Abstract
Purpose
Prognostic factors affecting outcomes in pediatric spinal cord ependymomas are limited. We sought to investigate potential associations between extent of resection and histologic grade on progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was performed to identify pediatric patients who underwent surgical resection for spinal cord ependymomas. Only manuscripts with clearly defined age, tumor grade, extent of resection, and clinical follow-up were included.
Results
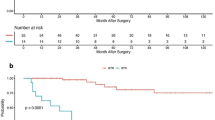
A total of 80 patients were identified with a histologic distribution as follows: 36 % myxopapillary (grade I), 54 % classical (grade II), and 10 % anaplastic (grade III). There was no association between tumor grade and PFS. The only factor associated with improved PFS was gross total resection (GTR), which remained significant in a multivariate model (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.248, p = 0.022). Moreover, older age (HR = 0.818, p = 0.026), GTR (HR = 0.042, p = 0.013), and anaplastic grade (HR = 19.847, p = 0.008) demonstrated a significant association with OS in a multivariate model.
Conclusions
Among pediatric patients with spinal cord ependymomas, PFS did not differ across histologic grades but was prolonged among patients who underwent GTR. Age, extent of resection, and tumor grade were all significantly associated with survival.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbahiwe HC, Wharam M, Batra S, Cohen K, Terezakis SA (2013) Management of pediatric myxopapillary ependymoma: the role of adjuvant radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:421–427
Aktug T, Hakguder G, Sarioglu S, Akgur FM, Olguner M, Pabuccuoglu U (2000) Sacrococcygeal extraspinal ependymomas: the role of coccygectomy. J Pediatr Surg 35:515–518
Akyurek S, Chang EL, Yu TK, Little D, Allen PK, McCutcheon I, Mahajan A, Maor MH, Woo SY (2006) Spinal myxopapillary ependymoma outcomes in patients treated with surgery and radiotherapy at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J Neurooncol 80:177–183
Al-Halabi H, Montes JL, Atkinson J, Farmer JP, Freeman CR (2010) Adjuvant radiotherapy in the treatment of pediatric myxopapillary ependymomas. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55:639–643
Allen JC, Siffert J, Hukin J (1998) Clinical manifestations of childhood ependymoma: a multitude of syndromes. Pediatr Neurosurg 28:49–55
Amirian ES, Armstrong TS, Aldape KD, Gilbert MR, Scheurer ME (2012) Predictors of survival among pediatric and adult ependymoma cases: a study using surveillance, epidemiology, and end results data from 1973 to 2007. Neuroepidemiology 39:116–124
Armstrong TS, Vera-Bolanos E, Bekele BN, Aldape K, Gilbert MR (2010) Adult ependymal tumors: prognosis and the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Neuro Oncol 12:862–870
Bagley CA, Kothbauer KF, Wilson S, Bookland MJ, Epstein FJ, Jallo GI (2007) Resection of myxopapillary ependymomas in children. J Neurosurg 106:261–267
Bagley CA, Wilson S, Kothbauer KF, Bookland MJ, Epstein F, Jallo GI (2009) Long term outcomes following surgical resection of myxopapillary ependymomas. Neurosurg Rev 32:321–334, discussion 334
Benesch M, Weber-Mzell D, Gerber NU, von Hoff K, Deinlein F, Krauss J, Warmuth-Metz M, Kortmann RD, Pietsch T, Driever PH, Quehenberger F, Urban C, Rutkowski S (2010) Ependymoma of the spinal cord in children and adolescents: a retrospective series from the HIT database. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:137–144
Cameron MM (1976) Surgical management of multiple neuraxial ependymomas. Case report. Eur Neurol 14:365–369
Cervoni L, Celli P, Fortuna A, Cantore G (1994) Recurrence of spinal ependymoma. Risk factors and long-term survival. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:2838–2841
