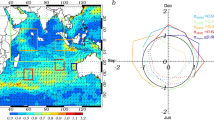
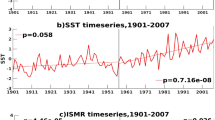
Abstract
Eastern equatorial Indian ocean (EEIO) is one of the most climatically sensitive regions in the global ocean, which plays a vital role in modulating Indian ocean dipole (IOD) and El Niño southern oscillation (ENSO). Here we present evidences for a paradoxical and perpetual lower co-variability between sea-surface temperature (SST) and air-temperature (Tair) indicating instantaneous thermal decoupling in the same region, where signals of the strongly coupled variability of SST anomalies and zonal winds associated with IOD originate at inter-annual time scale. The correlation minimum between anomalies of Tair and SST occurs in the eastern equatorial Indian ocean warm pool region (≈70°E–100°E, 5°S–5°N), associated with lower wind speeds and lower sensible heat fluxes. At sub-monthly and Madden–Julian oscillation time scales, correlation of both variables becomes very low. In above frequencies, precipitation positively contributes to the low correlation by dropping Tair considerably while leaving SST without any substantial instant impact. Precipitation is led by positive build up of SST and post-facto drop in it. The strong semi-annual response of SST to mixed layer variability and equatorial waves, with the absence of the same in the Tair, contributes further to the weak correlation at the sub-annual scale. The limited correlation found in the EEIO is mainly related to the annual warming of the region and ENSO which is hard to segregate from the impacts of IOD.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basher RE, Thompson CS (1996) Relationship of air temperatures in New Zealand to regional anomalies in sea-surface temperature and atmospheric circulation. Int J Climatol 16(4):405–425. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199604)16:4<405::AID-JOC14>3.0.CO;2-T
Bhat GS (2002) Near-surface variations and surface fluxes over the northern bay of bengal during the 1999 Indian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res: Atmos 107(D17):ACL 6-€œ1–ACL 6-€œ19. doi:10.1029/2001JD000382
Bretherton CS, Widmann M, Dymnikov VP, Wallace JM, Bladé I (1999) The effective number of spatial degrees of freedom of a time-varying field. J Clim 12(7):1990–2009. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<1990:TENOSD>2.0.CO;2
Cane MA, Sarachik E (1981) Response of a linear baroclinic equatorial ocean to periodic forcing. J Mar Res 39(4):651–693
Cayan DR (1980) Large-scale relationships between sea surface temperature and surface air temperature. Mon Weather Rev 108(1293–1301):1081. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)293:LSRBSS2.0.CO;2
Chatterjee P, Goswami B (2004) Structure, genesis and scale selection of the tropical quasi-biweekly mode. Q J R Meteorol Soc 130(599):1171–1194. doi:10.1256/qj.03.133
Cutler A, Swallow J (1984) Surface currents of the Indian ocean (to 25°S, 100°E): compiled from historical data archived by the Meteorological Office Bracknell, UK. Technical Report 187, Institude of Ocean Sciences, Institute of Oceanographic Sciences, Wormley, UK
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Andrae U, Balmaseda MA, Balsamo G, Bauer P, Bechtold P, Beljaars ACM, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Delsol C, Dragani R, Fuentes M, Geer AJ, Haimberger L, Healy SB, Hersbach H, Holm EV, Isaksen L, Kallberg P, Kohler M, Matricardi M, McNally AP, Monge-Sanz BM, Morcrette JJ, Park BK, Peubey C, de Rosnay P, Tavolato C, Thepaut JN, Vitart F (2011) The era-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137(656):553–597. doi:10.1002/qj.828
Drushka K, Sprintall J, Gille ST, Wijffels S (2012) In situ observations of Madden–Julian oscillation mixed layer dynamics in the Indian and Western Pacific Oceans. J Clim 25(7):2306–2328. doi:10.1175/jcli-d-11-00203.1
Drushka K, Sprintall J, Gille ST (2014) Subseasonal variations in salinity and barrier-layer thickness in the eastern equatorial Indian ocean. J Geophys Res Oceans 119(2):805–823. doi:10.1002/2013jc009422
Duncan B, Han W (2009) Indian ocean intraseasonal sea surface temperature variability during boreal summer: Madden–Julian oscillation versus submonthly forcing and processes. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2008jc004958
Duvel JP, Vialard J (2007) Indo-pacific sea surface temperature perturbations associated with intraseasonal oscillations of tropical convection. J Clim 20(13):3056–3082. doi:10.1175/jcli4144.1
Duvel JP, Roca R, Vialard J (2004) Ocean mixed layer temperature variations induced by intraseasonal convective perturbations over the Indian ocean. J Atmos Sci 61(9):1004–1023. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2004)0611004:omltvi2.0.co;2
