Abstract
Purpose
To report the vitamin D status in adults from seven European countries and to identify behavioural correlates.
Methods
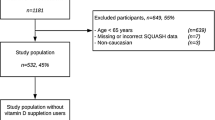
In total, 1075 eligible adult men and women from Ireland, Netherlands, Spain, Greece, UK, Poland and Germany, were included in the study.
Results
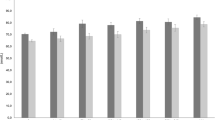
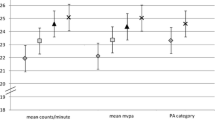
Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency, defined as 25-hydroxy vitamin D3 (25-OHD3) concentration of <30 and 30–49.9 nmol/L, respectively, were observed in 3.3 and 30.6% of the participants. The highest prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was found in the UK and the lowest in the Netherlands (8.2 vs. 1.1%, P < 0.05). In addition, the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency was higher in females compared with males (36.6 vs. 22.6%, P < 0.001), in winter compared with summer months (39.3 vs. 25.0%, P < 0.05) and in younger compared with older participants (36.0 vs. 24.4%, P < 0.05). Positive dose–response associations were also observed between 25-OHD3 concentrations and dietary vitamin D intake from foods and supplements, as well as with physical activity (PA) levels. Vitamin D intakes of ≥5 μg/day from foods and ≥5 μg/day from supplements, as well as engagement in ≥30 min/day of moderate- and vigorous-intensity PA were associated with higher odds (P < 0.05) for maintaining sufficient (≥50 nmol/L) 25-OHD3 concentrations.
Conclusions
The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency varied considerably among European adults. Dietary intakes of ≥10 μg/day of vitamin D from foods and/or supplements and at least 30 min/day of moderate- and vigorous-intensity PA were the minimum thresholds associated with vitamin D sufficiency.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor CL, Thomas PR, Aloia JF, Millard PS, Rosen CJ (2015) Questions about vitamin D for primary care practice: input from an NIH conference. Am J Med. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.05.025
Theodoratou E, Tzoulaki I, Zgaga L, Ioannidis JP (2014) Vitamin D and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials. BMJ 348:g2035. doi:10.1136/bmj.g2035
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357(3):266–281. doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Wang TJ, Pencina MJ, Booth SL, Jacques PF, Ingelsson E, Lanier K, Benjamin EJ, D’Agostino RB, Wolf M, Vasan RS (2008) Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 117(4):503–511. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.706127
Gulseth HL, Gjelstad IM, Birkeland KI, Drevon CA (2013) Vitamin D and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 11(6):968–984
van Schoor NM, Lips P (2011) Worldwide vitamin D status. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25(4):671–680. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2011.06.007
Hagenau T, Vest R, Gissel TN, Poulsen CS, Erlandsen M, Mosekilde L, Vestergaard P (2009) Global vitamin D levels in relation to age, gender, skin pigmentation and latitude: an ecologic meta-regression analysis. Osteoporos Int 20(1):133–140. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0626-y
Lips P (2007) Vitamin D status and nutrition in Europe and Asia. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 103(3–5):620–625. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.076
Hilger J, Friedel A, Herr R, Rausch T, Roos F, Wahl DA, Pierroz DD, Weber P, Hoffmann K (2014) A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide. Br J Nutr 111(1):23–45. doi:10.1017/S0007114513001840
Holick MF (2006) Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets. J Clin Invest 116(8):2062–2072. doi:10.1172/JCI29449