Chao ST, Kobayashi T, Benzel E, Reddy CA, Stevens GH, Prayson RA, Kalfas I, Schlenk R, Krishnaney A, Steinmetz MP, Bingaman W, Hahn J, Suh JH (2011) The role of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of spinal myxopapillary ependymomas. J Neurosurg Spine 14:59–64
Cho JC, Miller A, Kettner NW (2009) Cervical ependymoma in a male adolescent with neck and back pain. J Manip Physiol Ther 32:695–700
Choi GH, Oh JK, Kim TY, You NK, Lee HS, Yoon do H, Ha Y, Yi S, Kim DS, Choi JU, Kim KN (2012) The clinical features and surgical outcomes of pediatric patients with primary spinal cord tumor. Childs Nerv Syst 28:897–904
Clover LL, Hazuka MB, Kinzie JJ (1993) Spinal cord ependymomas treated with surgery and radiation therapy. A review of 11 cases. Am J Clin Oncol 16:350–353
Conter C, Carrie C, Bernier V, Geoffray A, Pagnier A, Gentet JC, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Chabaud S, Frappaz D (2009) Intracranial ependymomas in children: society of pediatric oncology experience with postoperative hyperfractionated local radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1536–1542
Di Marco A, Griso C, Pradella R, Campostrini F, Garusi GF (1988) Postoperative management of primary spinal cord ependymomas. Acta Oncol 27:371–375
Dulai MS, Caccamo DV, Briley AL, Edwards MS, Fisher PG, Lehman NL (2010) Intramedullary papillary ependymoma with choroid plexus differentiation and cerebrospinal fluid dissemination to the brain. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:511–517
Duong LM, McCarthy BJ, McLendon RE, Dolecek TA, Kruchko C, Douglas LL, Ajani UA (2012) Descriptive epidemiology of malignant and nonmalignant primary spinal cord, spinal meninges, and cauda equina tumors, United States, 2004–2007. Cancer 118:4220–4227
Engelhard HH, Villano JL, Porter KR, Stewart AK, Barua M, Barker FG, Newton HB (2010) Clinical presentation, histology, and treatment in 430 patients with primary tumors of the spinal cord, spinal meninges, or cauda equina. J Neurosurg Spine 13:67–77
Fischer G, Mansuy L (1980) Total removal of intramedullary ependymomas: follow-up study of 16 cases. Surg Neurol 14:243–249
Fujiyama K, Kishikawa M, Fujii H, Moriyama T, Fuchigami K, Iseki M, Shinkai K (1990) Anaplastic ependymoma of the spinal cord in childhood. A case report. Acta Pathol Jpn 40:376–382
Gilbert MR, Ruda R, Soffietti R (2010) Ependymomas in adults. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 10:240–247
Gomez DR, Missett BT, Wara WM, Lamborn KR, Prados MD, Chang S, Berger MS, Haas-Kogan DA (2005) High failure rate in spinal ependymomas with long-term follow-up. Neuro Oncol 7:254–259
Goto T, Ohata K, Takami T, Nishikawa M, Nishio A, Morino M, Tsuyuguchi N, Hara M (2003) Prevention of postoperative posterior tethering of spinal cord after resection of ependymoma. J Neurosurg 99:181–187
Grill J, Le Deley MC, Gambarelli D, Raquin MA, Couanet D, Pierre-Kahn A, Habrand JL, Doz F, Frappaz D, Gentet JC, Edan C, Chastagner P, Kalifa C (2001) Postoperative chemotherapy without irradiation for ependymoma in children under 5 years of age: a multicenter trial of the French Society of Pediatric Oncology. J Clin Oncol 19:1288–1296
Hanbali F, Fourney DR, Marmor E, Suki D, Rhines LD, Weinberg JS, McCutcheon IE, Suk I, Gokaslan ZL (2002) Spinal cord ependymoma: radical surgical resection and outcome. Neurosurgery 51:1162–1172, discussion 1172–1164
Helseth A, Mork SJ (1989) Primary intraspinal neoplasms in Norway, 1955 to 1986. A population-based survey of 467 patients. J Neurosurg 71:842–845
Helseth E, Due-Tonnessen B, Lote K, Skullerud K, Storm-Mathisen I, Wesenberg F, Lundar T (2001) Ependymoma in children and young adults (0–19 years): report of 25 consecutive cases. Childs Nerv Syst 17:24–30
Horn B, Heideman R, Geyer R, Pollack I, Packer R, Goldwein J, Tomita T, Schomberg P, Ater J, Luchtman-Jones L, Rivlin K, Lamborn K, Prados M, Bollen A, Berger M, Dahl G, McNeil E, Patterson K, Shaw D, Kubalik M, Russo C (1999) A multi-institutional retrospective study of intracranial ependymoma in children: identification of risk factors. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21:203–211