Fairall C, Bradley E, Rogers D, Edson J, Youngs G (1996) Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for tropical ocean-global atmosphere coupled-ocean atmosphere response. Geophys Res 101:3747–3764. doi:10.1029/95JC03205
Fairall C, Bradley EF, Hare J, Grachev A, Edson J (2003) Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes: updates and verification for the coare algorithm. J Clim 16(4):571–591. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<0571:BPOASF>2.0.CO;2
Fu LL (2007) Intraseasonal variability of the equatorial Indian ocean observed from sea surface height, wind, and temperature data. J Phys oceanogr 37(2):188–202. doi:10.1175/JPO3006.1
Fujita M, Takahashi HG, Hara M (2013) Diurnal cycle of precipitation over the eastern Indian ocean off Sumatra Island during different phases of Indian ocean dipole. Atmos Sci Lett 14(3):153–159. doi:10.1002/asl2.432
Gayen AK (1951) The frequency distribution of the product moment correlation coefficient in random samples of any size draw from non-normal universes. Biometrika 38(1–2):219–247. doi:10.1093/biomet/38.1-2.219
Girishkumar MS, Ravichandran M, Han W (2013) Observed intraseasonal thermocline variability in the Bay of Bengal. J Geophys Res Oceans 118(7):3336–3349. doi:10.1002/jgrc.20245
Gnanaseelan C, Deshpande A, McPhaden MJ (2012) Impact of Indian ocean dipole and el niño/southern oscillation wind-forcing on the wyrtki jets. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2012jc007918
Godfrey JS, Panel OOSD (1994) The role of the Indian ocean in the global climate system : recommendations regarding the Global Ocean Observing System. Ocean Observing System Development Panel, College Station
Grinsted A, Moore JC, Jevrejeva S (2004) Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlin Process Geophys 11(5/6):561–566. doi:10.5194/npg-11-561-2004
Han W, McCreary JP, Anderson DLT, Mariano AJ (1999) Dynamics of the eastern surface jets in the equatorial Indian ocean. J Phys Oceanogr 29(9):2191–2209. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<2191:DOTESJ>2.0.CO;2
Han W, Liu WT, Lin J (2006) Impact of atmospheric submonthly oscillations on sea surface temperature of the tropical Indian ocean. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2005gl025082
Han W, Yuan D, Liu WT, Halkides DJ (2007) Intraseasonal variability of Indian ocean sea surface temperature during boreal winter: Madden–Julian oscillation versus submonthly forcing and processes. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2006jc003791
Hastenrath S, Greischar L (1991) The monsoonal current regimes of the tropical Indian ocean: observed surface flow fields and their geostrophic and wind-driven components. J Geophys Res: Oceans (1978–2012) 96(C7):12,619–12,633. doi:10.1029/91JC00997
Hendon HH, Salby ML (1994) The life cycle of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J Atmos Sci 51(15):2225–2237. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1994)051<2225:TLCOTM>2.0.CO;2
Iskandar I, Masumoto Y, Mizuno K (2009) Subsurface equatorial zonal current in the eastern Indian ocean. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2008jc005188
Jayakumar A, Vialard J, Lengaigne M, Gnanaseelan C, McCreary JP, Kumar BP (2011) Processes controlling the surface temperature signature of the Madden–Julian oscillation in the thermocline ridge of the Indian ocean. Clim Dyn 37(11–12):2217–2234. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0953-5
Joseph S, Wallcraft AJ, Jensen TG, Ravichandran M, Shenoi SSC, Nayak S (2012) Weakening of spring wyrtki jets in the Indian ocean during 2006–2011. J Geophys Res: Oceans. doi:10.1029/2011JC007581
Kara AB, Hurlburt HE, Loh WY (2007) Which near-surface atmospheric variable drives air-sea temperature differences over the global ocean? J Geophys Res: Oceans. doi:10.1029/2006JC003833
Kessler WS (2005) The oceans. In: Intraseasonal variability in the atmosphere–ocean climate system. Springer, pp 175–222
Krishnamurti TN, Oosterhof D, Mehta A (1988) Air–sea interaction on the time scale of 30 to 50 days. J Atmos Sci 45(8):1304–1322
Kumar BP, Vialard J, Lengaigne M, Murty V, McPhaden M (2012) Tropflux: air–sea fluxes for the global tropical oceans description and evaluation. Clim Dyn 38(7–8):1521–1543
Kumar BP, Vialard J, Lengaigne M, Murty V, McPhaden M, Cronin M, Pinsard F, Reddy KG (2013) Tropflux wind stresses over the tropical oceans: evaluation and comparison with other products. Clim Dyn 40(7–8):2049–2071
Lau WKM, Waliser DE (2012) Intraseasonal variability in the atmosphere–ocean climate system. Springer Science & Business Media. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13914-7
Lin JL, Kiladis GN, Mapes BE, Weickmann KM, Sperber KR, Lin W, Wheeler MC, Schubert SD, Del Genio A, Donner LJ et al (2006) Tropical intraseasonal variability in 14 ipcc ar4 climate models. Part I: convective signals. J Clim 19(12):2665–2690
