Abstract
Objective
Evaluate the effects of neonatal malnutrition on the microbicidal response and viability of in vitro macrophages infected with Staphylococcus aureus sensitive/resistant to methicillin.
Methods
Male Wistar rats (n = 24) were divided into two distinct groups: nourished (rats breast-fed by mothers undergoing diet with 17 % casein) and malnourished (rats breast-fed by mothers undergoing diet with 8 % casein). Macrophages were recovered after surgical tracheostomy procedure by collecting bronchoalveolar lavage. Four systems were established: negative control, composed only by phagocytes; positive control, macrophages plus lipopolysaccharide; and two test systems, macrophages plus Staphylococcus aureus sensitive and resistant to methicillin. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. After this period, tests for the analysis of cell viability and microbicidal response were performed. In the statistical analysis, the Student’s t and ANOVA tests were used, accepting p < 0.05.
Results
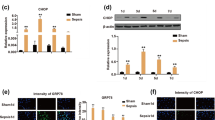
The neonatal malnutrition impaired the animals’ body weight. There was a lower expression of the inducible nitric oxide enzyme (iNOS), nitric oxide production, and viability of macrophages infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. However, increased production of superoxide anion in the malnourished group was detected.
Conclusion
Neonatal malnutrition focusing on critical periods of development promoted lower expression of iNOS, nitric oxide production, cell viability, and exacerbated reactive oxygen species production. The high levels of reactive oxygen species may favor the onset of serious and systemic infections with fatal outcome if associated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pereira KNF, Vitoriano ILS, Melo MPP, Aragão RS, Toscano AE, Silva HJ, De Castro RM (2009) Effects of malnutrition and/or neonatal inhibition of serotonin reuptake in neuromuscular development of the gastrointestinal tract: review of literature. Neurobiology 72(2):215–221
Robinson S, Fall C (2012) Infant nutrition and later health: a review of current evidence. Nutrition 4:859–874. doi:10.3390/nu4080859
Fisher RE, Steele M, Karrow AA (2012) Fetal programming of the neuroendocrine-immune system and metabolic disease. J Pregnancy 1:1–11. doi:10.1155/2012/792934
Iliakis D, Kressig RW (2014) The relationship between malnutrition and immune. Ther Umsch 71(1):55–61. doi:10.1024/0040-5930/a000481
Cruviel WM, Júnior DM, Araújo JAP, Catelan TTT, Souza AWS, Silva NP, Andrade LEC (2010) Fundamentos da imunidade inata com ênfase nos mecanismos moleculares e celulares da resposta inflamatória. Rev Bras Reumatol 50(4):434–461
França TGD, Ishikawa LLW, Zorzella-Pezavento SFG, Chiuso-Minicucci F, Guerino CPF, Cunha MLRS, Sartori A (2009) Immunization protected well nourished mice but not undernourished ones from lung injury in Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. BMC Microbiol 9:240. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-240
Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE (2008) The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Genet Evol 8(6):747–763. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007
Zecconi A, Scali F (2013) Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors in evasion from innate immune defenses in human and animal diseases. Immunol Lett 150(1–2):12–22
Faria NA, Oliveira DC, Westh H, Monnet DL, Larsen AR, Skov R, De Lencastre H (2005) Epidemiology of emerging methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Denmark: a nationwide study in a country with low prevalence of MRSA infection. J Clin Microbiol 43:1836–1842
Gordon RJ, Lowy FD (2008) Pathogenesis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis 16:209–213
Shibabaw A, Abebe T, Mihret A (2014) Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of nasal Staphylococcus aureus among Dessie Referral Hospital health care workers, Dessie, Northeast Ethiopia. Internat J Infect Dis, 2:1–4. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2014.03.1386
Morais NG, Costa TB, Almeida TM, Severo MS, De Castro CMMB (2013) Parâmetros imunológicos de macrófagos frente à infecção por Staphylococcus aureus meticilina sensível/resistente. J Bras Patol Med Lab 49(2):84–90. doi:10.1590/S1676-24442013000200002
Too HP (2003) Real time PCR quantification of GFR-2 alternatively spliced isoforms in murine brain and peripheral tissues. Mol Brain Res Amst 114:146–154
Gonçalves SC, Régis-da-Silva CG, Brito MEF, Brandão-Filho SP, Paiva-Cavalcanti M (2012) Application of the mammalian glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene for sample quality control in multiplex PCR for diagnosis of leishmaniasis. J Venom Anim Toxins incl Trop Dis 18(2):188–197
Araujo FRG, De Castro CMMB, Rocha JA, Sampaio B, Diniz MFA, Eve LB, Montarroyos UR (2012) Perialveolar bacterial microbiota and bacteraemia after dental alveolitis in adult rats that had been subjected to neonatal malnutrition. Br J Nutr 107:996–1005. doi:10.1017/S000711451100393X