Hoshimaru M, Koyama T, Hashimoto N, Kikuchi H (1999) Results of microsurgical treatment for intramedullary spinal cord ependymomas: analysis of 36 cases. Neurosurgery 44:264–269
Jaing TH, Wang HS, Tsay PK, Tseng CK, Jung SM, Lin KL, Lui TN (2004) Multivariate analysis of clinical prognostic factors in children with intracranial ependymomas. J Neurooncol 68:255–261
Jatana KR, Jacob A, Slone HW, Ray-Chaudhury A, Welling DB (2008) Spinal myxopapillary ependymoma metastatic to bilateral internal auditory canals. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 117:98–102
Johnson JM, Jessurun J, Leonard A (1999) Sacrococcygeal ependymoma: case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg 34:1405–1407
Johnson RA, Wright KD, Poppleton H, Mohankumar KM, Finkelstein D, Pounds SB, Rand V, Leary SE, White E, Eden C, Hogg T, Northcott P, Mack S, Neale G, Wang YD, Coyle B, Atkinson J, DeWire M, Kranenburg TA, Gillespie Y, Allen JC, Merchant T, Boop FA, Sanford RA, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Taylor MD, Grundy RG, Gilbertson RJ (2010) Cross-species genomics matches driver mutations and cell compartments to model ependymoma. Nature 466:632–636
Kabler HA, Syska BE, Springer BL, Singer JI (2008) Ependymoma as a cause of low back pain in a young healthy athlete. Pediatr Emerg Care 24:685–687
Kaner T, Sasani M, Oktenoglu T, Solmaz B, Sarloglu AC, Ozer AF (2010) Clinical analysis of 21 cases of spinal cord ependymoma : positive clinical results of gross total resection. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 47:102–106
Kocak Z, Garipagaoglu M, Adli M, Uzal MC, Kurtman C (2004) Spinal cord ependymomas in adults: analysis of 15 cases. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 23:201–206
Lee TT, Gromelski EB, Green BA (1998) Surgical treatment of spinal ependymoma and post-operative radiotherapy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:309–313
Lin YH, Huang CI, Wong TT, Chen MH, Shiau CY, Wang LW, Ming-Tak Ho D, Yen SH (2005) Treatment of spinal cord ependymomas by surgery with or without postoperative radiotherapy. J Neurooncol 71:205–210
Lonjon M, Goh KY, Epstein FJ (1998) Intramedullary spinal cord ependymomas in children: treatment, results and follow-up. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:178–183
Massimino M, Gandola L, Giangaspero F, Sandri A, Valagussa P, Perilongo G, Garre ML, Ricardi U, Forni M, Genitori L, Scarzello G, Spreafico F, Barra S, Mascarin M, Pollo B, Gardiman M, Cama A, Navarria P, Brisigotti M, Collini P, Balter R, Fidani P, Stefanelli M, Burnelli R, Potepan P, Podda M, Sotti G, Madon E (2004) Hyperfractionated radiotherapy and chemotherapy for childhood ependymoma: final results of the first prospective AIEOP (Associazione Italiana di Ematologia-Oncologia Pediatrica) study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1336–1345
Mavroudis C, Townsend JJ, Wilson CB (1977) A metastasizing ependymoma of the cauda equina. Case report. J Neurosurg 47:771–775
McGuire CS, Sainani KL, Fisher PG (2009) Both location and age predict survival in ependymoma: a SEER study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 52:65–69
McGuire CS, Sainani KL, Fisher PG (2009) Incidence patterns for ependymoma: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results study. J Neurosurg 110:725–729
McLaughlin MP, Marcus RB Jr, Buatti JM, McCollough WM, Mickle JP, Kedar A, Maria BL, Million RR (1998) Ependymoma: results, prognostic factors and treatment recommendations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:845–850
McLendon RE, Schiffer D, Rosenblum MK, Wiestler OD, Kros JM, Korshunov A, Ng H-K (2007) World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon
