Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to determine of caudate nucleus changes in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
Methods
A total of 13 children (four males and nine females) with history of Sydenham’s chorea and 13 healthy controls were included in to the study. Diffusion cranial magnetic resonance imaging was performed in all subjects before prednisone treatment. Prednisone (2 mg/kg/day, maximum dose 60 mg/day) was used during 4 weeks and then progressively discontinued (20 % of the initial dose was reduced at each 5 days). Two months later, magnetic resonance imaging was repeated.
Results
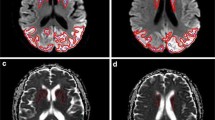
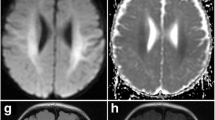
Before and after 8 weeks of prednisone treatment, apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) were calculated for right and left caudate nucleus. The ADC values were significantly different before treatment and 2 months after imaging. For the left caudate nucleus, ADC values before treatment (0.69 ± 0.038) were significantly lower than after treatment (0.95 ± 0.04). For the right caudate nucleus, ADC values before treatment (0.72 ± 0.06 × 10−3) were significantly lower than after treatment (0.93 ± 0.04 × 10−3).
Conclusions
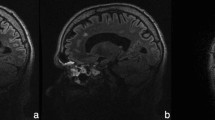
Although cranial and caudate nucleus magnetic resonance imaging findings were normal, the low ADC value findings in our study support the autoimmune inflammation in basal ganglia of Sydenham’s chorea.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Special Writing Group of the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young of the American Heart Association (1992) Guidelines for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever. Jones Criteria, 1992 update. JAMA 268:2069–2073
Bonthius DJ, Karacay B (2003) Sydenham’s chorea: not gone and not forgotten. Semin Pediatr Neurol 10:11–19
Oosterveer DM, Overweg-Plandsoen WC, Roos RA (2010) Sydenham’s chorea: a practical overview of the current literature. Pediatr Neurol 43:1–6
Church AJ, Dale RC, Cardoso F et al (2003) CSF and serum immune parameters in Sydenham’s chorea: evidence of an autoimmune syndrome? J Neuroimmunol 136:149–153
Paz JA, Silva CA, Marques-Dias MJ (2006) Randomized double-blind study with prednisone in Sydenham’s chorea. Pediatr Neurol 34:264–269
Church AJ, Cardoso F, Dale RC, Lees AJ, Thompson EJ, Giovannoni G (2002) Anti-basal ganglia antibodies in acute and persistent Sydenham’s chorea. Neurology 59:227–231
Swedo SE, Leonard HL, Schapiro MB et al (1993) Sydenham’s chorea: physical and psychological symptoms of St Vitus dance. Pediatrics 91:706–713
Giedd JN, Rapoport JL, Kruesi MJ et al (1995) Sydenham’s chorea: magnetic resonance imaging of the basal ganglia. Neurology 45:2199–2202
Giedd JN, Rapoport JL, Leonard HL, Richter D, Swedo SE (1996) Case study: acute basal ganglia enlargement and obsessive–compulsive symptoms in an adolescent boy. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 35:913–915
Swedo SE, Leonard HL, Kiessling LS (1994) Speculations on antineuronal antibody-mediated neuropsychiatric disorders of childhood. Pediatrics 93:323–326
Ikuta N, Hirata M, Sasabe F, Negoro K, Morimatsu M (1998) High-signal basal ganglia on T1-weighted images in a patient with Sydenham’s chorea. Neuroradiology 40:659–661
Castillo M, Kwock L, Arbelaez A (1999) Sydenham’s chorea: MRI and proton spectroscopy. Neuroradiology 41:943–945
Ziegler LH (1927) The neuropathological findings in a case of acute Sydenham’s chorea. J Nerv Ment Dis 65:273–281
Dale RC, Heyman I, Surtees RAH, Church AJ, Giovannoni G, Goodman R et al (2004) Dyskinesias and associated psychiatric disorders following streptococcal infections. Arch Dis Child 89:604–610
Garćia Gonzálezs L, Mayol Canals MM, Villalobos Arévalo P, Vázquez Ruis M, Cabacas Garcia A (2007) Sydenham’s chorea: report of a case treated with carbamazepine with excellent clinical response. An Pediatr 66:80–83
Cardoso F, Maia D, Cunningham MC, Valenca G (2003) Treatment of Sydenham’s chorea with corticosteroids. Mov Disord 18:1374–1377
Singer HS, Loiselle C (2003) PANDAS: a commentary. J Psychosom Res 55:31–39
Genel F, Arslanoglu S, Uran N, Saylan B (2002) Sydenham’s chorea: clinical findings and comparison of the efficacies of sodium valproate and carbamazepine regimens. Brain Dev 24:73–76
Asbahr FR, Garvey MA, Snider LA, Zanetta DM, Elkis H, Swedo SE (2005) Obsessive–compulsive symptoms among patients with Sydenham chorea. Biol Psychiatry 57:1073–1076
Griffıths SP, Gersony WM (1990) Acute rheumatic fever in New York City (1969 to 1988): a comparative study of two decades. J Pediatr 116:882–887
McNeil SA, Halperin SA, Langley JM et al (2005) Safety and immunogenicity of 26-valent group a streptococcus vaccine in healthy adult volunteers. Clin Infect Dis 41:1114–1122
Ozer S, Hallioglu O, Ozkutlu S et al (2005) Childhood acute rheumatic fever in Ankara. Turk J Pediatr 47:120–124
Cardoso F, Vargas AP, Oliveira DL, Guerra AA, Amaral SV (1999) Persistent Sydenham’s chorea. Mov Disord 14:805–807
Aron AM, Freeman JM, Carter S (1965) The natural history of Sydenham’s chorea: review of the literature and long-term evaluation with emphasis on cardiac sequelae. Am J Med 38:83–95
Barash J, Margalith D, Matitiau A (2005) Corticosteroid treatment in patients with Sydenham’s chorea. Pediatr Neurol 32:205–207
Garvey MA, Snider LA, Leitman SF, Werden R, Swedo SE (2005) Treatment of Sydenham’s chorea with intravenous immunoglobulin, plasma exchange, or prednisone. J Child Neurol 20:424–429
Traill Z, Pike M, Byrne J (1995) Sydenham’s chorea: a case showing striatal abnormalities on CT an MRI. Dev Med Child Neurol 37:270–273
Emery ES, Vieco PT (1997) Sydenham chorea: magnetic resonance imaging reveals permanent basal ganglia injury. Neurology 48:531–533
Zomorrodi A, Wald ER (2006) Sydenham’s chorea in western Pennsylvania. Pediatrics 117:675–679
Alkan A, Kutlu R, Kocak G et al (2004) Brain MR spectroscopy in children with a history of rheumatic fever with a special emphasis on neuropsychiatric complication. Eur J Radiol 49:224–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumus, H., Gumus, G., Per, H. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in Sydenham’s chorea. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 125–130 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1898-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1898-2