao JF, Li ZM, Meng QJ, Yang Q (2008) CNTs/UHMWPE composites with a two-dimensional conductive network. Mater Lett 62:3530–3532
Hu HL, Zhang G, Xiao LG, Wang HJ, Zhang QS, Zhao ZD (2012) Preparation and electrical conductivity of graphene/ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composites with a segregated structure. Carbon 50:4596–4599
Tan YQ, Song YH, Cao Q, Zheng Q (2011) Characterization of carbon black-filled immiscible polypropylene/polystyrene blends. Polym Int 60:823–832
Xu HP, Dang ZM, Shi DH, Bai JB (2008) Remarkable selective localization of modified nanoscaled carbon black and positive temperature coefficient effect in binary-polymer matrix composites. J Mater Chem 18:2685–2690
Göldel A, Kasaliwal G, Pötschke P (2009) Selective localization and migration of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in blends of polycarbonate and poly(styrene-acrylonitrile). Macromol Rapid Commun 30:423–429
Li B, Zhang YC, Li ZM, Li SN, Zhao XN (2010) Easy fabrication and resistivity-temperature behavior of an anisotropically conductive carbon nanotube-polymer composite. J Phys Chem B 114:689–696
Feng JY, Chan CM (2000) Double positive temperature coefficient effects of carbon black-filled polymer blends containing two semicrystalline polymers. Polymer 41:4559–4565
Gao JF, Li ZM, Peng S, Yan DX (2009) Temperature-resistivity behaviour of CNTs/UHMWPE composites with a two-dimensional conductive network. Polym-Plast Technol 48:478–481
Meyer J (1974) Stability of polymer composites as positive-temperature-coefficient resistors. Polym Eng Sci 14:706–716
Balberg I, Azulay D, Toker D, Millo O (2004) Percolation and tunneling in composite materials. Int J Mod Phys B 18:2091–2121
Bin Y, Xu C, Zhu D, Matsuo M (2002) Electrical properties of polyethylene and carbon black particle blends prepared by gelation/crystallization from solution. Carbon 40:195–199
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Henan Talents Fostering joint Funds (Contract Number U1204507) and National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, Contract Number 2012CB025903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 86 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Li, Z., Liu, X. et al. Temperature-resistivity characteristics of a segregated conductive CB/PP/UHMWPE composite. Colloid Polym Sci 292, 2891–2898 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3334-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3334-5