Abstract
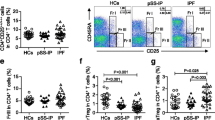
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been reported to play a pivotal role in the vascular remodeling of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Recent studies have revealed that Tregs are heterogeneous and can be characterized by three phenotypically and functionally different subsets. In this study, we investigated the roles of Treg subsets in the pathogenesis of PAH in eight patients with PAH and 14 healthy controls. Tregs and their subsets in peripheral blood samples were analyzed by flow cytometry. Treg subsets were defined as CD4+CD45RA+FoxP3low resting Tregs (rTregs), CD4+CD45RA−FoxP3high activated Tregs (aTregs), and CD4+CD45RA−FoxP3low non-suppressive Tregs (non-Tregs). The proportion of Tregs among CD4+ T cells was significantly higher in PAH patients than in controls (6.54 ± 1.10 vs. 3.81 ± 0.28 %, p < 0.05). Of the three subsets, the proportion of non-Tregs was significantly elevated in PAH patients compared with controls (4.06 ± 0.40 vs. 2.79 ± 0.14 %, p < 0.01), whereas those of rTregs and aTregs were not different between the two groups. Moreover, the expression levels of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, a functional cell surface molecule, in aTregs (p < 0.05) and non-Tregs (p < 0.05) were significantly higher in PAH patients compared with controls. These results suggested the non-Treg subset was expanded and functionally activated in peripheral lymphocytes obtained from IPAH patients. We hypothesize that immunoreactions involving the specific activation of the non-Treg subset might play a role in the vascular remodeling of PAH.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicolls MR, Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Rai PR, Badesch DB, Voelkel NF (2005) Autoimmunity and pulmonary hypertension: a perspective. Eur Respir J 26:1110–1118
Sanchez O, Marcos E, Perros F, Fadel E, Tu L, Humbert M, Dartevelle P, Simonneau G, Adnot S, Eddahibi S (2007) Role of endothelium-derived CC chemokine ligand 2 in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:1041–1047
Hall S, Brogan P, Haworth SG, Klein N (2009) Contribution of inflammation to the pathology of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension in children. Thorax 64:778–783
Soon E, Holmes AM, Treacy CM, Doughty NJ, Southgate L, Machado RD, Trembath RC, Jennings S, Barker L, Nicklin P, Walker C, Budd DC, Pepke-Zaba J, Morrell NW (2010) Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines predict survival in idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 122:920–927
Sugiura T, Yamanaka S, Takeuchi H, Morimoto N, Kamioka M, Matsumura Y (2014) Autoimmunity and pulmonary hypertension in patients with Graves’ disease. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-014-0518-3
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M (2008) Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 133:775–787
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA (2010) FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10:490–500
Tamosiuniene R, Tian W, Dhillon G, Wang L, Sung YK, Gera L, Patterson AJ, Agrawal R, Rabinovitch M, Ambler K, Long CS, Voelkel NF, Nicolls MR (2011) Regulatory T cells limit vascular endothelial injury and prevent pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 109:867–879
Ulrich S, Nicolls MR, Taraseviciene L, Speich R, Voelkel N (2008) Increased regulatory and decreased CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in the blood of patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respiration 75:272–280
Austin ED, Rock MT, Mosse CA, Vnencak-Jones CL, Yoder SM, Robbins IM, Loyd JE, Meyrick BO (2010) T lymphocyte subset abnormalities in the blood and lung in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir Med 104:454–462
Huertas A, Tu L, Gambaryan N, Girerd B, Perros F, Montani D, Fabre D, Fadel E, Eddahibi S, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Guignabert C, Humbert M (2012) Leptin and regulatory T-lymphocytes in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 40:895–904
Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A, Shima T, Wing K, Niwa A, Parizot C, Taflin C, Heike T, Valeyre D, Mathian A, Nakahata T, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M, Amoura Z, Gorochov G, Sakaguchi S (2009) Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 30:899–911
