Abstract
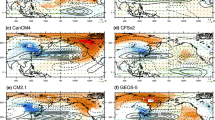
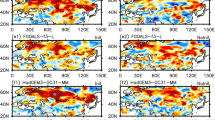
The interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) circulation from the Development of a European Multi-Model Ensemble (MME) System for Seasonal to Inter-Annual Prediction (DEMETER) hindcasts was evaluated against observation reanalysis data. We evaluated the DEMETER coupled general circulation models (CGCMs)’ retrospective prediction of the typical EAWM and its associated atmospheric circulation. Results show that the EAWM can be reasonably predicted with statistically significant accuracy, yet the major bias of the hindcast models is the underestimation of the related anomalies. The temporal correlation coefficient (TCC) of the MME-produced EAWM index, defined as the first EOF mode of 850-hPa air temperature within the EAWM domain (20°–60°N, 90°–150°E), was 0.595. This coefficient was higher than those of the corresponding individual models (range: 0.39–0.51) for the period 1969–2001; this result indicates the advantage of the super-ensemble approach. This study also showed that the ensemble models can reasonably reproduce the major modes and their interannual variabilities for sea level pressure, geopotential height, surface air temperature, and wind fields in Eurasia. Therefore, the prediction of EAWM interannual variability is feasible using multimodel ensemble systems and that they may also reveal the associated mechanisms of the EAWM interannual variability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, W., S. Yang, and R. H. Huang, 2005: Relationship between stationary planetary wave activity and the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D14110.
Cui, X. P., and Z. B. Sun, 1999: East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation analysis. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 22, 321–325. (in Chinese)
Déqué, M., 2001: Seasonal predictability of tropical rainfall: Probabilistic formulation and validation. Tellus, 53A, 500–512.
Fan, K., 2009: Predicting winter surface air temperature in Northeast China. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 2, 14–17.
Gong, D. Y., S. W. Wang, and J. H. Zhu, 2001: East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 2073–2076.
Gregory, D., J. J. Morcrette, C. Jakob, A. C. M. Beljaars, and T. Stockdale, 2000: Revision of convection, radiation and cloud schemes in the ECMWF Integrated Forecasting System. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 126, 1685–1710.
Guo, Q. Y., 1994: Relationship between the variations of East Asian winter monsoon and temperature anomalies in China. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorological, 5, 218–225. (in Chinese)
Han, Z., S. L. Li, and M. Mu, 2011: The role of warm North Atlantic SST in the formation of positive height anomalies over the Ural Mountains during January 2008. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 28, 246–256, doi: 10.1007/s00376-010-0069-1.
Jhun, J. G., and E. J. Lee, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J. Climate, 17, 711–726.
Ji, L. R., S. Q. Sun, K. Arpe, and L. Bengtsson, 1997: Model study on the interannual variability of Asian winter monsoon and its influence. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 1–22.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Lau, N. C., and M. J. Nath, 2000: Impact of ENSO on the variability of the Asian-Australian monsoons as simulated in GCM experiments. J. Climate, 13, 4287–4309.
Madec, G., P. Delecluse, M. Imbard, and C. Levy, 1997: OPA release 8, ocean general circulation model reference manual. LODYC Internal Rep., Paris, France, 200pp. [Available from LODYC/IPSL, 4 Place Jussieu 75252 Paris Cedex 05, France.]
Marsland, S. J., H. Haak, J. H. Jungclaus, M. Latif, and F. Röske, 2003: The Max-Planck-Institute global ocean/sea ice model with orthogonal curvilinear coordinates. Ocean Modelling, 5, 91–127.
Palmer, T. N., and Coauthors, 2004: Development of a European multimodel ensemble system for seasonalto-interannual prediction (DEMETER). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 85, 853–872.
Qian, Z. L., H. J. Wang, and J. Q. Sun, 2011: The hindcast of winter and spring Arctic and Antarctic Oscillation with the coupled climate models. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 25, 340–354.
Roeckner, E., 1996: The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM-4: Model description and simulation of present-day climate. Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie Tech. Rep. 218, Hamburg, Germany, 90pp. [Available from Max-Planck Institut für Meteorologie, Bundesstr. 55, D-20146 Hamburg, Germany.]