Merchant TE, Kiehna EN, Thompson SJ, Heideman R, Sanford RA, Kun LE (2000) Pediatric low-grade and ependymal spinal cord tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 32:30–36
Merchant TE, Jenkins JJ, Burger PC, Sanford RA, Sherwood SH, Jones-Wallace D, Heideman RL, Thompson SJ, Helton KJ, Kun LE (2002) Influence of tumor grade on time to progression after irradiation for localized ependymoma in children. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:52–57
Modena P, Lualdi E, Facchinetti F, Veltman J, Reid JF, Minardi S, Janssen I, Giangaspero F, Forni M, Finocchiaro G, Genitori L, Giordano F, Riccardi R, Schoenmakers EF, Massimino M, Sozzi G (2006) Identification of tumor-specific molecular signatures in intracranial ependymoma and association with clinical characteristics. J Clin Oncol 24:5223–5233
Moon K, Filis AK, Cohen AR (2010) Mobile spinal ependymoma. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:85–88
Mork SJ, Loken AC (1977) Ependymoma: a follow-up study of 101 cases. Cancer 40:907–915
Mork SJ, Risberg G, Krogness K (1980) Case report. Anaplastic ependymoma of the spinal cord. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 6:307–311
Morris DM, Steinert HR, Wiernik PH (1983) Ineffectiveness of chemotherapy in patients with metastatic ependymoma of the cauda equina. J Surg Oncol 22:33–36
Mridha AR, Sharma MC, Sarkar C, Suri V, Rishi A, Garg A, Suri A (2007) Myxopapillary ependymoma of lumbosacral region with metastasis to both cerebellopontine angles: report of a rare case. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1209–1213
Nagasawa DT, Trang A, Choy W, Spasic M, Yew A, Zarinkhou G, Garcia HM, Yang I (2013) Genetic expression profiles of adult and pediatric ependymomas: molecular pathways, prognostic indicators, and therapeutic targets. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:388–399
Naidu MR, Dinakar I (1989) Intramedullary mass lesions of the spinal cord. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 91:135–138
Newton HB, Henson J, Walker RW (1992) Extraneural metastases in ependymoma. J Neurooncol 14:135–142
Nishio S, Morioka T, Fujii K, Inamura T, Fukui M (2000) Spinal cord gliomas: management and outcome with reference to adjuvant therapy. J Clin Neurosci 7:20–23
O’Sullivan C, Jenkin RD, Doherty MA, Hoffman HJ, Greenberg ML (1994) Spinal cord tumors in children: long-term results of combined surgical and radiation treatment. J Neurosurg 81:507–512
Oh MC, Sayegh ET, Safaee M, Sun MZ, Kaur G, Kim JM, Aranda D, Molinaro AM, Gupta N, Parsa AT (2013) Prognosis by tumor location for pediatric spinal cord ependymomas. J Neurosurg Pediatr 11:282–288
Ohata K, Takami T, Gotou T, El-Bahy K, Morino M, Maeda M, Inoue Y, Hakuba A (1999) Surgical outcome of intramedullary spinal cord ependymoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:341–346, discussion 346–347
Oya N, Shibamoto Y, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Hiraoka M (2002) Postoperative radiotherapy for intracranial ependymoma: analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. J Neurooncol 56:87–94
Payne NS 2nd, McDonald JV (1973) Rupture of spinal cord ependymoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 39:662–665
Peker S, Ozgen S, Ozek MM, Pamir MN (2004) Surgical treatment of intramedullary spinal cord ependymomas: can outcome be predicted by tumor parameters? J Spinal Disord Tech 17:516–521
Pica A, Miller R, Villa S, Kadish SP, Anacak Y, Abusaris H, Ozyigit G, Baumert BG, Zaucha R, Haller G, Weber DC (2009) The results of surgery, with or without radiotherapy, for primary spinal myxopapillary ependymoma: a retrospective study from the rare cancer network. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1114–1120
Prayson RA (1999) Clinicopathologic study of 61 patients with ependymoma including MIB-1 immunohistochemistry. Ann Diagn Pathol 3:11–18
