Abstract
Purpose
Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPGs) are inoperable and lethal high-grade gliomas lacking definitive therapy. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) and its downstream signaling molecules are the most commonly overexpressed oncogenes in DIPG. This study tested the effective concentration of PDGFR pathway inhibitors in cell culture and then toxicity of these small-molecule kinase inhibitors delivered to the mouse brainstem via convection-enhanced delivery (CED) for potential clinical application.
Methods
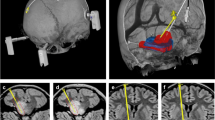
Effective concentrations of small-molecule kinase inhibitors were first established in cell culture from a mouse brainstem glioma model. Sixteen mice underwent CED, a local drug delivery technique, of saline or of single and multidrug combinations of dasatinib (2 M), everolimus (20 M), and perifosine (0.63 mM) in the pons. Animals were kept alive for 3 days following the completion of infusion.
Results
No animals displayed any immediate or delayed neurological deficits postoperatively. Histological analysis revealed edema, microgliosis, acute inflammation, and/or axonal injury in the experimental animals consistent with mild acute drug toxicity.
Conclusions
Brainstem CED of small-molecule kinase inhibitors in the mouse did not cause serious acute toxicities. Future studies will be necessary to evaluate longer-term safety to prepare for potential clinical application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hargrave D, Bartels U, Bouffet E (2006) Diffuse brainstem glioma in children: critical review of clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 7:241–248
Paugh BS, Broniscer A, Qu C, Miller CP, Zhang J, Tatevossian RG, Olson JM, Geyer JR, Chi SN, da Silva NS, Onar-Thomas A, Baker JN, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Baker SJ (2011) Genome-wide analyses identify recurrent amplifications of receptor tyrosine kinases and cell-cycle regulatory genes in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Clin Oncol 29:3999–4006
Puget S, Philippe C, Bax DA, Job B, Varlet P, Junier MP, Andreiuolo F, Carvalho D, Reis R, Guerrini-Rousseau L, Roujeau T, Dessen P, Richon C, Lazar V, Le Teuff G, Sainte-Rose C, Geoerger B, Vassal G, Jones C, Grill J (2012) Mesenchymal transition and PDGFRA amplification/mutation are key distinct oncogenic events in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. PLoS One 7:e30313
Zarghooni M, Bartels U, Lee E, Buczkowicz P, Morrison A, Huang A, Bouffet E, Hawkins C (2010) Whole-genome profiling of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas highlights platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase as potential therapeutic targets. J Clin Oncol 28:1337–1344
Becher OJ, Hambardzumyan D, Walker TR, Helmy K, Nazarian J, Albrecht S, Hiner RL, Gall S, Huse JT, Jabado N, MacDonald TJ, Holland EC (2010) Preclinical evaluation of radiation and perifosine in a genetically and histologically accurate model of brainstem glioma. Cancer Res 70:2548–2557
Bobo RH, Laske DW, Akbasak A, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL, Oldfield EH (1994) Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:2076–2080
Groothuis DR, Ward S, Itskovich AC, Dobrescu C, Allen CV, Dills C, Levy RM (1999) Comparison of 14C-sucrose delivery to the brain by intravenous, intraventricular, and convection-enhanced intracerebral infusion. J Neurosurg 90:321–331
Peng W, Cotrina ML, Han X, Yu H, Bekar L, Blum L, Takano T, Tian GF, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M (2009) Systemic administration of an antagonist of the ATP-sensitive receptor P2X7 improves recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:12489–12493
Mennel S, Meyer CH, Schmidt JC, Kaempf S, Thumann G (2008) Trityl dyes patent blue V and brilliant blue G—clinical relevance and in vitro analysis of the function of the outer blood-retinal barrier. Dev Ophthalmol 42:101–114
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129:1261–1274
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN (2006) TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124:471–484
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Janne PA (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316:1039–1043
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM, Moasser MM (2007) Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 445:437–441
Niederst MJ, Engelman JA (2013) Bypass mechanisms of resistance to receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition in lung cancer. Sci Signal 6:re6
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ (2013) Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19:2240–2247
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Tran H, Brunet A, Griffith EC, Greenberg ME (2003) The many forks in FOXO’s road. Science’s STKE: Sig Transduct Knowl Environ 2003:RE5
Funding
This study was supported by the Matthew Larson Foundation (to Z.Z.), New York Community Trust Research Grant (to M.M.S.), and St. Baldrick’s Foundation Summer Fellowship (to R.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Ho, S.L., Singh, R. et al. Toxicity evaluation of convection-enhanced delivery of small-molecule kinase inhibitors in naïve mouse brainstem. Childs Nerv Syst 31, 557–562 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2640-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2640-7