Abstract
Purpose
The clinical diagnosis of most common single-suture craniosynostosis is easily set, based on the stereotype of deformities and knowledge of the mechanisms of cranial deformations. However, synostosis of unilateral lambdoid suture, probably due to its lower incidence and similarity with other non-synostotic deformities affecting the posterior portion of the skull, makes its clinical diagnosis more difficult and imprecise. The aim of this study is to evaluate the most easily and accurate clinical characteristics to be recognized in the synostotic occipital plagiocephaly.
Methods
This study consisted of clinical evaluation of eight patients with synostotic occipital plagiocephaly, whose diagnosis was further corroborated by computed tomography.
Results
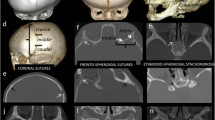
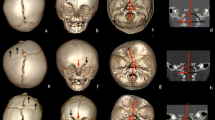
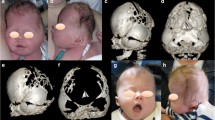
We identified the following: unilateral occipital flattening in eight out of eight patients (100 %), bulging of ipsilateral mastoid process in eight out of eight (100 %), “edge effect” of ipsilateral lambdoid suture in eight out of eight (100 %), inferior deviation of the ear in eight out of eight (100 %), “Dumbo” ears in eight out of eight (100 %), horizontal slant of the bimastoid line in seven out of eight (87.5 %), tilt of the head viewed from behind in seven out of eight (87.5 %), trapezoidal contour of the skull in top view in six out of eight (75 %), contralateral parietal bossing in six out of eight (75 %), and bossing of the contralateral forehead three out of eight (37.5 %).
Conclusions
The most important clinical features specific to the clinical diagnosis of synostotic occipital plagiocephaly, not present in the positional posterior plagiocephaly, were bulging of the ipsilateral mastoid process, edge effect of the synostotic lambdoid suture, tilt of the head, and slant of the bimastoid line viewed from behind, inferior deviation of the ear, and contralateral parietal bossing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
French LR, Jackson IT, Melton LJ (1990) A population-based study of craniosynostosis. J Clin Epidemiol 43:69–73
Huang MH, Gruss JS, Clarren SK, Mouradian WE, Cunningham ML, Roberts TS, Loeser JD, Cornell CJ (1996) The differential diagnosis of posterior plagiocephaly: true lambdoid synostosis versus positional molding. Plast Reconstr Surg 98:765
Rekate HL (1998) Occipital plagiocephaly: a critical review of the literature. J Neurosurg 89:24–30
Shillito J Jr, Matson DD (1968) Craniosynostosis: a review of 519 surgical patients. Pediatrics 41:829–853
Shuper A, Merlob P, Grunebaum M et al (1985) The incidence of isolated craniosynostosis in the newborn infant. Am J Dis Child 139:85–86
Sun P, Persing J (1999) Craniosynostosis. In: Albright L, Pollack I, Adelson D (eds) Principles and practice of pediatric neurosurgery. Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., New York, pp 219–242
Hutchison BL, Hutchison LA, Thompson JM, Mitchell EA (2004) Plagiocephaly and brachycephaly in the first two years of life: a prospective cohort study. Pediatrics 114:970–980
Mulliken JB, Vander Woude DL, Hansen M (1999) Analysis of posterior plagiocephaly: deformational versus synostotic. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:371–380
Fearon JA, Singh DJ, Beals SP, Yu JC (2007) The diagnosis and treatment of single-sutural synostoses: are computed tomographic scan necessary? Plast Reconstr Surg 120:132
Liu Y, Kadlub N, Freitas RS, Persing J, Duncan C, Shin JH (2008) The misdiagnosis of craniosynostosis as deformational plagiocephaly. J Craniofac Surg 19:132–136
Delashaw JB, Persing JA, Broaddus WC, Jane JA (1989) Cranial vault growth in craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 70:159–165
Ruiz RL, Ritter AM, Turvey TA, Costello B, Ricalde P (2004) Nonsyndromic craniosynostosis: diagnosis and contemporary surgical management. Oral and Maxillofaci Surg Clin N Am 16:447–463
Muakkassa KF, Hoffman HJ, Hinton DR, Hendrick B, Humprherys RP, Ash J (1984) Lambdoid synostosis. Part 2: review of cases managed at the Hospital for Sick Children, 1972–1982. J Neurosurg 61:340–347
Bertelsen TI (1958) The premature synostosis of the cranial sutures. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl 51:1–176
Knudson HW, Flaherty RA (1960) Craniosynostosis. AJR 84:454–460
Pople IK, Sanford RA, Muhlbauer MS (1996) Clinical presentation and management of 100 infants with occipital plagiocephaly. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:1–6
Vander Kolk CA, Carson BS (1994) Lambdoid synostosis. Plast Clin North Am 21:575–584
Kane AA, Mitchell LE, Craven KP, Marsh JL (1996) Observations on a recent increase in plagiocephaly without synostosis. Pediatrics 97:877–885
Brenner DJ, Elliston CD, Hall EJ, Berdon WE (2001) Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:289–296
Frush DP, Donnely LF, Rosen NS (2003) Computed tomography and radiation risks: what pediatric health care providers should know. Pediatrics 112:951–957
Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP, McHugh K, Lee C, Kim KP, Howe NL, Ronckers CM, Rajaraman P, Craft A, Parker L, Gonzalez AB (2012) Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumors: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 380:499–505
National Cancer Institute (2012) Radiation risks and pediatric computed tomography (CT): a guide for health care providers. Available at: www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/causes/radiation-risks-pediatric-ct. Reviewed July 6th, 2012. Accessed 1 Aug 2013
Hall P, Adami HO, Trichopoulos D, Pedersen NP, Lagiou P, Ekbom A, Ingvar M, Lundell M, Granath F (2004) Effect of low doses of ionizing radiation in infancy on cognitive function in adulthood: Swedish population based cohort study. MNJ 328:19–21
Dias MS, Klein DM, Backstrom JW (1996) Occipital plagiocephaly: deformation or lambdoid synostosis? I. Morphometric analysis and results of unilateral lambdoid craniectomy. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:61–68
Roger GF (2011) Deformational plagiocephaly, brachycephaly, and scaphocephaly. Part I: terminology, diagnosis, and etiopathogenesis. J Craniofac Surg 22:9–16
Ehret FW, Whelan MF, Ellenbogen RG, Cunningham ML, Gruss JS (2004) Differential diagnosis of the trapezoid-shaped head. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 41:13–19
Smart JM Jr, Reid RR, Sigh DJ, Bartlett SP (2007) True lambdoid craniosynostosis: long-term results of surgical and conservative therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:993–1003
David DJ, Menard RM (2000) Occipital plagiocephaly. Br J Plast Surg 53:367–377
Lin KY, Polin RS, Gampper T, Jane JA (1997) Occipital flattening in the infant skull. Neurosurg Focus 15:2e4
Smartt JM, Elliott RM, Reid RR, Bartlett SP (2011) Analysis of differences in the cranial base and facial skeleton of patients with lambdoid synostosis and deformational plagiocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:303–312
Funding
Authors received no financial support for this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matushita, H., Alonso, N., Cardeal, D.D. et al. Major clinical features of synostotic occipital plagiocephaly: mechanisms of cranial deformations. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 1217–1224 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2414-7