Engelsen O, Brustad M, Aksnes L, Lund E (2005) Daily duration of vitamin D synthesis in human skin with relation to latitude, total ozone, altitude, ground cover, aerosols and cloud thickness. Photochem Photobiol 81(6):1287–1290. doi:10.1562/2004-11-19-rn-375
Moschonis G, Tanagra S, Koutsikas K, Nikolaidou A, Androutsos O, Manios Y (2009) Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and body composition in postmenopausal women: the postmenopausal Health Study. Menopause 16(4):701–707. doi:10.1097/gme.0b013e318199d5d5
Lips P, van Schoor NM, de Jongh RT (2014) Diet, sun, and lifestyle as determinants of vitamin D status. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1317:92–98. doi:10.1111/nyas.12443
Touvier M, Deschasaux M, Montourcy M, Sutton A, Charnaux N, Kesse-Guyot E, Assmann KE, Fezeu L, Latino-Martel P, Druesne-Pecollo N, Guinot C, Latreille J, Malvy D, Galan P, Hercberg S, Le Clerc S, Souberbielle JC, Ezzedine K (2015) Determinants of vitamin D status in caucasian adults: influence of sun exposure, dietary intake, sociodemographic, lifestyle, anthropometric, and genetic factors. J Invest Dermatol 135(2):378–388. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.400
Wanner M, Richard A, Martin B, Linseisen J, Rohrmann S (2015) Associations between objective and self-reported physical activity and vitamin D serum levels in the US population. Cancer Causes Control 26(6):881–891. doi:10.1007/s10552-015-0563-y
Calvo MS, Whiting SJ, Barton CN (2005) Vitamin D intake: a global perspective of current status. J Nutr 135(2):310–316
Flynn A, Hirvonen T, Mensink GB, Ocke MC, Serra-Majem L, Stos K, Szponar L, Tetens I, Turrini A, Fletcher R, Wildemann T (2009) Intake of selected nutrients from foods, from fortification and from supplements in various European countries. Food Nutr Res. doi:10.3402/fnr.v53i0.2038
Celis-Morales C, Livingstone KM, Marsaux CF, Forster H, O’Donovan CB, Woolhead C, Macready AL, Fallaize R, Navas-Carretero S, San-Cristobal R, Kolossa S, Hartwig K, Tsirigoti L, Lambrinou CP, Moschonis G, Godlewska M, Surwillo A, Grimaldi K, Bouwman J, Daly EJ, Akujobi V, O’Riordan R, Hoonhout J, Claassen A, Hoeller U, Gundersen TE, Kaland SE, Matthews JN, Manios Y, Traczyk I, Drevon CA, Gibney ER, Brennan L, Walsh MC, Lovegrove JA, Alfredo Martinez J, Saris WH, Daniel H, Gibney M, Mathers JC (2015) Design and baseline characteristics of the Food4Me study: a web-based randomised controlled trial of personalised nutrition in seven European countries. Genes Nutr 10 (1):450. doi:10.1007/s12263-014-0450-2
Hoeller U, Baur M, Roos FF, Brennan L, Daniel H, Fallaize R, Forster H, Gibney ER, Gibney M, Godlewska M, Hartwig K, Kolossa S, Lambrinou CP, Livingstone KM, Lovegrove JA, Macready AL, Manios Y, Marsaux CF, Martinez JA, Celis-Morales C, Moschonis G, Navas-Carretero S, O’Donovan CB, San-Cristobal R, Saris WH, Surwillo A, Traczyk I, Tsirigoti L, Walsh MC, Woolhead C, Mathers JC, Weber P (2015) Application of dried blood spots to determine vitamin D status in a large nutritional study with unsupervised sampling: the Food4Me project. Br J Nutr. doi:10.1017/S0007114515004298
Livingstone KM, Celis-Morales C, Navas-Carretero S, San-Cristobal R, O’Donovan CB, Forster H, Woolhead C, Marsaux CF, Macready AL, Fallaize R, Kolossa S, Tsirigoti L, Lambrinou CP, Moschonis G, Godlewska M, Surwillo A, Drevon CA, Manios Y, Traczyk I, Gibney ER, Brennan L, Walsh MC, Lovegrove JA, Alfredo Martinez J, Saris WH, Daniel H, Gibney M, Mathers JC (2015) Profile of European adults interested in internet-based personalised nutrition: the Food4Me study. Eur J Nutr. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-0897-y
