Abstract
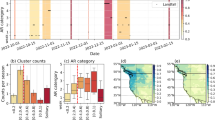
The global monsoon domain has been recently determined utilizing two criteria: difference of local maximum and minimum pentad-mean precipitation rates exceeding 4 mm day−1, and wind reversal of low-level cross-equatorial flow. In this paper, 22 major dry–wet alteration regions under six categories were first derived through the k-means clustering method from the climatological evolution of global precipitation. Considering the seasonal influences of the low-level cross-equatorial flow in these major dry–wet alternation regions, the global monsoon was objectively divided into 16 major regions under five climatological precipitation categories. Nine monsoon regions are distributed between Asia and Australia while four regions are from Africa to the Southwest Indian Ocean and three regions in Americas. Precipitation trends during rainy seasons of 1981–2010 were examined in the 16 monsoon regions. Four regions with decreasing trends of precipitation are located in Africa and the Southwest Indian Ocean while three regions with increasing trends are situated in Americas. Six regions of increasing precipitation trends are concentrated in Asia and the biggest increasing trend is found in south China.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams DK, Comrie AC (1997) The North American monsoon. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(10):2197–2213
An Z, Wu G, Li J, Sun Y, Liu Y, Zhou W, Cai Y, Duan A, Li L, Mao J (2015) Global monsoon dynamics and climate change. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 43:29–77. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054623
Balasubramaniyan R, Hüllermeier E, Weskamp N, Kmper J (2005) Clustering of gene expression data using a local shape-based similarity measure. Bioinform/Comput Appl Biosci 21:1069–1077. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti095
Barrett BS, Longoria MIE (2013) Variability of precipitation and temperature in Guanajuato, Mexico. Atmsfera 26(4):521–536
Benjamin S, Serge J (2003) The west African monsoon dynamics. Part II: the ‘preonset’ and ‘onset’ of the summer monsoon. J Clim 16:3407–3427
Chang CP, Wang Z, McBride J, Liu CH (2005) Annual cycle of Southeast Asia-Maritime continent rainfall and the asymmetric monsoon transition. J Clim 18(2):287–301. doi:10.1175/JCLI-3257.1
Chen L, Zhu Q, Luo H, He J, Dong M, Feng Z (1991) The East Asian monsoon. Beijing Meteorological Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Christiansen B (2007) Atmospheric circulation regimes: can cluster analysis provide the number? J Clim 20:2229–2250. doi:10.1175/JCLI4107.1
Draxler RR, Stunder B, Rolph G, Taylor A (1999) HYSPLIT4 users guide. NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL ARL 230:35
Gao H, Xue F (2006) Seasonal variation of the cross-equatorial flows and their influences on the onset of South China Sea summer monsoon. Clim Environ Res 11(1):57–68
Gasse F, Van Campo E (1994) Abrupt post-glacial climate events in West Asia and North Africa monsoon domains. Earth Planet Sci Lett 126(4):435–456
Godfred-Spenning CR, Reason CJC (2002) Interannual variability of lower-tropospheric moisture transport during the Australian monsoon. Int J Climatol 22(5):509–532
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) Algorithm AS 136: a \(k\)-means clustering algorithm. Appl Stat 28(1):100–108. doi:10.2307/2346830
Hu H, Qian W (2007) Identifying the northernmost summer monsoon location in East Asia. Prog Nat Sci 17(7):812–820
Johnson NC (2013) How many ENSO flavors can we distinguish? J Clim 26(13):4816–4827
Johnson NC, Feldstein SB (2010) The continuum of North Pacific sea level pressure patterns: intraseasonal, interannual, and interdecadal variability. J Clim 23:851–867. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI3099.1
Kajikawa Y, Wang B, Yang J (2010) A multi-time scale Australian monsoon index. Int J Climatol 30(8):1114–1120
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang SK, Hnilo J, Fiorino M, Potter G (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(11):1631–1643
Khromov SP (1957) Die geographische verbreitung der monsune. Petermanns Geogr Mitt 101:234–237
Kumar MRR, Shenoi SSC, Schluessel P (1999) On the role of the cross equatorial flow on summer monsoon rainfall over India using NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis Data. Meteorol Atmos Phys 70(3–4):201–213