Costa TB, Morais NG, Almeida TM, Severo MS, De Castro CMMB (2012) Early malnutrition and production of IFN-δ, IL-12 and IL-10 by macrophages/lymphocytes: in vitro study of cell infection by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Nutr 25(5):607–619. doi:10.1590/S1415-52732012000500006
Porto SMMS, Viana MT, Silva KMF, Diniz MFA, De Castro CMMB (2007) Desnutrição neonatal e microbiota normal da cavidade oral em ratos. Rev Bras Nutr 20(6):625–632
Jones KDJ, Berkley JA, Warner JO (2013) Perinatal nutrition and immunity to infection. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 21(4):564–576
Mcgettrick AF, O’neill LAJ (2010) Localisation and trafficking of Toll-like receptors: an important mode of regulation. Curr Opin Immunol 22(1):20–27
Schaible UE, Kaufmann SHE (2007) Malnutrition and infection: complex mechanisms and global impacts. PLoS Med 4(5):806–812. doi:10.1371/journal/pmed.0040115.t001
Ferreira WTS, Galvão BA, Ferraz PKN, De Castro CMMB, De Castro RM (2008) Perinatal malnutrition programs sustained alterations in nitric oxide release by activated macrophages in response to fluoxetine in adult rat. NeuroImmunoModulation 23:120–129
Wang J, Wu Z, Li D, Li N, Dindot SV, Satterfield C, Bazer FW, Wu G (2009) Nutrition, epigenetics, and metabolic syndrome. Antioxid Redox Signal 17(2):282–302
Foster TJ (2009) Colonization and infection of the human host by staphylococci: adhesion, survival and immune evasion. J Vet Dermatol 20(5–6):456–470
Kim JJ, Jo EJ (2013) NLRP3 inflammasome and host protection against bacterial infection. Korean Med Sci 28:1415–1423
Pumerantz A, Muppidi K, Agnihotri S, Guerrac C, Venketaraman V, Wangb J, Betageri G (2010) Preparation of liposomal vancomycin and intracellular killing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Internat J Antimicrob Agents 32:1–5
Richardson AR, Libby SJ, Fang FC (2008) A nitric oxide-inducible lactate dehydrogenase enables staphylococcus aureus to resist innate immunity. Science 319:1–21. doi:10.1126/science.1155207
Macedo EMC, Amorim MAF, Silva ACS, Castro CMMB (2010) Effects of copper, zinc and magnesium deficiency on the immune system of severely malnourished children. Rev Paul Pediatr 28(3):329–336
Sarni ROS, Souza FIS, Cocco RR, Mallozi MC, Solé D (2010) Micronutrients, immunologic system and allergic diseases. Rev Bras Alerg Imunopatol 33(1):8–13
Köhler J, Breitbacha K (2011) NADPH-oxidase but not inducible nitric oxide synthase contributes to resistance in a murine Staphylococcus aureus Newman pneumonia model. Microbes Infect 13(11):914–922
Kurokawa K, Gong J, Ryu K, Zheng L, Chae J, Kim M, Lee BL (2011) Biochemical characterization of evasion from peptidoglycan recognition by Staphylococcus aureus D-alanylated wall teichoic acid in insect innate immunity. Dev Comp Immunol 35(8):835–839
Graves SF, Kobayashi SD, DeLeo FR (2010) Community-associated methicillin resistantStaphylococcus aureus immune evasion and virulence. J Mol Med 88:109–114
Nizet V (2007) Understanding how leading bacterial pathogens subvert innate immunity to reveal novel therapeutic targets. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120(1):13–22. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2007.06.005
Rivadeneira DE, Grobmyer SR, Naama HA, Mackrell PJ, Mestre JR, Stapleton PP, Daly JM (2010) Malnutrition-induced macrophage apoptosis. Surgery 129(5):617–625
Grivicich I, Regner A, Rocha AB (2007) Apoptosis: programmed cell death. R Bras Cancer 53(3):335–343
Ribeiro R, Sousa DWN, Oliveira TS, Fernandes KPS, Junior JAS (2012) Intense physical activity: role of nitric oxide in apoptosis. Ter Man 10(48):1–5
Schroder K, Tschopp J (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140(19):821–832
Carvalho RLB, Berezin EM, Mimica ML (2012) Detection of lukS-PV and lukF-PV in Staphylococcus aureus pediatric isolates. Arq Med Hosp Fac Cienc Med Santa Casa São Paulo 57(2):59–62
Kobayashi SD, DeLeo FR (2009) Role of neutrophils in innate immunity: a systems biology-level approach. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 1:309–333
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank CAPES, the National Council for Science and Technology (CNPq), Brazil, for their financial support, and Laboratory Aggeu Magalhães Research Center, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation - CPqAM/FIOCRUZ.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article from the thesis MORAIS, N.G., entitled “Effect of neonatal malnutrition on intracellular signaling and viability of alveolar macrophages infected in vitro with methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus”—Federal University of Pernambuco; 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Morais, N.G., da Costa, T.B., Pedrosa, A.L.F. et al. Effect of neonatal malnutrition on expression of nitric oxide synthase enzyme, production of free radicals and in vitro viability of alveolar macrophages infected with methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Eur J Nutr 55, 403–411 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0861-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0861-x