Preston-Martin S (1990) Descriptive epidemiology of primary tumors of the spinal cord and spinal meninges in Los Angeles County, 1972–1985. Neuroepidemiology 9:106–111
Puget S, Grill J, Valent A, Bieche I, Dantas-Barbosa C, Kauffmann A, Dessen P, Lacroix L, Geoerger B, Job B, Dirven C, Varlet P, Peyre M, Dirks PB, Sainte-Rose C, Vassal G (2009) Candidate genes on chromosome 9q33-34 involved in the progression of childhood ependymomas. J Clin Oncol 27:1884–1892
Schellinger KA, Propp JM, Villano JL, McCarthy BJ (2008) Descriptive epidemiology of primary spinal cord tumors. J Neurooncol 87:173–179
Schiffer D, Chio A, Giordana MT, Migheli A, Palma L, Pollo B, Soffietti R, Tribolo A (1991) Histologic prognostic factors in ependymoma. Childs Nerv Syst 7:177–182
Schiffer D (1997) Brain tumors: biology, pathology, and clinical references. Springer, Berlin
Scott M (1974) Infiltrating ependymomas of the cauda equina. Treatment by conservative surgery plus radiotherapy. J Neurosurg 41:446–448
Smyth MD, Horn BN, Russo C, Berger MS (2000) Intracranial ependymomas of childhood: current management strategies. Pediatr Neurosurg 33:138–150
Stephen JH, Sievert AJ, Madsen PJ, Judkins AR, Resnick AC, Storm PB, Rushing EJ, Santi M (2012) Spinal cord ependymomas and myxopapillary ependymomas in the first 2 decades of life: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical characterization of 19 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9:646–653
Taylor MD, Poppleton H, Fuller C, Su X, Liu Y, Jensen P, Magdaleno S, Dalton J, Calabrese C, Board J, Macdonald T, Rutka J, Guha A, Gajjar A, Curran T, Gilbertson RJ (2005) Radial glia cells are candidate stem cells of ependymoma. Cancer Cell 8:323–335
Timmermann B, Kortmann RD, Kuhl J, Meisner C, Slavc I, Pietsch T, Bamberg M (2000) Combined postoperative irradiation and chemotherapy for anaplastic ependymomas in childhood: results of the German prospective trials HIT 88/89 and HIT 91. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:287–295
Volpp PB, Han K, Kagan AR, Tome M (2007) Outcomes in treatment for intradural spinal cord ependymomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:1199–1204
Wahab SH, Simpson JR, Michalski JM, Mansur DB (2007) Long term outcome with post-operative radiation therapy for spinal canal ependymoma. J Neurooncol 83:85–89
Waldron JN, Laperriere NJ, Jaakkimainen L, Simpson WJ, Payne D, Milosevic M, Wong CS (1993) Spinal cord ependymomas: a retrospective analysis of 59 cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27:223–229
Wen BC, Hussey DH, Hitchon PW, Schelper RL, Vigliotti AP, Doornbos JF, VanGilder JC (1991) The role of radiation therapy in the management of ependymomas of the spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 20:781–786
Whitaker SJ, Bessell EM, Ashley SE, Bloom HJ, Bell BA, Brada M (1991) Postoperative radiotherapy in the management of spinal cord ependymoma. J Neurosurg 74:720–728
Yasui T, Hakuba A, Katsuyama J, Nishimura S (1988) Microsurgical removal of intramedullary spinal cord tumours: report of 22 cases. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 43:9–12
Acknowledgments
Mr. Safaee was supported by a grant from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. Dr. Oh was supported by the Neurosurgery Research and Education Foundation from the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Dr. Parsa was partially funded by the Reza and Georgianna Khatib Endowed Chair in Skull Base Tumor Surgery.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michael Safaee and Michael C. Oh are contributed equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safaee, M., Oh, M.C., Kim, J.M. et al. Histologic grade and extent of resection are associated with survival in pediatric spinal cord ependymomas. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 2057–2064 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2149-x