Lau K, Yang S (1997) Climatology and interannual variability of the Southeast Asian summer monsoon. Adv Atmos Sci 14(2):141–162
Li C, Li S (2014) Interannual seesaw between the Somali and the Australian cross-equatorial flows and its connection to the East Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 27:3966–3981. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00288.1
Li J, Zeng Q (2002) A unified monsoon index. Geophys Res Lett 29(8):115–121
Li J, Zeng Q (2003) A new monsoon index and the geographical distribution of the global monsoons. Adv Atmos Sci 20(2):299–302
Lin R, Zhou T, Qian Y (2014) Evaluation of global monsoon precipitation changes based on five reanalysis datasets. J Clim 27(3):1271–1289
Lin YW, Chou C (2014) The role of the New Guinea cross-equatorial flow in the interannual variability of the western North Pacific summer monsoon. Environ Res Lett 9(4):044003. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/9/4/044003
Liu H, Ni Z (2009) Clustering method of time series based on EMD and \(k\)-means algorithm. Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 22(5):803–808
Mao J, Chan JCL (2005) Intraseasonal variability of the South China Sea Summer Monsoon. J Clim 18:2388–2402. doi:10.1175/JCLI3395.1
Michelangeli PA, Vautard R, Legras B (1995) Weather regimes: recurrence and quasi stationarity. J Atmos Sci 52:1237–1256. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1995)052(1237:WRRAQS)2.0.CO;2
Mooley D, Parthasarathy B (1984) Fluctuations in all-India summer monsoon rainfall during 1871–1978. Clim Change 6(3):287–301
Murakami T, Matsumoto J (1994) Summer monsoon over the Asian continent and western North Pacific. J Meteor Soc Japan 72:719–745
Nguyen DQ, Renwick J, McGregor J (2014) Variations of monsoon rainfall: a simple unified index. Geophys Res Lett 41(2):575–581
Nicholson SE, Kim J (1997) The relationship of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation to African rainfall. Int J Climatol 17(2):117–135
Pham X, Fontaine B, Philippon N (2010) Onset of the summer monsoon over the southern Vietnam and its predictability. Theor Appl Climatol 99(1–2):105–113
Qian W (2000) Dry/wet alternation and global monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 27(22):3679–3682
Qian W (2009) Global climate system. Peking University Press, Beijing
Qian W, Jiang N (2015) The global monsoon definition using the difference of local minimum and maximum pentad precipitation rates associated with cross-equatorial flow reversal. Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-015-1448-4
Qian W, Tang S (2010) Identifying global monsoon troughs and global atmospheric centers of action on a pentad scale. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 3(1):1–6
Qian W, Yang S (2000) Onset of the regional monsoon over Southeast Asia. Meteorol Atmos Phys 75(1–2):29–38
Qian W, Ye Q, Zhu Y (1998a) Monsoonal oscillation revealed by the upper-troposphere water vapor band brightness temperature. Chin Sci Bull 43(17):1489–1494
Qian W, Zhu Y, Xie A, Ye Q (1998b) Seasonal and interannual variations of upper tropospheric water vapor band brightness temperature over the global monsoon regions. Adv Atmos Sci 15:337–345
Qian W, Deng Y, Zhu Y, Dong W (2002) Demarcating the worldwide monsoon. Theor Appl Climatol 71(1–2):1–16
Ramage CS (1971) Monsoon meteorology (Vol. 15 of International geophysics series). Academic Press, New York
Riddle E, Stoner M, Johnson N, L’Heureux M, Collins D, Feldstein S (2013) The impact of the MJO on clusters of wintertime circulation anomalies over the North American region. Clim Dyn 40(7–8):1749–1766. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1493-y
Salinger MJ, Mcgree S, Beucher F, Power SB, Delage F (2014) A new index for variations in the position of the South Pacific convergence zone 1910/11-2011/2012. Clim Dyn 43(3–4):1–12
Someshwar D, Ashrit R, Moncrieff MW, Das Gupta M, Dudhia J, Liu C, Kalsi S (2007) Simulation of intense organized convective precipitation observed during the Arabian Sea Monsoon Experiment (ARMEX). J Geophys Res Atmos. doi:10.1029/2006JD007627
Song C, Pei T (2012) Research progress in time series clustering methods based on characteristics. Prog Geogr 31(10):1307–1317
Steinbach M, Tan PN, Kumar V, Klooster S, Potter C (2003) Discovery of climate indices using clustering. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM, New York, NY, USA, KDD ’03, pp 446–455. doi:10.1145/956750.956801
