Abstract
Introduction
Hepatic resection is the only curative treatment option for primary or metastatic malignancies of the liver. Although R1 resections can also lead to prolonged survival, the main surgical goal is complete tumor resection (R0). To achieve this, additional treatment of the resection margin with ablation devices is discussed. Using a porcine in vivo model, we therefore analyzed the effect of different ablation devices on depth and completeness of hepatic parenchymal cell destruction.
Methods
Swabian–Hall strain pigs underwent ablation on the surface of the right, middle, or left liver lobe using seven different types of high-frequency (HF)-, cryotherapy (Cryo)-, or argon plasma coagulation (APC) devices. Penetration depth and volume were analyzed from histological sections. Severity of parenchymal cell destruction was assessed by a histomorphological score.
Results
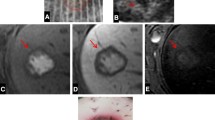
The greatest penetration depth was achieved with Cryo (10.4 ± 1.7 mm), whereas HF and APC exhibited a smaller penetration depth. However, HF and APC compared to Cryo achieved complete destruction of the intralobular architecture and hepatocellular morphology depending on the application time and the adjusted power.
Conclusion
HF, APC, and Cryo applied to the liver surface induce different parenchymal penetration depth and cell destruction. HF and APC are considered to be standard surgical instruments and therefore recommended as standard treatment, whereas Cryo may be used only if particularly deep penetration is required.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M, Cléries R (2004) Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterol 127(5 Suppl 1):5–16
John AR, Khan S, Mirza DF, Mayer AD, Buckels JA, Bramhall SR (2006) Multivariate and univariate analysis of prognostic factors following resection in HCC: the Birmingham experience. Dig Surg 23:103–109
Patel T (2001) Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatol 33:1353–1357
Power DG, Kemeny NE (2010) Role of adjuvant therapy after resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Clin Oncol 28(13):2300–2309
Richter S, Kollmar O, Schuld J, Moussavian MR, Igna D, Schilling MK (2009) Randomized clinical trial of efficacy and costs of three dissection devices in liver resection. Br J Surg 96:593–601
Belghiti J, Hiramatsu K, Benoist S, Massault P, Sauvanet A, Farges O (2000) Seven hundred forty-seven hepatectomies in the 1990s: an update to evaluate the actual risk of liver resection. J Am Coll Surg 191:38–46
Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, DeMatteo RP, Gonen M, Burke EC, Bodniewicz BJ, Youssef BM, Klimstra D, Blumgart LH (2001) Staging, resectability, and outcome in 225 patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 234(4):507–517, discussion 517-519
Nakayama H, Masuda H, Shibata M, Amano S, Fukuzawa M (2003) Incidence of bile leakage after three types of hepatic parenchymal transection. Hepatogastroenterology 50:1517–1520
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Lam CM, Yuen WK, Yeung C, Wong J (2004) Improving perioperative outcome expands the role of hepatectomy in management of benign and malignant hepatobiliary diseases: analysis of 1222 consecutive patients from a prospective database. Ann Surg 240:698–708, discussion 708-710
Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Fruhauf NR, Domland M, Paul A, Kind EM, Malago M, Broelsch CE (2005) Extended hepatectomy for intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma (ICC): when is it worthwhile? Single center experience with 27 resections in 50 patients over a 5-year period. Ann Surg 241:134–143
Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Dunn JA, Almond J, Beger HG, Pederzoli P, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fernandez-Cruz L, Lacaine F, Buckels J, Deakin M, Adab FA, Sutton R, Imrie C, Ihse I, Tihanyi T, Olah A, Pedrazzoli S, Spooner D, Kerr DJ, Friess H, Buchler MW (2001) Influence of resection margins on survival for patients with pancreatic cancer treated by adjuvant chemoradiation and/or chemotherapy in the ESPAC-1 randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 234:758–768
Neuhaus P, Jonas S, Bechstein WO, Lohmann R, Radke C, Kling N, Wex C, Lobeck H, Hintze R (1999) Extended resections for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg 230:808–818, discussion 819
Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Wong J (2000) Significance of resection margin in hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical reappraisal. Ann Surg 231:544–551
Todoroki T, Kawamoto T, Koike N, Fukao K, Shoda J, Takahashi H (2001) Treatment strategy for patients with middle and lower third bile duct cancer. Br J Surg 88:364–370
Bhardwaj N, Strickland AD, Ahmad F, Atanesyan L, West K, Lloyd DM (2009) A comparative histological evaluation of the ablations produced by microwave, cryotherapy and radiofrequency in the liver. Pathol 41:168–172
Brace CL, Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Frey TM, Mukherjee R, Lee FT Jr (2007) Radiofrequency ablation with a high-power generator: device efficacy in an in vivo porcine liver model. Int J Hyperthermia 23:387–394
Kianmanesh R, Ogata S, Paradis V, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J (2008) Heat-zone effect after surface application of dissecting sealer on the "in situ margin" after tumorectomy for liver tumors. J Am Coll Surg 206:1122–1128
Gruenberger T, Jourdan JL, Zhao J, King J, Morris DL (2001) Reduction in recurrence risk for involved or inadequate margins with edge cryotherapy after liver resection for colorectal metastases. Arch Surg 136:1154–1157
Hou RM, Chu F, Zhao J, Morris DL (2007) The effects of surgical margin and edge cryotherapy after liver resection for colorectal cancer metastases. HPB (Oxford) 9:201–207
Gananadha S, Daniel S, Zhao J, Morris DL (2005) An experimental evaluation of ablation devices for the local treatment of the liver resection edge. Eur J Surg Oncol 31:528–532
Yamagata M, Matsumata T, Ikeda Y, Hayashi H, Sugimachi K (1995) Recurrence near the resection line of hepatocellular carcinoma in the anterosuperior subsegment of the liver—the effect of the argon beam coagulator. Hepatogastroenterology 42:9–12
Kollmar O, Richter S, Schilling MK, Menger MD, Pistorius GA (2004) Advanced hepatic tissue destruction in ablative cryosurgery: potentials of intermittent freezing and selective vascular inflow occlusion. Cryobiology 48:263–72
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the excellent technical assistance of Janine Becker.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sperling, J., Ziemann, C., Schuld, J. et al. A comparative evaluation of ablations produced by high-frequency coagulation-, argon plasma coagulation-, and cryotherapy devices in porcine liver. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 1229–1235 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1504-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1504-9