Abstract
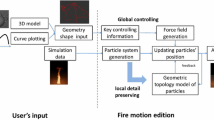
We propose a framework for generating, animating, and controlling fire-flakes to correspond with the movements of flame. Not only do fire-flakes themselves display a distinctively complex and elaborate movement, but also they are heavily influenced by where the heat transforms into flame and how the flame moves. It is difficult for designers to generate and simulate synchronous movement of fire-flakes and flame because the movement of flame tends to be chaotic and constantly changing. We provide a novel framework that can improve on the current processes both effectively and efficiently. We first propose a fire-flake motion model that simulates movement harmoniously with the movement of flame. We then introduce automatic generation of fire-flakes by analyzing temperature fields and the velocity fields input from the fire simulation. Lastly, our sample-based control method enables the formation of a target shape by gathering fire-flakes together into one location while maintaining their inherent movement without external forces. We also provide various parameters that the designer can use to control the effects of the forces determining the amount, velocity, and movement of fire-flakes. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first visual simulation method to generate fire-flakes in coordination with flame, and we believe it will contribute not only to research, but also to the animation industry.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaudoin, P., Paquet, S., Poulin, P.: Realistic and controllable fire simulation. Graph. Interface 2001, 159–166 (2001)
Bridson, R., Houriham, J., Nordenstam, M.: Curl-noise for procedural fluid flow. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers, SIGGRAPH ’07. ACM, New York (2007). doi:10.1145/1275808.1276435
Feldman, B.E., O’brien, J.F., Arikan, O.: Animating suspended particle explosions. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 22, 708–715 (2003)
Hong, J.M., Lee, H.Y., Yoon, J.C., Kim, C.H.: Bubbles alive. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Papers, SIGGRAPH ’08, pp. 48:1–48:4. ACM, New York (2008). doi:10.1145/1399504.1360647
Hong, J.M., Shinar, T., Fedkiw, R.: Wrinkled flames and cellular patterns. ACM Trans. Graph. (2007). doi:10.1145/1276377.1276436
Horvath, C., Geiger, W.: Directable, high-resolution simulation of fire on the GPU. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(3), 41:1–41:8 (2009). doi:10.1145/1531326.1531347
Kawada, G., Kanai, T.: Procedural fluid modeling of explosion phenomena based on physical properties. In: Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA ’11, pp. 167–176. ACM, New York (2011). doi:10.1145/2019406.2019429
Kim, P.R., Lee, H.Y., Kim, J.H., Kim, C.H.: Controlling shapes of air bubbles in a multi-phase fluid simulation. Vis. Comput. 28(6), 597–602 (2012). doi:10.1007/s00371-012-0696-x
Kim, T., Lee, J., Kim, C.H.: Physics-inspired controllable flame animation. Vis. Comput. (2016). doi:10.1007/s00371-016-1267-3
Kwatra, N., Grétarsson, J.T., Fedkiw, R.: Practical animation of compressible flow for shock waves and related phenomena. In: Proceedings of the 2010 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, SCA ’10, pp. 207–215. Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville (2010). URL http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1921427.1921458
Lamorlette, A., Foster, N.: Structural modeling of flames for a production environment. ACM Trans. Graph. 21(3), 729–735 (2002). doi:10.1145/566654.566644
Melek, Z., Keyser, J.: Interactive simulation of fire. In: Proceedings of 10th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications 2002. pp. 431–432 (2002). doi:10.1109/PCCGA.2002.1167889
Nguyen, D.Q., Fedkiw, R., Jensen, H.W.: Physically based modeling and animation of fire. ACM Trans. Graph. 21(3), 721–728 (2002). doi:10.1145/566654.566643
Selle, A., Rasmussen, N., Fedkiw, R.: A vortex particle method for smoke, water and explosions. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 910–914 (2005). doi:10.1145/1073204.1073282
Stam, J.: Stable fluids. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’99, pp. 121–128. ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., New York (1999). doi:10.1145/311535.311548
Stam, J., Fiume, E.: Turbulent wind fields for gaseous phenomena. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’93, pp. 369–376. ACM, New York (1993). doi:10.1145/166117.166163
Zhao, H., Fan, R., Wang, C.C., Jin, X., Meng, Y.: Fireworks controller. Comput. Animat. Virtual World 20(2–3), 185–194 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 190973 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T., Hong, E., Im, J. et al. Visual simulation of fire-flakes synchronized with flame. Vis Comput 33, 1029–1038 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1374-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1374-9