Tao S, Chen L (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In: Chang C-P, Krishnamurti TN (eds) Monsoon meteorology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 60–92
Trenberth KE, Stepaniak DP, Caron JM (2000) The global monsoon as seen through the divergent atmospheric circulation. J Clim 13(22):3969–3993
Vincent DG (1994) The South Pacific Convergence Zone (SPCZ): a review. Mon Weather Rev 122(9):1949–1970. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1994)
Wang B (1994) Climatic regimes of tropical convection and rainfall. J Clim 7(7):1109–1118
Wang B, Ding Q (2006) Changes in global monsoon precipitation over the past 56 years. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2005GL025347
Wang B, Ding Q (2008) Global monsoon: dominant mode of annual variation in the tropics. Dyn Atmos Oceans 44(3):165–183
Wang B, Fan Z (1999) Choice of South Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80(4):629–638
Wang B, Lin H (2002) Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J Clim 15(4):386–398
Wang B, Wu R, Lau KM (2001) Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific-East Asian monsoons. J Clim 14(20):4073–4090
Wang B, Lin H, Zhang Y, Lu MM (2004) Definition of South China Sea monsoon onset and commencement of the East Asia summer monsoon. J Clim 17(4):699–710
Wang B, Yang J, Zhou T, Wang B (2008) Interdecadal changes in the major modes of Asian-Australian monsoon variability: strengthening relationship with ENSO since the late 1970s. J Clim 21(8):1771–1789
Wang B, Liu J, Kim HJ, Webster PJ, Yim SY (2012) Recent change of the global monsoon precipitation (1979–2008). Clim Dyn 39(5):1123–1135
Wang H, Fu R (2002) Cross-equatorial flow and seasonal cycle of precipitation over South America. J Clim 15(13):1591–1608
Wang H, Xue F (2003) The interannual variability of Somali jet and its influences on the inter-hemispheric water vapor transport and the East Asian summer rainfall. Chin J Geophys 46(1):11–20
Wang H, Xue F, Zhou G (2002) The spring monsoon in South China and its relationship to large-scale circulation features. Adv Atmos Sci 19(4):651–664
Wang J, Li M (1982) Cross-equator flow from Australia and monsoon over China. Chin J Atmos Sci 6:1–10
Webster PJ (1987) The elementary monsoon. In: Fein JS, Stephens PL (eds) Monsoons. Wiley, New York, pp 3–32
Wiel KVD, Matthews AJ, Joshi MM, Stevens DP (2015) Why the South Pacific Convergence Zone is diagonal. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2668-0
Xie L (2013) Vertical structure of summer Somali cross-equatorial flow and its relationship with South Asian monsoon. J Meteorol Sci 33(1):37–42
Xie P, Arkin PA (1997) Global precipitation: a 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(11):2539–2558
Xue F, Zeng Q, Huang R, Li C, Lu R, Zhou T (2015) Recent advances in monsoon studies in China. Adv Atmos Sci 32(2):206–229
Yao F, Zhao X (2015) Changes in spatiotemporal pattern of precipitation over China during 1980–2012. Environ Earth Sci 73(4):1649–1662
Zeng Q, Li J (2002) Interactions between the Northern and Southern Hemispheric atmospheres and the essence of monsoon. Chin J Atmos Sci 26(4):433–448
Zeng X, Lu E (2004) Globally unified monsoon onset and retreat indexes. J Clim 17(11):2241–2248
Zhang S, Wang B (2008) Global summer monsoon rainy seasons. Int J Climatol 28(12):1563–1578
Zhang Y, Li T, Wang B, Wu G (2002) Onset of the summer monsoon over the Indochina Peninsula: climatology and interannual variations. J Clim 15(22):3206–3221
Zhou J, Lau K (1998) Does a monsoon climate exist over South America? J Clim 11(5):1020–1040
Zhou T, Zhang L, Li H (2008) Changes in global land monsoon area and total rainfall accumulation over the last half century. Geophys Res Lett 35(16):134–143
Zhou W, Chan JCL (2007) ENSO and the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. Int J Climatol 27(2):157–167
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful for the constructive comments from the two anonymous reviewers, which are crucial in improving this manuscript. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41375073), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA05090407) and the Global Change and Air-Sea Interaction Program (GASI-03-02-01-02)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, N., Qian, W. & Leung, J.CH. The global monsoon division combining the k-means clustering method and low-level cross-equatorial flow. Clim Dyn 47, 2345–2359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2967-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2967-5