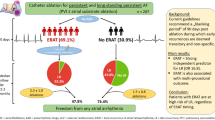
Abstract
Catheter ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE), also known as defragmentation ablation, may be considered for the treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) beyond pulmonary vein isolation (PVI). Concomitant antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) therapy is common, but the relevance of AAD administration and its optimal timing during ablation remain unclear. Therefore, we investigated the use and timing of AADs during defragmentation ablation and their possible implications for AF termination and ablation success in a large cohort of patients. Retrospectively, we included 200 consecutive patients (age: 61 ± 12 years, LA diameter: 47 ± 8 mm) with persistent AF (episode duration 47 ± 72 weeks) who underwent de novo ablation including CFAE ablation. In all patients, PVI was performed prior to CFAE ablation. The use and timing of AADs were registered. The follow-ups consisted of Holter ECGs and clinical visits. Termination of AF was achieved in 132 patients (66 %). Intraprocedural AADs were administered in 168/200 patients (84 %) 45 ± 27 min after completion of PVI. Amiodarone was used in the majority of the patients (160/168). The timing of AAD administration was predicted by the atrial fibrillation cycle length (AFCL). At follow-up, 88 patients (46 %) were free from atrial arrhythmia. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that administration of AAD early after PVI, LA size, duration of AF history, sex and AFCL were predictors of AF termination. The administration of AAD and its timing were not predictive of outcome, and age was the sole independent predictor of AF recurrence. The administration of AAD during ablation was common in this large cohort of persistent AF patients. The choice to administer AAD therapy and the timing of the administration during ablation were influenced by AFCL, and these factors did not significantly influence the moderate single procedure success rate in this retrospective analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AADs:
-
Antiarrhythmic drugs
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- AFCL:
-
Atrial fibrillation cycle length
- CA:
-
Catheter ablation
- CFAE:
-
Complex fractionated atrial electrograms
- PVI:
-
Pulmonary vein isolation
- SR:
-
Sinus rhythm
References
Brooks AG, Stiles MK, Laborderie J, Lau DH, Kuklik P, Shipp NJ, Hsu LF, Sanders P (2010) Outcomes of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review. Heart Rhythm 7:835–846
Hayward RM, Upadhyay GA, Mela T, Ellinor PT, Barrett CD, Heist EK, Verma A, Choudhry NK, Singh JP (2011) Pulmonary vein isolation with complex fractionated atrial electrogram ablation for paroxysmal and nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm 8:994–1000
January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Cleveland JC, Cigarroa JE, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD, Field ME, Murray KT, Sacco RL, Stevenson WG, Tchou PJ, Tracy CM, Yancy CW (2014) 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on practice guidelines and the heart rhythm society. Circulation 130:2071–2104
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ, Davies DW, DiMarco J, Edgerton J, Ellenbogen K, Ezekowitz MD, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jalife J, Jais P, Kalman J, Keane D, Kim YH, Kirchhof P, Klein G, Kottkamp H, Kumagai K, Lindsay BD, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Reddy V, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ, Tsao HM, Wilber D, Heart Rhythm Society Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation (2012) 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: a report of the heart rhythm society (HRS) task force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the european heart rhythm association (EHRA), a registered branch of the european society of cardiology (ESC) and the european cardiac arrhythmia society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the american college of cardiology (ACC), american heart association (AHA), the asia pacific heart rhythm society (APHRS), and the society of thoracic surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American college of cardiology foundation, the American heart association, the European cardiac arrhythmia society, the European heart rhythm association, the society of thoracic surgeons, the Asia pacific heart rhythm society, and the heart rhythm society. Heart Rhythm 9:632–696.e21
Schreiber D, Rostock T, Fröhlich M, Sultan A, Servatius H, Hoffmann BA, Lüker J, Berner I, Schäffer B, Wegscheider K, Lezius S, Willems S, Steven D (2015) Five-year follow up after catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation using the “stepwise approach” and prognostic factors for success. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:308–317
Scherr D, Khairy P, Miyazaki S, Aurillac-Lavignolle V, Pascale P, Wilton SB, Ramoul K, Komatsu Y, Roten L, Jadidi A, Linton N, Pedersen M, Daly M, O’Neill M, Knecht S, Weerasooriya R, Rostock T, Manninger M, Cochet H, Shah AJ, Yeim S, Denis A, Derval N, Hocini M, Sacher F, Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P (2014) Five-year outcome of catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation using termination of atrial fibrillation as a procedural endpoint. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:18–24
Verma A, Jiang CY, Betts TR, Chen J, Deisenhofer I, Mantovan R, Macle L, Morillo CA, Haverkamp W, Weerasooriya R, Albenque JP, Nardi S, Menardi E, Novak P, Sanders P, Investigators STARAFII (2015) Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 372:1812–1822
Verma A, Mantovan R, Macle L, De Martino G, Chen J, Morillo CA, Novak P, Calzolari V, Guerra PG, Nair G, Torrecilla EG, Khaykin Y (2010) Substrate and trigger ablation for reduction of atrial fibrillation (STAR AF): a randomized, multicentre, international trial. Eur Heart J 31:1344–1356
Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, Schwab M, Sunsaneewitayakul B, Vasavakul T, Khunnawat C, Ngarmukos T (2004) A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:2044–2053
Haissaguerre M, Sanders P, Hocini M, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Sacher F, Rostock T, Hsu LF, Bordachar P, Reuter S, Roudaut R, Clémenty J, Jaïs P (2005) Catheter ablation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: critical structures for termination. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 16:1125–1137
Rostock T, Salukhe TV, Steven D, Drewitz I, Hoffmann BA, Bock K, Servatius H, Müllerleile K, Sultan A, Gosau N, Meinertz T, Wegscheider K, Willems S (2011) Long-term single- and multiple-procedure outcome and predictors of success after catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 8:1391–1397
Tilz RR, Rillig A, Thum AM, Arya A, Wohlmuth P, Metzner A, Mathew S, Yoshiga Y, Wissner E, Kuck KH, Ouyang F (2012) Catheter ablation of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: 5-year outcomes of the hamburg sequential ablation strategy. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:1921–1929
Fiala M, Bulková V, Škňouřil L, Nevřalová R, Toman O, Januška J, Špinar J, Wichterle D (2015) Sinus rhythm restoration and arrhythmia noninducibility are major predictors of arrhythmia-free outcome after ablation for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: a prospective study. Heart Rhythm 12:687–698
Nademanee K, Lockwood E, Oketani N, Gidney B (2010) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation guided by complex fractionated atrial electrogram mapping of atrial fibrillation substrate. J Cardiol 55:1–12
Miwa Y, Minamiguchi H, Bhandari AK, Cannom DS, Ho IC (2014) Amiodarone reduces the amount of ablation during catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. Europace 16:1007–1014
Mohanty S, Di Biase L, Mohanty P, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Bai R, Burkhardt JD, Gallinghouse JG, Horton R, Sanchez JE, Hranitzky PM, Zagrodzky J, Al-Ahmad A, Pelargonio G, Lakkireddy D, Reddy M, Forleo G, Rossillo A, Themistoklakis S, Hongo R, Beheiry S, Casella M, Dello Russo A, Tondo C, Natale A (2014) Effect of periprocedural amiodarone on procedure outcome in longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation undergoing extended pulmonary vein antrum isolation: results from a randomized study (SPECULATE). Heart Rhythm 12:477–483
Oral H, Chugh A, Ozaydin M, Good E, Fortino J, Sankaran S, Reich S, Igic P, Elmouchi D, Tschopp D, Wimmer A, Dey S, Crawford T, Pelosi F, Jongnarangsin K, Bogun F, Morady F (2006) Risk of thromboembolic events after percutaneous left atrial radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 114:759–765
Ammar S, Hessling G, Reents T, Paulik M, Fichtner S, Schön P, Dillier R, Kathan S, Jilek C, Kolb C, Haller B, Deisenhofer I (2013) Importance of sinus rhythm as endpoint of persistent atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 24:388–395
Scherr D, Khairy P, Miyazaki S, Aurillac-Lavignolle V, Pascale P, Wilton SB, Ramoul K, Komatsu Y, Roten L, Jadidi A, Linton N, Pedersen M, Daly M, O’Neill M, Knecht S, Weerasooriya R, Rostock T, Manninger M, Cochet H, Shah AJ, Yeim S, Denis A, Derval N, Hocini M, Sacher F, Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P (2014) Five-Year outcome of catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation using termination of atrial fibrillation as a procedural endpoint. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 8:18–24
Pecha S, Aydin MA, Ahmadzade T, Hartel F, Hoffmann B, Steven D, Willems S, Reichenspurner H, Wagner FM (2015) Implantable loop recorder monitoring after concomitant surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF): insights from more than 200 continuously monitored patients. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-015-0735-4
Goy JJ, Kaufmann U, Kappenberger L, Sigwart U (1988) Restoration of sinus rhythm with flecainide in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 62(6):38D–40D
Wang Z, Feng J, Nattel S (1995) Idiopathic atrial fibrillation in dogs: electrophysiologic determinants and mechanisms of antiarrhythmic action of flecainide. J Am Coll Cardiol 26:277–286
Shinagawa K, Shiroshita-Takeshita A, Schram G, Nattel S (2003) Effects of antiarrhythmic drugs on fibrillation in the remodeled atrium: insights into the mechanism of the superior efficacy of amiodarone. Circulation 107:1440–1446
Donovan KD, Power BM, Hockings BE, Dobb GJ, Lee KY (1995) Intravenous flecainide versus amiodarone for recent-onset atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 75:693–697
Hoshiyama T, Yamabe H, Koyama J, Kanazawa H, Ogawa H (2015) Left atrial electrophysiologic feature specific for the genesis of complex fractionated atrial electrogram during atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-015-0672-2
Singh SM, Davila A, Kim SJ, Houghtaling C, Dukkipati SR, Reddy VY (2010) Intraprocedural use of ibutilide to organize and guide ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms: preliminary assessment of a modified step-wise approach to ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 21:608–616
Shan Z, Van Der Voort PH, Blaauw Y, Duytschaever M, Allessie MA (2004) Fractionation of electrograms and linking of activation during pharmacologic cardioversion of persistent atrial fibrillation in the goat. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15:572–580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lüker, J., Sultan, A., Sehner, S. et al. Use of antiarrhythmic drugs during ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: observations from a large single-centre cohort. Heart Vessels 31, 1669–1675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0771-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0771-0