Fallaize R, Forster H, Macready AL, Walsh MC, Mathers JC, Brennan L, Gibney ER, Gibney MJ, Lovegrove JA (2014) Online dietary intake estimation: reproducibility and validity of the Food4Me food frequency questionnaire against a 4-day weighed food record. J Med Internet Res 16(8):e190. doi:10.2196/jmir.3355
Forster H, Fallaize R, Gallagher C, O’Donovan CB, Woolhead C, Walsh MC, Macready AL, Lovegrove JA, Mathers JC, Gibney MJ, Brennan L, Gibney ER (2014) Online dietary intake estimation: the Food4Me food frequency questionnaire. J Med Internet Res 16(6):e150. doi:10.2196/jmir.3105
Livingstone KM, Celis-Morales C, Navas-Carretero S, San-Cristobal R, Macready AL, Fallaize R, Forster H, Woolhead C, O’Donovan CB, Marsaux CF, Kolossa S, Tsirigoti L, Lambrinou CP, Moschonis G, Godlewska M, Surwillo A, Drevon CA, Manios Y, Traczyk I, Gibney ER, Brennan L, Walsh MC, Lovegrove JA, Saris WH, Daniel H, Gibney M, Martinez JA, Mathers JC, Food4Me S (2016) Effect of an Internet-based, personalized nutrition randomized trial on dietary changes associated with the Mediterranean diet: the Food4Me Study. Am J Clin Nutr 104(2):288–297. doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.129049
Celis-Morales C, Livingstone KM, Woolhead C, Forster H, O’Donovan CB, Macready AL, Fallaize R, Marsaux CF, Tsirigoti L, Efstathopoulou E, Moschonis G, Navas-Carretero S, San-Cristobal R, Kolossa S, Klein UL, Hallmann J, Godlewska M, Surwillo A, Drevon CA, Bouwman J, Grimaldi K, Parnell LD, Manios Y, Traczyk I, Gibney ER, Brennan L, Walsh MC, Lovegrove JA, Martinez JA, Daniel H, Saris WH, Gibney M, Mathers JC (2015) How reliable is internet-based self-reported identity, socio-demographic and obesity measures in European adults? Genes Nutr 10 (5):476. doi:10.1007/s12263-015-0476-0
McCance RAW (2002) Royal Society of Chemistry; McCance and Widdowson’s the composition of foods, 7th edn. London.
Institute of Medicine Food and Nutrition Board (2011) Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D. Washington (DC): National Academy Press.
Bonomi AG, Plasqui G, Goris AH, Westerterp KR (2010) Estimation of free-living energy expenditure using a novel activity monitor designed to minimize obtrusiveness. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(9):1845–1851. doi:10.1038/oby.2010.34
Plasqui G, Joosen AM, Kester AD, Goris AH, Westerterp KR (2005) Measuring free-living energy expenditure and physical activity with triaxial accelerometry. Obes Res 13(8):1363–1369. doi:10.1038/oby.2005.165
Plasqui G, Westerterp KR (2007) Physical activity assessment with accelerometers: an evaluation against doubly labeled water. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15(10):2371–2379. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.281
Choi L, Liu Z, Matthews CE, Buchowski MS (2011) Validation of accelerometer wear and nonwear time classification algorithm. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(2):357–364. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ed61a3
Marsaux CF, Celis-Morales C, Fallaize R, Macready AL, Kolossa S, Woolhead C, O’Donovan CB, Forster H, Navas-Carretero S, San-Cristobal R, Lambrinou CP, Moschonis G, Surwillo A, Godlewska M, Goris A, Hoonhout J, Drevon CA, Manios Y, Traczyk I, Walsh MC, Gibney ER, Brennan L, Martinez JA, Lovegrove JA, Gibney MJ, Daniel H, Mathers JC, Saris WH (2015) Effects of a web-based personalized intervention on physical activity in European adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res 17(10):e231. doi:10.2196/jmir.4660
World Health Organization (2010) Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Recommended population levels of physical activity for health. World Health Organization, World Health
