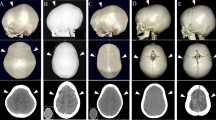
Abstract
Purpose
Numerous techniques are used to correct sagittal synostosis. Although cosmetic results and operative complications are well documented, little is known about functional outcome. In our institution, the technique for extended strip craniectomy evolved over time. This study compares cosmetic results, complications, and signs of raised intracranial pressure (ICP) between the variants of the extended strip craniectomy.
Methods
Seventy-nine consecutive patients undergoing early extended strip craniectomy for scaphocephaly (2002–2008) were included. Four techniques were used: A, a simple bilateral parietal flap with out-fracturing of the bone flap; B, C, and D included remodeling of the parietal flap by adding triangular cuts and bending or suturing the resulting fingers. In technique D, the sagittal strip was rotated and fixed between the parietal flaps. Data on head circumference (HC), skull X-ray, and fundoscopy were collected prospectively.
Results
For all patients, the average cranial index (CI) was 74 after 3 months and 72 after 2 years. Although technique D resulted in the best initial improvement, there was no significant percentage increase in CI after 24 months between the four techniques. Postoperatively, 9 % of the patients developed papilledema, 42 % developed a fontanel bulge, and 57 % had diminished HC. Four patients were reoperated on because of raised ICP.
Conclusions
Postoperative CI is mainly determined by preoperative CI and hardly affected by type of extended strip craniectomy. Signs of raised ICP occurred more frequently than expected, therefore structural follow-up is required to detect such signs. Technique and timing of surgery should aim at creating sufficient intracranial volume.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo MA, Pollack IF (2010) A single-center experience with symptomatic postoperative calvarial growth restriction after extended strip craniectomy for sagittal craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5(1):131–135
Agrawal D, Steinbok P, Cochrane DD (2006) Long-term anthropometric outcomes following surgery for isolated sagittal craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg 105:357–360
Albright AL (1985) Operative normalization of skull shape in sagittal synostosis. Neurosurgery 17:329–331
Alvarez-Garijo JA, Cavadas PC, Vila MM, Alvarez-Llanas A (2001) Sagittal synostosis: results of surgical treatment in 210 patients. Childs Nerv Syst 17:64–68
Anderson FM, Johnson FL (1956) Craniosynsotosis: a modification in surgical treatment. Surgery 40:961–970
Antunes S, Arnaud E, Cruz A, Marchac D, Renier D (2009) Scaphocephaly: part I: indices for scaphocephalic frontal and occipital morphology evaluation: long-term results. J Craniofac Surg 20:1837–1842
Arnaud E, Renier D, Marchac D (1995) Prognosis for mental function in scaphocephaly. J Neurosurg 83:476–479
Arnaud E, Capon-Degardin N, Michienzi J, Di Rocco F, Renier D (2009) Scaphocephaly part II: secondary coronal synostosis after scaphocephalic surgical correction. J Craniofac Surg 20(2):1843–1850
Becker DB, Petersen JD, Kane AA, Cradock MM, Pilgram TK, Marsh JL (2005) Speech, cognitive, and behavioral outcomes in nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(2):400–407
Bellew M, Chumas P, Mueller R, Liddington M, Russell J (2005) Pre- and postoperative developmental attainment in sagittal synostosis. Arch Dis Child 90(4):346–350
Boop FA, Chadduck WM, Shewmake K, Teo C (1996) Outcome analysis of 85 patients undergoing the Pi procedure for correction of sagittal synostosis. J Neurosurg 85:50–55
Boulos PT, Lin KY, Jane JA Jr, Jane JA Sr (2004) Correction of sagittal synostosis using a modified Pi method. Clin Plast Surg 31(3):489–498
Cohen SR, Cho DC, Nichols SL, Simms C, Cross KP, Burstein FD (2004) American society of maxillofacial surgeons outcome study: preoperative and postoperative neurodevelopmental findings in single-suture craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(4):841–847
Da Costa AC, Walters I, Savarirayan R, Anderson VA, Wrennall JA, Meara JG (2006) Intellectual outcomes in children and adolescents with syndromic and nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(1):175–181
David LR, Proffer P, Hurst WJ, Glazier S, Argenta LC (2004) Spring-mediated cranial reshaping for synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 15:810–816
Fearon JA, McLaughlin EB, Kolar JC (2006) Sagittal craniosynostosis: surgical outcomes and long term growth. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:532–541
Florisson JM, van Veelen ML, Bannink N, van Adrichem LN, van der Meulen JJ, Bartels MC, Mathijssen IM (2010) Papiledema in isolated single-suture craniosynostosis: prevalence and predictive factors. J Craniofac Surg 21(1):20–24
Friede H, Lauritzen C, Figueroa AA (1996) Roentgencephalometric follow-up after early osteotomies in patients with scaphocephaly. J Craniofac Surg 7(2):96–101
Gault DT, Renier D, Marchac D, Jones BM (1992) Intracranial pressure and intracranial volume in children with craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 90:377–381
Greene CS Jr, Winston KR (1988) Treatment of scaphocephaly with sagittal craniectomy and biparietal morcellation. Neurosurgery 23(2):196–202
Greensmith AL, Holmes AD, Lo P (2008) Complete correction of severe scaphocephaly: the Melbourne method of total vault remodeling. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:1300–1310
Guimaraes-Ferreira J, Gewalli F, David L, Olsson R, Friede H, Lauritzen CG (2003) Spring mediated cranioplasty compared with the modified Pi-plasty for sagittal synostosis. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 37:208–215
