Abstract
Purpose
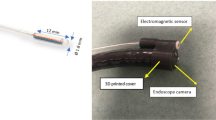
Accurate measurement of polyp size during colonoscopy is important because the size is a surrogate marker of cancer, but a standardized measurement technique to measure polyp size has yet to be determined. We have developed a new device “a novel calibrated hood.” We assessed polyp size by visual estimation and measurement using the calibrated hood.
Methods
Patients who underwent polypectomy from November 2012 to September 2013 and who had received screening colonoscopy within 6 months prior to the polypectomy were included in this study. Polypectomy was performed attaching the calibrated hood. The endoscopist measured the polyp size using the calibrated hood. Polyp size was compared between visual estimation and measurement using the calibrated hood.
Results
Seventy-five patients with 157 polyps were included. Seventy-seven polyps fulfilled the selection criteria. Mean polyp size by visual estimation was 6.57 ± 2.15, and by using calibrated hood was 5.94 ± 1.73 (p = 0.005). There was a significant difference between measurements using the calibrated hood vs. visual estimation by inexperienced trainees; however, there was no difference in case of well-experienced endoscopists. By visual estimation, 11 of 19 polyps were decided for ≥5 mm despite being less than 5 mm, and 5 of 58 polyps were decided for <5 mm despite being 5 mm or larger in diameter.
Conclusion
Visual estimation of polyp size is not accurate. It is important to measure the size by an objective way, and the calibrated hood is useful in measuring polyp size, from the standpoint of accurately determining indication for polypectomy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panish JF (1979) Management of patients with polypoid lesions of the colon—current concepts and controversies. Am J Gastroenterol 71:315–324
Tsai FC, Strum WB (2011) Prevalence of advanced adenomas in small and diminutive colon polyps using direct measurement of size. Dig Dis Sci 56:2384–2388
Atkin WS, Morson BC, Cuzick J (1992) Long-term risk of colorectal cancer after excision of rectosigmoid adenomas. N Engl J Med 326:658–662
Kashida H, Kudo SE (2006) Early colorectal cancer: concept, diagnosis, and management. Int J Clin Oncol 11:1–8
Hyun YS, Han DS, Bae JH et al (2011) Graduated injection needles and snares for polypectomy are useful for measuring colorectal polyp size. Dig Liver Dis 43:391–394
Moug SJ, Vernall N, Saldanha J et al (2010) Endoscopists’ estimation of size should not determine surveillance of colonic polyps. Color Dis 12:646–650
Gopalswamy N, Shenoy VN, Choudhry U et al (1997) Is in vivo measurement of size of polyps during colonoscopy accurate? Gastrointest Endosc 46:497–502
Kume K, Watanabe T, Yoshikawa I et al (2014) Endoscopic measurement of polyp size using a novel calibrated hood. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014:714294
Schoen RE, Gerber LD, Margulies C (1997) The pathologic measurement of polyp size is preferable to the endoscopic estimate. Gastrointest Endosc 46:492–496
Morales TG, Sampliner RE, Garewal HS et al (1996) The difference in colon polyp size before and after removal. Gastrointest Endosc 43:25–28
Margulies C, Krevsky B, Catalano MF (1994) How accurate are endoscopic estimates of size? Gastrointest Endosc 40:174–177
de Vries AH, Bipat S, Dekker E et al (2010) Polyp measurement based on CT colonography and colonoscopy: variability and systematic differences. Eur Radiol 20:1404–1413
Kim HH, Park SJ, Park MI et al (2012) Transparent-cap-fitted colonoscopy shows higher performance with cecal intubation time in difficult cases. World J Gastroenterol 18:1953–1958
Westwood DA, Alexakis N, Connor SJ (2012) Transparent cap-assisted colonoscopy versus standard adult colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 55:218–225
de Wijkerslooth TR, Stoop EM, Bossuyt PM et al (2012) Adenoma detection with cap-assisted colonoscopy versus regular colonoscopy: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 61:1426–1434
Rastogi A, Bansal A, Rao DS et al (2012) Higher adenoma detection rates with cap-assisted colonoscopy: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 61:402–408
Chang CY, Chiu HM, Wang HP et al (2010) An endoscopic training model to improve accuracy of colonic polyp size measurement. Int J Color Dis 25:655–660
Acknowledgments
The authors received no funding for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, T., Kume, K., Yoshikawa, I. et al. Usefulness of a novel calibrated hood to determine indications for colon polypectomy: visual estimation of polyp size is not accurate. Int J Colorectal Dis 30, 933–938 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-015-2203-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-015-2203-0