Abstract
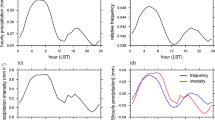
This study analyzed the interdecadal changes in the diurnal variability of summer (June–August) precipitation over eastern China during the period 1966–2005 using hourly station rain gauge data. The results revealed that rainfall diurnal variations experienced significant interdecadal changes. Over the area to the south of the Yangtze River, as well as the area between the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, the percentages of morning rainfall (0000–1200 LST) to total rainfall in terms of amount, frequency and intensity, all exhibited increasing interdecadal trends. On the contrary, over North China, decreasing trends were found. As a result, diurnal rainfall peaks also presented pronounced interdecadal variations. Over the area between the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, there were 16 out of 46 stations with afternoon (1200–0000 LST) frequency peaks in the first 20 years of the 40-year period of study, while only eight remained in the latter 20 years. In North China, seven stations experienced the opposite changes, which accounted for about 21% of the total number of stations. The possible causes for the interdecadal changes in diurnal features were discussed. As the rainfall in the active monsoon period presents morning diurnal peaks, with afternoon peaks in the break period, the decrease (increase) of rainfall in the active monsoon period over North China (the area south of the Yangtze River and the area between the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers) may contribute to interdecadal changes in diurnal rainfall variability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, G. X., W. M. Sha, and T. Iwasaki, 2009: Diurnal variation of precipitation over southeastern China: 2. Impact of the diurnal monsoon variability. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D13103, doi: 10.1029/2008JD011103.
Chen, H., R. Yu, J. Li, W. Yuan, and T. Zhou, 2010: Why nocturnal long-duration rainfall presents an eastward-delayed diurnal phase of rainfall down the Yangtze River valley. J. Climate, 23, 905–917.
Geng, B., and H. Yamada, 2007: Diurnal variations of the Meiyu/Baiu rain belt. SOLA, 3, 61–64.
Hu, Z. Z., 1997: Interdecadal variability of summer climate over East Asia and its association with 500 hPa height and global sea surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 19403–19412.
Li, J., R. Yu, W. Yuan, and H. Chen, 2011: Changes in duration-related characteristics of late-summer precipitation over eastern China in the past 40 years. J. Climate, 24, 5683–5690.
Luo, J., Z. Wang, and J. Zhou, 2003: Geographic causes of the daily variation of rain storm in the Mei-Yu frontal jet. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 26, 371–377. (in Chinese)
Menon, S., J. Hansen, L. Nazarenko, and Y. F. Luo, 2002: Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 297, 2250–2253.
Sorooshian, S., X. Gao, K. Hsu, R. A. Maddox, Y. Hong, H. V. Gupta, and B. Imam, 2002: Diurnal variability of tropical rainfall retrieved from combined GOES and TRMM satellite information. J. Climate, 15, 983–1001.
Wu, R. G., and L. T. Chen, 1998: Decadal variation of summer rainfall in the Yangtze-Huaihe River valley and its relationship to atmospheric circulation anomalies over East Asia and western North Pacific. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 4, 510–522.
Yin, S. Q., D. L. Chen, and Y. Xie, 2009: Diurnal variations of precipitation during the warm season over China. Int. J. Climatol., 29, 1154–1170.
Yu, R., B. Wang, and T. Zhou, 2004: Tropospheric cooling and summer monsoon weakening trend over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, doi: 10.1029/2004GL021270.
Yu, R., T. Zhou, A. Xiong, Y. Zhu, and J. Li, 2007a: Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L01704. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028129.
Yu, R., Y. Xu, T. Zhou, and J. Li, 2007b: Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L13703, doi: 10.1029/2007GL030315.
Yu, R., J. Li, W. Yuan, and H. Chen, 2010: Changes in characteristics of late-summer precipitation over eastern China in the past 40 years revealed by hourly precipitation data. J. Climate, 23, 3390–3396.
Yuan, W., R. Yu, H. Chen, J. Li, and M. Zhang, 2010: Subseasonal characteristics of diurnal variation in summer monsoon rainfall over central eastern China. J. Climate, 23, 6684–6695.
Zhai, P., X. Zhang, H. Wan, and X. Pan, 2005: Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J. Climate, 18, 1096–1108.
Zhou, L. T., 2009: Difference in the interdecadal variability of spring and summer sensible heat fluxes over Northwest China. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 2, 119–123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Yu, R. & Li, J. Changes in the diurnal cycles of precipitation over eastern China in the past 40 years. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 30, 461–467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2092-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-2092-x