Buckner JH (2010) Mechanisms of impaired regulation by CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 10:849–859
Yoshioka N, Suto A, Abe R, Saito N, Murata J, Hayashi-Ujiie I, Hoshina D, Fujita Y, Shimizu H (2013) Disturbed balance in three subpopulations of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis patients. Clin Immunol 148:89–91
Takahashi T, Tagami T, Yamazaki S, Uede T, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi N, Mak TW, Sakaguchi S (2000) Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells constitutively expressing cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Exp Med 192:303–310
Tran DQ (2013) In vitro suppression assay for functional assessment of human regulatory T cells. Methods Mol Biol 979:199–212
Machado RD, Eickelberg O, Elliott CG, Geraci MW, Hanaoka M, Loyd JE, Newman JH, Phillips JA 3rd, Soubrier F, Trembath RC, Chung WK (2009) Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:S32–S42
Morrell NW (2006) Pulmonary hypertension due to BMPR2 mutation: a new paradigm for tissue remodeling? Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:680–686
Girerd B, Montani D, Coulet F, Sztrymf B, Yaici A, Jais X, Tregouet D, Reis A, Drouin-Garraud V, Fraisse A, Sitbon O, O’Callaghan DS, Simonneau G, Soubrier F, Humbert M (2010) Clinical outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients carrying an ACVRL1 (ALK1) mutation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181:851–861
Bertolino P, Deckers M, Lebrin F, ten Dijke P (2005) Transforming growth factor-beta signal transduction in angiogenesis and vascular disorders. Chest 128:585S–590S
Zhang YE (2009) Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res 19:128–139
Long L, Crosby A, Yang X, Southwood M, Upton PD, Kim DK, Morrell NW (2009) Altered bone morphogenetic protein and transforming growth factor-beta signaling in rat models of pulmonary hypertension: potential for activin receptor-like kinase-5 inhibition in prevention and progression of disease. Circulation 119:566–576
Pardali E, Ten Dijke P (2012) TGFbeta signaling and cardiovascular diseases. Int J Biol Sci 8:195–213
Morrell NW, Yang X, Upton PD, Jourdan KB, Morgan N, Sheares KK, Trembath RC (2001) Altered growth responses of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from patients with primary pulmonary hypertension to transforming growth factor-beta(1) and bone morphogenetic proteins. Circulation 104:790–795
Atkinson C, Stewart S, Upton PD, Machado R, Thomson JR, Trembath RC, Morrell NW (2002) Primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with reduced pulmonary vascular expression of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor. Circulation 105:1672–1678
Takahashi H, Goto N, Kojima Y, Tsuda Y, Morio Y, Muramatsu M, Fukuchi Y (2006) Downregulation of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290:L450–L458
Morty RE, Nejman B, Kwapiszewska G, Hecker M, Zakrzewicz A, Kouri FM, Peters DM, Dumitrascu R, Seeger W, Knaus P, Schermuly RT, Eickelberg O (2007) Dysregulated bone morphogenetic protein signaling in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1072–1078
Davies RJ, Holmes AM, Deighton J, Long L, Yang X, Barker L, Walker C, Budd DC, Upton PD, Morrell NW (2012) BMP type II receptor deficiency confers resistance to growth inhibition by TGF-beta in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: role of proinflammatory cytokines. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 302:L604–L615
Guo Y, Su L, Li Y, Guo N, Xie L, Zhang D, Zhang X, Li H, Zhang G, Wang Y, Liu C (2014) The synergistic therapeutic effect of hepatocyte growth factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on pulmonary hypertension in rats. Heart Vessels 29:520–531
Ouyang W, Beckett O, Ma Q, Li MO (2010) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling curbs thymic negative selection promoting regulatory T cell development. Immunity 32:642–653
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Analysis Center of Life Science, Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sada, Y., Dohi, Y., Uga, S. et al. Non-suppressive regulatory T cell subset expansion in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Vessels 31, 1319–1326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0727-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-015-0727-4