Abstract
Introduction
The cephalic index (CI) of the head can be measured manually using a caliper, the original technique, but it is also possible to determine it using skull X-ray, 2DCT and 3DCT images, 3D photo and with help of plagiocephalometry (PCM).
Patients and methods
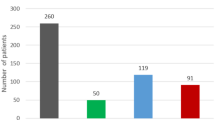
In this study, the manual caliper determination is statistically compared with other measuring methods for scaphocephaly patients (n = 39).
Results
The CI mean differences for the most representative data are sequentially 3.74, 2.16, 1.09 and 0.97 for the 2DCT, PCM, 3D photo and 3DCT techniques. The CI 2DCT values show a significant difference (p < 0.01) in reference to CI manually, while the other techniques show a p > 0.05.
Conclusion
The conclusions are that significantly different results are achieved when using 2DCT relative to the manual caliper determination. No significant difference is observed between the 3D techniques and the manual method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Brace RA (1977) Fitting straight lines to experimental data. Am J Physiol 233:R94–R99
Christofides EA, Steinmann ME (2010) A novel anthropometric chart for craniofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg 21:352–357
Farkas LG, Posnick JC, Hreczko TM (1992) Anthropometric growth study of the head. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 29:303–308
Frühwald J, Schicho KA, Figl M, Benesch T, Watzinger F et al (2008) Accuracy of craniofacial measurements: computed tomography and three-dimensional computed tomography compared with stereolithographic models. J Craniofac Surg 19:22–26
Hankinson TC, Fontana EJ, Anderson RC, Feldstein NA (2010) Surgical treatment of single-suture craniosynostosis: an argument for quantitative methods to evaluate cosmetic outcomes. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:193–197
Marcus JR, Domeshek LF, Das R, Marshall S, Nightingale R et al (2008) Objective three-dimensional analysis of cranial morphology. Eplasty 8:e20
Marcus JR, Stokes TH, Mukundan S, Forrest CR (2006) Quantitative and qualitative assessment of morphology in sagittal synostosis: mid-sagittal vector analysis. J Craniofac Surg 17:680–686
Plank LH, Giavedoni B, Lombardo JR, Geil MD, Reisner A (2006) Comparison of infant head shape changes in deformational plagiocephaly following treatment with a cranial remolding orthosis using a noninvasive laser shape digitizer. J Craniofac Surg 17:1084–1091
Ruiz-Correa S, Sze RW, Starr JR, Lin HT, Speltz ML et al (2006) New scaphocephaly severity indices of sagittal craniosynostosis: a comparative study with cranial index quantifications. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 43:211–221
Schaaf H, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Malik CY, Streckbein P, Preuss M et al (2010) Accuracy of three-dimensional photogrammetric images in non-synostotic cranial deformities. Neuropediatrics 41:24–29
Shah MN, Kane AA, Petersen JD, Woo AS, Naidoo SD et al (2011) Endoscopically assisted versus open repair of sagittal craniosynostosis: the St. Louis Children’s Hospital experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:165–170
van Adrichem LN, van Vlimmeren LA, Cadanova D, Helders PJ, Engelbert RH et al (2008) Validation of a simple method for measuring cranial deformities (plagiocephalometry). J Craniofac Surg 19:15–21
van Vlimmeren LA, Takken T, van Adrichem LN, van der Graaf Y, Helders PJ et al (2006) Plagiocephalometry: a non-invasive method to quantify asymmetry of the skull; a reliability study. Eur J Pediatr 165:149–157
Wilbrand JF, Szczukowski A, Blecher JC, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Christophis P et al (2012) Objectification of cranial vault correction for craniosynostosis by three-dimensional photography. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40(8):726–730
Wilbrand JF, Wilbrand M, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Blecher JC, Christophis P et al (2011) Value and reliability of anthropometric measurements of cranial deformity in early childhood. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 39:24–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Lindert, E.J., Siepel, F.J., Delye, H. et al. Validation of cephalic index measurements in scaphocephaly. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 1007–1014 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2059-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2059-y