Ingraham FD, Alexander E, Matson DD (1984) Clinical studies in craniosynostosis. Analysis of fifty cases and description of a method of surgical treatment. Surgery 24:518–541
Jane JA, Edgerton MT, Futrell MT, Park TS (1978) Immediate correction of sagittal synostosis. J Neurosurg 49(5):705–710
Jimenez DF, Barone C, McGee ME, Cartwright CC, Baker CL (2004) Endoscopy-assisted wide vertex craniectomy, barrel stave osteotomies, and postoperative helmet molding therapy in the management of sagittal suture craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 100:407–417
Kaiser G (1988) Sagittal synostosis—its clinical significance and the results of three different methods of craniectomy. Childs Nerv Syst 4:223–230
Kandasamy J, Anderson K, Dunne J, Grogan J, Duncan C, Sinha A, May P (2011) Treatment of scaphocephaly with combined vertex craniectomy and bilateral microbarrel staving. J Craniofac Surg 22:42–46
Kapp-Simon KA, Leroux B, Cunnigham M, Speltz ML (2005) Multisite study of infants with single-suture craniosynostosis: preliminary report of presurgery development. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 42(4):377–384
Kapp-Simon KA, Speltz ML, Cunningham ML, Patel PK, Tomita T (2007) Neurodevelopment of children with single suture craniosynostosis: a review. Childs Nerv Syst 23(3):269–281
Lane LC (1892) Pioneer craniectomy for the relief of mental imbecility due to premature sutural closure and microcephalus. JAMA 18:49–50
Lannelongue M (1890) De la craniectomie dans la microcéphalie. C R Acad Sci III 110:1382
Lauritzen C, Sugawara Y, Kocabalkan O, Olsson R (1998) Spring mediated dynamic craniofacial reshaping. Case report. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 32(3):331–338
Magge SN, Westerveld M, Pruzinsky T, Persing JA (2002) Long-term neuropsychological effects of sagittal craniosynostosis on child development. J Craniofac Surg 13(1):99–104
Marsh JL, Jenny A, Galic M, Picker S, Vannier MW (1991) Surgical management of sagittal synostosis: a quantitative evaluation of two different techniques. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2:629–640
Marucci DD, Johnston CP, Anslow P, Jayamohan J, Richards PG, Wilkie AO, Wall SA (2008) Implications of a vertex bulge following modified strip craniectomy for sagittal synostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 122(1):217–224
Massimi L, Di Rocco C (2012) Mini-invasive surgical technique for sagittal craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 28(9):1341–1345
Murray DJ, Kelleher MO, McGillivary A, Allcutt D, Earley MJ (2007) A review of 53 cases of sagittal suturectomy in one unit. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60:991–997
Mutchnick IS, Maugans TA (2012) Nonendoscopic, minimally invasive calvarial vault remodeling without postoperative helmeting for sagittal synostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9(3):222–227
Panchal J, Marsh JL, Park TS (1999) Sagittal craniosynostosis outcome assessment for two methods and timings of intervention. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1574–1584
Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Marchac D, Hirsch JF (1982) Intracranial pressure in craniostenosis. J Neurosurg 57:370–377
Renier D, El-Ghouzzi V, Bonaventure J, Le Merrer M, Lajeunie E (2000) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 mutation in nonsyndromic coronal synostosis: clinical spectrum, prevalence, and surgical outcome. J Neurosurg 92(4):631–636
Ridgway EB, Berry-Candelario J, Grondin RT, Rogers GF, Proctor MR (2011) The management of sagittal synostosis using endoscopic suturectomy and postoperative helmet therapy. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7(6):620–626
Rougerie J, Derome J, Anquez L (1972) Craniostenosis and cranio-facial dysmorphism. Principles of a new method of treatment and its results. Neurochirurgie 18(5):429–440
Shipster C, Hearst D, Somerville A, Stackhouse J, Hayward R, Wade A (2003) Speech, language, and cognitive development in children with isolated sagittal synostosis. Dev Med Child Neurol 45(1):34–43
Simmons DR, Peyton WT (1947) Premature closure of cranial sutures. J Pediatr 31:528–547
Sutton LN, Barlett SP, Duhaime AC, Markakis D (1993) Total cranial vault reconstruction for the older child with scaphocephaly. Pediatr Neurosurg 19(2):63–72
Tessier P (1967) Total facial osteotomy. Crouzon’s syndrome, Apert’s syndrome: oxycephaly, scaphocephaly, turricephaly. Ann Chir Plast 12(4):273–286
Thompson DNP, Malcolm GP, Jones BM, Harkness WJ, Hayward RD (1995) Intracranial pressure in single suture craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:235–275
Toma R, Greensmith AL, Meara JG, Da Costa AC, Ellis LA, Willams SK, Holmes AD (2010) AD Quantitative morphometric outcomes following the Melbourne method of total vault remodeling for scaphocephaly. J Craniofac Surg 21(3):637–643
Venes JL, Sayers M (1976) Sagittal synosectomy. Technical note. J Neurosurg 4:390–393
Vinchon M, Pellerin P, Guerreschi P, Baroncini M, Dhellemmes P (2012) Atypical scaphocephaly: a review. Childs Nerv Syst 28(9):1319–1325
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Clinical trial registration
This study was not subject to the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act (WMO) since this study does not involve any form of invasion of the study participant’s integrity.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Veelen, ML.C., Eelkman Rooda, O.H.J., de Jong, T. et al. Results of early surgery for sagittal suture synostosis: long-term follow-up and the occurrence of raised intracranial pressure. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 997–1005 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2024-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2024-9