Abstract
Purpose
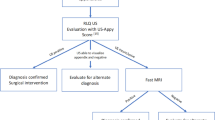
Despite significant radiation exposure involved with computed tomography (CT) in evaluation of pediatric appendicitis, its use is still widespread. The goal of this study was to assess the effect of a staged imaging pathway for appendicitis to significantly decrease CT use while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
Methods
Chart review was performed for patients evaluated for appendicitis over a 12-month period prior to and after pathway implementation.
Results
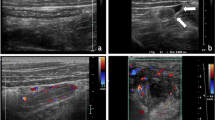
There was a significant decrease in CT use as initial imaging after implementation of the pathway; 87.1–13.4 % for evaluations positive for appendicitis (decrease 84.6 %, p < 0.0001) and 82.6–9.2 % for evaluations negative for appendicitis (decrease 88.9 %, p < 0.0001). Use of CT during any point in the evaluation decreased from 91.7 to 25.1 % (decrease 72.6 %, p < 0.0001). The negative appendectomy rate was similar; 5.4 % prior, 4.9 % post (p = 0.955). The missed appendicitis rate did not statistically change; 1.1 % prior, 3.7 % post (p = 0.523). The perforation rate was not statistically altered; 6.5 % prior; 9.8 % post (p = 0.421). 350 less patients underwent CT during the year following the pathway.
Conclusions
The staged imaging pathway resulted in a marked decrease in children exposed to CT without compromising diagnostic accuracy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hung MH, Lin LH, Chen DF (2012) Clinical manifestations in children with ruptured appendicitis. Pediatr Emerg Care 28(5):433–435
Becker T, Kharbanda A, Bachur R (2007) Atypical clinical features of pediatric appendicitis. Acad Emerg Med 14(2):124–129 Epub 2006 Dec 27
Sung T, Callahan MJ, Taylor GA (2006) Clinical and imaging mimickers of acute appendicitis in the pediatric population. Am J Roentgenol 186(1):67–74
Nance ML, Adamson WT, Hedrick HL (2000) Appendicitis in the young child: a continuing diagnostic challenge. Pediatr Emerg Care 16(3):160–162
Sakellaris G, Tilemis S, Charissis G (2005) Acute appendicitis in preschool-age children. Eur J Pediatr 164(2):80–83
Preston DL, Cullings H, Suyama A et al (2008) Solid cancer incidence in atomic bomb survivors exposed in utero or as young children. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(6):428–436
de González Berrington (2004) A, Darby S. Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries. Lancet 363:345–351
Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP et al (2012) Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 380(9840):499–505
Frush D (2007) Image Gently: The Alliance for Radiation Safety in Pediatric Imaging. Available at: http://www.imagegently.org/. Accessed 14 Jan 2016
Coran AG (2012) Pediatric Surgery, 7th edn. Elsevier Inc, Philadelphia, pp 1255–1263
Fahimi J, Herring A, Harries A et al. (2012) Computed tomography use among children presenting to emergency departments with abdominal pain. Pediatrics 130(5):1069–1075
Doria AS, Moineddin R, Kellenberger CJ et al (2006) US or CT for diagnosis of appendicitis in children and adults? A meta-analysis. Radiology 241:83–94
Garcia Peña BM, Mandl KD, Kraus SJ et al (1999) Ultrasonography and limited computed tomography in the diagnosis and management of appendicitis in children. JAMA 282(11):1041–1046
Garcia Peña BM, Cook EF, Mandl KD (2004) Selective imaging strategies for the diagnosis of appendicitis in children. Pediatrics 113(1 Pt 1):24–28
Kosloske AM, Love CL, Rohrer JE et al (2004) The diagnosis of appendicitis in children: outcomes of a strategy based on pediatric surgical evaluation. Pediatrics 113(1 Pt 1):29–34
Krishnamoorthi R, Ramarajan N, Wang NE et al (2011) Effectiveness of a staged US and CT protocol for the diagnosis of pediatric appendicitis: reducing radiation exposure in the age of ALARA. Radiology 259(1):231–239
Ramarajan N, Krishnamoorthi R, Barth R et al (2009) An interdisciplinary initiative to reduce radiation exposure: evaluation of appendicitis in a pediatric emergency department with clinical assessment supported by a staged ultrasound and computed tomography pathway. Acad Emerg Med 16(11):1258–1265
Santillanes G, Simms S, Gausche-Hill M, Diament M et al (2012) Prospective evaluation of a clinical practice guideline for diagnosis of appendicitis in children. Acad Emerg Med 19(8):886–893
Russell WS, Schuh AM, Hill JG et al (2013) Clinical practice guidelines for pediatric appendicitis evaluation can decrease computed tomography utilization while maintaining diagnostic accuracy. Pediatr Emerg Care 29(5):568–573
Saito JM, Yan Y, Evashwick TW et al (2013) Use and accuracy of diagnostic imaging by hospital type in pediatric appendicitis. Pediatrics 131(1):e37–e44. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-1665
Paterson A, Frush DP, Donnelly LF (2001) Helical CT of the body: are settings adjusted for pediatric patients? Am J Roentgenol 176(2):297–301
Jacobs JE, Birnbaum BA, Macari M et al (2001) Acute appendicitis: comparison of helical CT diagnosis focused technique with oral contrast material versus nonfocused technique with oral and intravenous contrast material. Radiology 220:683–690
Siegel MJ (2011) Pediatric Radiology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 366–370
Siegel MJ (1999) Pediatric Body CT. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 216–219
Arch ME, Frush DP (2008) Pediatric body MDCT: a 5-year follow-up survey of scanning parameters used by pediatric radiologists. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191(2):611–617
Brenner DJ, Hall EJ (2007) Computed tomography—an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 357(22):2277–2284 Review
Kids’ Inpatient Database (KID) (2012) Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Available at http://hcupnet.ahrq.gov/
Dolgin SE, Beck AR, Tartter PI (1992) The risk of perforation when children with possible appendicitis are observed in the hospital. Surg Gynecol Obset 175:320–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, M., Habis, A., Glynn, L. et al. Staged imaging pathway for the evaluation of pediatric appendicitis. Pediatr Surg Int 32, 671–678 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3896-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-3896-z