Shi, N., and Y. S. Yang, 1998: Main characteristics of East Asian summer/winter monsoon index for 1873-1996. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 21, 208–214. (in Chinese)
Sun, J. Q., H. J. Wang, W. Yuan, and H. P. Chen, 2010: Spatial-temporal features of intense snowfall events in China and their possible change. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D16110.
Takaya, K., and H. Nakamura, 2005a: Mechanisms of intraseasonal amplification of the cold Siberian high. J. Atmos. Sci., 62, 4423–4440.
Takaya, K., and H. Nakamura, 2005b: Geographical dependence of upper-level blocking formation associated with intraseasonal amplification of the Siberian high. J. Atmos. Sci., 62, 4441–4449.
Uppala, S. M., and Coauthors, 2005: The ERA-40 Re-Analysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 2961–3012.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and X. H. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Wang, B., and Coauthors, 2009a: Advance and prospectus of seasonal prediction: Assessment of the APCC/CliPAS 14-model ensemble retrospective seasonal prediction (1980–2004). Climate Dyn., 33, 93–117.
Wang, B., Z. W. Wu, C. P. Chang, J. Liu, J. P. Li, and T. J. Zhou, 2010: Another look at interannualto-interdecadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon: The northern and southern temperature modes. J. Climate, 23, 1495–1512.
Wang, H. J., 2001: The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 376–386.
Wang, H. J., and D. B. Jiang, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon intensity index and atmospheric circulation comparison between strong and weak composite. Quaternary Sciences, 24, 19–27. (in Chinese)
Wang, H. J., and J. Q. Sun, 2009: Variability of Northeast China river break-up date. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26, 701–706, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9035-1.
Wang, H. J., E. T. Yu, and S. Yang, 2011: An exceptionally heavy snowfall in Northeast China: Large-scale circulation anomalies and hindcast of the NCAR WRF model. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 113, 11–25.
Wang, L., and W. Chen, 2010: How well do existing indices measure the strength of the East Asian winter monsoon? Adv. Atmos. Sci., 27, 855–870, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9094-3.
Wang, L., W. Chen, and R. H. Huang, 2008: Interdecadal modulation of PDO on the impact of ENSO on the east Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L20702.
Wang, L., W. Chen, W. Zhou, and R. H. Huang, 2009b: Interannual variations of East Asian trough axis at 500 hPa and its association with the East Asian winter monsoon pathway. J. Climate, 22, 600–614.
Wang, L., R. H. Huang, L. Gu, W. Chen, and L. H. Kang, 2009c: Interdecadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon and their association with quasi-stationary planetary wave activity. J. Climate, 22, 4860–4872.
Webster, P. J., and S. Yang, 1992: Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 118, 877–926.
Wolff, J. E., E. Maier-Reimer, and S. Legutke, 1997: The Hamburg Ocean primitive equation model. Deutsches Klimarechenzentrum Tech. Rep. 13, Hamburg, Germany, 13pp. [Available from Model and Data Group c/o Max-Planck Institut für Meteorologie, Bundesstr. 55, D-20146 Hamburg, Germany.]
Wu, R., J. L. Kinter III, and B. P. Kirtman, 2005: Discrepancy of interdecadal changes in the Asian region between the NCEP-NCAR reanalysis and observations. J. Climate, 18, 3048–3067.
Yan, H. M., W. Zhou, H. Yang, and Y. Cai, 2009: Definition of a East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation characteristics. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 32, 367–376. (in Chinese)
Zhang, C. J., and H. Q. Zhang, 2010: Potential impacts of East Asian winter monsoon on climate variability and predictability in the Australian summer monsoon region. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 101, 161–177.
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the’ 86/87 and’ 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhang, Y., K. R. Sperber, and J. S. Boyle, 1997: Climatology and interannual variation of the East Asian winter monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 2605–2619.
Zhou, W., J. C. L. Chan, W. Chen, J. Ling, J. G. Pinto, and Y. P. Shao, 2009: Synoptic-scale controls of persistent low temperature and icy weather over southern China in January 2008. Mon. Wea. Rev., 137, 3978–3991.
Zhu, C.W., W. S. Lee, H.W. Kang, and C. K. Park, 2005: A proper monsoon index for seasonal and interannual variations of the East Asian monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L02811.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Wang, H. Predictability of the East Asian winter monsoon interannual variability as indicated by the DEMETER CGCMS. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 29, 441–454 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-1115-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-1115-3