Madden RA, Julian PR (1972) Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40–50 day period. J Atmos Sci 29(6):1109–1123
Madden RA, Julian PR (1994) Observations of the 40–50-day tropical oscillation-a review. Mon Weather Rev 122(5):814–837
Masson S, Delecluse P, Boulanger JP, Menkes C (2002) A model study of the seasonal variability and formation mechanisms of the barrier layer in the eastern equatorial Indian ocean. J Geophys Res 107(C12):SRF 18–1–SRF 18–20. doi:10.1029/2001jc000832
Masumoto Y (2005) Intraseasonal variability in the upper layer currents observed in the eastern equatorial Indian ocean. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2004gl021896
McPhaden M (1982) Variability in the central Indian ocean. Part I: ocean dynamics. J Mar Res 40:157–176
McPhaden MJ, Meyers G, Ando K, Masumoto Y, Murty VSN, Ravichandran M, Syamsudin F, Vialard J, Yu L, Yu W (2009) Rama: The research moored array for African–Asian–Australian monsoon analysis and prediction*. Bull Am Meteor Soc 90(4):459–480. doi:10.1175/2008BAMS2608.1
Meehl GA (1997) The South Asian monsoon and the tropospheric biennial oscillation. J Clim 10(8):1921–1943. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<1921:TSAMAT>2.0.CO;2
Miyama T, McCreary JP Jr, Sengupta D, Senan R (2006) Dynamics of biweekly oscillations in the equatorial Indian ocean*. J Phys Oceanogr 36(5):827–846. doi:10.1175/JPO2897.1
Nagura M, McPhaden MJ (2008) The dynamics of zonal current variations in the central equatorial Indian ocean. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2008gl035961
Rahaman H, Ravichandran M (2013) Evaluation of near-surface air temperature and specific humidity from hybrid global products and their impact on latent heat flux in the north Indian ocean. J Geophys Res: Oceans 118(2):1034–1047. doi:10.1002/jgrc.20085
Rao R, Kumar MG, Ravichandran M, Rao A, Gopalakrishna V, Thadathil P (2010) Interannual variability of kelvin wave propagation in the wave guides of the equatorial Indian ocean, the coastal Bay of Bengal and the southeastern Arabian sea during 1993–2006. Deep Sea Res Part I 57(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2009.10.008
Rao SA (2004) Abrupt termination of Indian ocean dipole events in response to intraseasonal disturbances. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2004gl020842
Reppin J, Schott FA, Fischer J, Quadfasel D (1999) Equatorial currents and transports in the upper central Indian ocean: annual cycle and interannual variability. J Geophys Res 104(C7):15,495–15,514. doi:10.1029/1999jc900093
Roll HU (1965) Physics of the marine atmosphere, vol 7. Academic Press, Cambridge
Roxy M, Tanimoto Y (2012) Influence of sea surface temperature on the intraseasonal variability of the south China sea summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 39(5):1209–1218. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1118-x
Roxy M, Tanimoto Y, Preethi B, Terray P, Krishnan R (2013) Intraseasonal sst-precipitation relationship and its spatial variability over the tropical summer monsoon region. Clim Dyn 41(1):45–61. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1547-1
Saji N, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran P, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian ocean. Nature 401(6751):360–363
Schiller A, Godfrey J (2003) Indian ocean intraseasonal variability in an ocean general circulation model. J Clim 16(1):21–39. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<0021:IOIVIA>2.0.CO;2
Schott FA, McCreary JP (2001) The monsoon circulation of the Indian ocean. Prog Oceanogr 51(1):1–123. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(01)00083-0
Sengupta D, Ravichandran M (2001) Oscillations of Bay of Bengal sea surface temperature during the 1998 summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 28(10):2033–2036. doi:10.1029/2000GL012548
Shankar D, Vinayachandran P, Unnikrishnan A (2002) The monsoon currents in the north Indian ocean. Prog Oceanogr 52(1):63–120. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(02)00024-1
Shenoi S, Saji P, Almeida A (1999) Near-surface circulation and kinetic energy in the tropical Indian ocean derived from lagrangian drifters. J Mar Res 57(6):885–907. doi:10.1357/002224099321514088
Shetye SR, Gouveia AD (1998) Coastal circulation in the north Indian ocean. Coastal segment (14,S-W) The Sea Chapter 18, vol 11. Wiley, pp 523–556
Shinoda T, Hendon HH (1998) Mixed layer modeling of intraseasonal variability in the tropical western Pacific and Indian oceans. J Clim 11(10):2668–2685. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011<2668:MLMOIV>2.0.CO;2