Binkley N, Krueger D, Cowgill CS, Plum L, Lake E, Hansen KE, DeLuca HF, Drezner MK (2004) Assay variation confounds the diagnosis of hypovitaminosis D: a call for standardization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(7):3152–3157. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031979
Wallace AM, Gibson S, de la Hunty A, Lamberg-Allardt C, Ashwell M (2010) Measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the clinical laboratory: current procedures, performance characteristics and limitations. Steroids 75(7):477–488. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.02.012
Cashman KD, Dowling KG, Skrabakova Z, Gonzalez-Gross M, Valtuena J, De Henauw S, Moreno L, Damsgaard CT, Michaelsen KF, Molgaard C, Jorde R, Grimnes G, Moschonis G, Mavrogianni C, Manios Y, Thamm M, Mensink GB, Rabenberg M, Busch MA, Cox L, Meadows S, Goldberg G, Prentice A, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Pilz S, Swart KM, van Schoor NM, Lips P, Eiriksdottir G, Gudnason V, Cotch MF, Koskinen S, Lamberg-Allardt C, Durazo-Arvizu RA, Sempos CT, Kiely M (2016) Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic? Am J Clin Nutr. doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.120873
Lanham-New SA, Buttriss JL, Miles LM, Ashwell M, Berry JL, Boucher BJ, Cashman KD, Cooper C, Darling AL, Francis RM, Fraser WD, de Groot CP, Hypponen E, Kiely M, Lamberg-Allardt C, Macdonald HM, Martineau AR, Masud T, Mavroeidi A, Nowson C, Prentice A, Stone EM, Reddy S, Vieth R, Williams CM (2011) Proceedings of the rank forum on Vitamin D. Br J Nutr 105(1):144–156. doi:10.1017/S0007114510002576
MacLaughlin J, Holick MF (1985) Aging decreases the capacity of human skin to produce vitamin D3. J Clin Invest 76(4):1536–1538. doi:10.1172/JCI112134
Lips P, van Ginkel FC, Jongen MJ, Rubertus F, van der Vijgh WJ, Netelenbos JC (1987) Determinants of vitamin D status in patients with hip fracture and in elderly control subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 46(6):1005–1010
Hill TR, Granic A, Davies K, Collerton J, Martin-Ruiz C, Siervo M, Mathers JC, Adamson AJ, Francis RM, Pearce SH, Razvi S, Kirkwood TB, Jagger C (2016) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and its determinants in the very old: the Newcastle 85+ study. Osteoporos Int 27(3):1199–1208. doi:10.1007/s00198-015-3366-9
DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL (2001) Endocrinology. 4th edn. W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia
Roman Vinas B, Ribas Barba L, Ngo J, Gurinovic M, Novakovic R, Cavelaars A, de Groot LC, van’t Veer P, Matthys C, Serra Majem L (2011) Projected prevalence of inadequate nutrient intakes in Europe. Ann Nutr Metab 59(2–4):84–95. doi:10.1159/000332762
Kiely M, Black LJ (2012) Dietary strategies to maintain adequacy of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 243:14–23. doi:10.3109/00365513.2012.681893
Skeie G, Braaten T, Hjartaker A, Lentjes M, Amiano P, Jakszyn P, Pala V, Palanca A, Niekerk EM, Verhagen H, Avloniti K, Psaltopoulou T, Niravong M, Touvier M, Nimptsch K, Haubrock J, Walker L, Spencer EA, Roswall N, Olsen A, Wallstrom P, Nilsson S, Casagrande C, Deharveng G, Hellstrom V, Boutron-Ruault MC, Tjonneland A, Joensen AM, Clavel-Chapelon F, Trichopoulou A, Martinez C, Rodriguez L, Frasca G, Sacerdote C, Peeters PH, Linseisen J, Schienkiewitz A, Welch AA, Manjer J, Ferrari P, Riboli E, Bingham S, Engeset D, Lund E, Slimani N (2009) Use of dietary supplements in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition calibration study. Eur J Clin Nutr 63(Suppl 4):S226–S238. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2009.83
Black LJ, Walton J, Flynn A, Cashman KD, Kiely M (2015) Small increments in vitamin D intake by Irish adults over a decade show that strategic initiatives to fortify the food supply are needed. J Nutr 145(5):969–976. doi:10.3945/jn.114.209106
