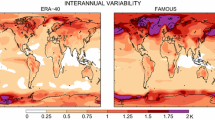
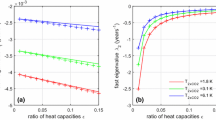
Abstract
An acceleration scheme is proposed in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model for the simulation of long term climate evolutions forced by climate forcing of longer than millennia time scales. In this “coordinated acceleration” scheme, both the surface forcing and the deep ocean are accelerated simultaneously by the same factor. The acceleration scheme is evaluated in a 3-dimensional ocean general circulation model and in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model of intermediate complexity. For millennial climate evolution, our acceleration scheme produces reasonably good simulations with an acceleration factor of about 5. For climate evolution of even longer time scales, the acceleration factor can be increased further.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bretherton FP (1982) Ocean climate modeling. Progress in oceanogaphy Vol 11, Pergamon, Oxford, pp 93–129
Bryan K (1984) Accelerating the convergence to equilibrium of ocean-climate models. J Phys Oceanogr 14: 666–673
Chang P, Ji L, Li H (1997) A decadal climate variation in the tropical Atlantic Ocean from thermodynamic air-sea interactions. Nature 385: 516–518
Delworth T (1996) North Atlantic interannual variability in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. J Clim 9: 2356–2375
Ganopolski A, Petoukhov V, Rahmstorf S, Brovkin V, Claussen M, Eliseev A, Kubatzki C (2001) CLIMBER-2: a climate system model of intermediate complexity. Part II: model sensitivity. Clim Dyn 17(10): 735–751
Gu D, Philander SGH (1997) Interdecadal climate fluctuations that depend on exchanges between the tropics and extratropics. Science 275: 805–807
Latif M, Barnett TP (1994) Causes of decadal climate variability over the North Pacific and North America. Science 266: 634–637
Liu Z, Gallimore R, Kutzbach J, Xu W, Golubev Y, Behling P, Siegle R (1999) Modeling long term climate change with the equilibrium asynchronous coupling scheme. Clim Dyn 15: 325–340
Luyten J, Pedlosky J, Stommel H (1983) The ventilated thermocline. J Phys Oceanogr 13: 292–309
Manabe S, Bryan K (1969) Climate calculations with a combined ocean-atmosphere model. J Atmos Sci 26: 786–789
Pacanowski RC, Griffies S (1998) MOM 3.0 Manual, NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton, USA 08542
Petoukhov V, Ganopolski A, Brovkin V, Claussen M, Eliseev A, Kubatzki C, Rahmstorf S (2000) CLIMBER-2: a climate system model of intermediate complexity. Part I: model description and performance for present climate. Clim Dyn 16(1): 1–17
Philander SGH (1990) El Nino, La Nina, and the Southern Oscillation. Academic Press, San Diego, USA
Sausen R, Voss R (1996) Techniques for asynchronous and periodically-synchronous coupling of atmosphere and ocean models. Part I: general strategy and application to the cyclo-stationary case. Clim Dyn 12: 313–323
Schlesinger ME (1979) Discussion of “A global ocean-atmosphere model with seasonal variation for future studies of climate sensitivity”. Dyn Atmos Oceans 3: 427–432
Voss R, Sausen R (1996) Techniques for asynchronous and periodically-synchronous coupling of atmosphere and ocean models. Part I: impact of variability. Clim Dyn 12: 605–614
Voss R, Sausen R, Cubasch U (1998) Periodically synchronously coupled integrations with the atmosphere-ocean general circulation model ECHAM3/LSG. Clim Dyn 14: 249–266
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers, whose comments have helped improving the paper substantially. This is CCR contribution 843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Lewis, W. & Ganopolski, A. An acceleration scheme for the simulation of long term climate evolution. Climate Dynamics 22, 771–781 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-004-0416-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-004-0416-y