Slingo J, Sperber K, Boyle J, Ceron JP, Dix M, Dugas B, Ebisuzaki W, Fyfe J, Gregory D, Gueremy JF et al (1996) Intraseasonal oscillations in 15 atmospheric general circulation models: results from an amip diagnostic subproject. Clim Dyn 12(5):325–357. doi:10.1007/BF00231106
Sprintall J, Tomczak M (1992) Evidence of the barrier layer in the surface layer of the tropics. J Geophys Res 97:7305–7316. doi:10.1029/92JC00407
Sura P, Newman M (2008) The impact of rapid wind variability upon air–sea thermal coupling. J Clim 21(4):621–637. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1708.1
Trenberth KE, Shea DJ (2005) Relationships between precipitation and surface temperature. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2005GL022760.l14703
Vialard J, Jayakumar A, Gnanaseelan C, Lengaigne M, Sengupta D, Goswami B (2012) Processes of 30–90 days sea surface temperature variability in the northern Indian ocean during boreal summer. Clim Dyn 38(9–10):1901–1916. doi:10.1007/s00382-011-1015-3
Waliser DE, Lau K, Kim JH (1999) The influence of coupled sea surface temperatures on the Madden–Julian oscillation: a model perturbation experiment. J Atmos Sci 56(3):333–358. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1999)056<0333:TIOCSS>2.0.CO;2
Waliser DE, Murtugudde R, Lucas LE (2003) Indo-pacific ocean response to atmospheric intraseasonal variability: 1. Austral summer and the Madden–Julian oscillation. J Geophy Res: Oceans (1978–2012). doi:10.1029/2002JC001620
Waliser DE, Murtugudde R, Lucas LE (2004) Indo-pacific ocean response to atmospheric intraseasonal variability: 2. Boreal summer and the intraseasonal oscillation. J Geophys Res: Oceans (1978–2012). doi:10.1029/2003JC002002
Webster PJ, Moore AM, Loschnigg JP, Leben RR (1999) Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian ocean during 1997–1998. Nature 401(6751):356–360
Wheeler M, Kiladis GN (1999) Convectively coupled equatorial waves: analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber-frequency domain. J Atmos Sci 56(3):374–399. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1999)056<0374:CCEWAO>2.0.CO;2
Wheeler MC, Hendon HH (2004) An all-season real-time multivariate mjo index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon Weather Rev 132(8):1917–1932. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<1917:AARMMI>2.0.CO;2
Wu R, Kirtman BP (2005) Roles of Indian and pacific ocean air–sea coupling in tropical atmospheric variability. Clim Dyn 25(2–3):155–170. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0003-x
Wu R, Kirtman BP (2007) Regimes of seasonal air–sea interaction and implications for performance of forced simulations. Clim Dyn 29(4):393–410. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0246-9
Wu R, Kirtman BP, Pegion K (2006) Local air–sea relationship in observations and model simulations. J Clim 19(19):4914–4932. doi:10.1175/JCLI3904.1.
Wyrtki K (1973) An equatorial jet in Indain ocean. Science 181:262–264. doi:10.1126/science.181.4096.262
Zhang GJ, Ramanathan V, McPhaden MJ (1995) Convection-evaporation feedback in the equatorial pacific. J Clim 8(12):3040–3051. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1995)008<3040:CEFITE>2.0.CO;2
Zhang Y, Rossow WB, Stackhouse PW (2006) Comparison of different global information sources used in surface radiative flux calculation: Radiative properties of the near-surface atmosphere. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2005jd006873
Zhang Y, Rossow WB, Stackhouse PW (2007) Comparison of different global information sources used in surface radiative flux calculation: Radiative properties of the surface. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2005jd007008
Acknowledgments
Ministry of Earth Sciences and Director INCOIS are acknowledged for the infrastructural support. Authors wish to acknowledge use of the Ferret program for data analysis and graphics in this paper. Ferret is a product of NOAA’s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory. (Information is available at http://ferret.pmel.noaa.gov/Ferret/). We thank editor Dr. Jean-Claude Duplessy and three anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments which improved the quality of this work. Colleagues from MOG group at INCOIS are acknowledged for their support. This is INCOIS Publication NO: 266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In the original publication of this article the Fig. 9 was published incorrectly; this error has now been corrected.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3379-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, S., Ravichandran, M., Kumar, B.P. et al. Ocean atmosphere thermal decoupling in the eastern equatorial Indian ocean. Clim Dyn 49, 575–594 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3359-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3359-1