Cashman KD (2015) Vitamin D: dietary requirements and food fortification as a means of helping achieve adequate vitamin D status. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 148:19–26. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.01.023
Calvo MS, Whiting SJ (2006) Public health strategies to overcome barriers to optimal vitamin D status in populations with special needs. J Nutr 136(4):1135–1139
Autier P, Gandini S, Mullie P (2012) A systematic review: influence of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(8):2606–2613. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-1238
Glerup H, Mikkelsen K, Poulsen L, Hass E, Overbeck S, Thomsen J, Charles P, Eriksen EF (2000) Commonly recommended daily intake of vitamin D is not sufficient if sunlight exposure is limited. J Intern Med 247(2):260–268
Jones G, Dwyer T (1998) Bone mass in prepubertal children: gender differences and the role of physical activity and sunlight exposure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(12):4274–4279. doi:10.1210/jcem.83.12.5353
Sato Y, Iwamoto J, Kanoko T, Satoh K (2005) Amelioration of osteoporosis and hypovitaminosis D by sunlight exposure in hospitalized, elderly women with Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res 20(8):1327–1333. doi:10.1359/JBMR.050402
Holick MF (2011) Vitamin D deficiency in 2010: health benefits of vitamin D and sunlight: a D-bate. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(2):73–75. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2010.234
Berger C, Greene-Finestone LS, Langsetmo L, Kreiger N, Joseph L, Kovacs CS, Richards JB, Hidiroglou N, Sarafin K, Davison KS, Adachi JD, Brown J, Hanley DA, Prior JC, Goltzman D (2012) Temporal trends and determinants of longitudinal change in 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels. J Bone Miner Res 27(6):1381–1389. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1587
Thuesen B, Husemoen L, Fenger M, Jakobsen J, Schwarz P, Toft U, Ovesen L, Jorgensen T, Linneberg A (2012) Determinants of vitamin D status in a general population of Danish adults. Bone 50(3):605–610. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.12.016
Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A (2007) Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(8):1423–1434. doi:10.1249/mss.0b013e3180616b27
Pursey K, Burrows TL, Stanwell P, Collins CE (2014) How accurate is web-based self-reported height, weight, and body mass index in young adults? J Med Internet Res 16(1):e4. doi:10.2196/jmir.2909
Lassale C, Peneau S, Touvier M, Julia C, Galan P, Hercberg S, Kesse-Guyot E (2013) Validity of web-based self-reported weight and height: results of the Nutrinet-Sante study. J Med Internet Res 15(8):e152. doi:10.2196/jmir.2575
Acknowledgements
Study approval: The Food4Me study has been reviewed and approved by seven independent ethical research committees in each of the countries involved in the trial. Patient consent: All participants, both screened and randomised, have given consent to take part in this study. Funding statement: This work was supported by the European Commission under the Food, Agriculture, Fisheries and Biotechnology Theme of the 7th Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development [265494].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manios, Y., Moschonis, G., Lambrinou, C.P. et al. Associations of vitamin D status with dietary intakes and physical activity levels among adults from seven European countries: the Food4Me study. Eur J Nutr 57, 1357–1368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1415-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1415-1