Abstract
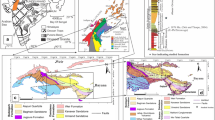
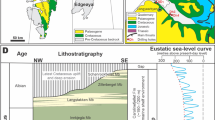
This study analyses a 30-m-thick, sand-dominated succession intercalated between offshore mudstones in the Lower Cretaceous record of the Neuquén Basin, Argentina, defining facies associated with unidirectional currents as sand dunes (simple and compound), rippled sand sheets and heterolithic sheets. These facies associations are related to the development of an offshore, forward-accreting dunefield developed as a response to the onset of a tidal-transport system. The reported stratigraphic record results from the combination of the gradual downcurrent decrease of the current speed together with the long-term climbing of the entire system. Maximum amplification of the tidal effect associated with incoming oceanic tides to this epicontinental sea would develop at the time of more efficient connection between the basin and the open ocean. Thus, the onset of the offshore tidal system approximately corresponds to the time of maximum flooding conditions (or immediately after). The short-term evolution of the tidal-transport system is more complex and characterized by the vertical stacking of small-scale cycles defined by the alternation of episodes of construction and destruction of the dunefield. The development of these cycles could be the response to changes in tidal current speed and transport capacity.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JRL (1980) Sand waves; a model of origin and internal structure. Sed Geol 26:281–328
Anastas A, Dalrymple RW, James NP, Nelson CS (1997) Cross-stratified calcarenites from New Zealand; subaqueous dunes in a cool-water, Oligo-Miocene seaway. Sedimentology 44:869–891
Anastas A, Dalrymple RW, James NP, Nelson CS (2006) Lithofacies and dynamics of a cool-water carbonate seaway; mid-Tertiary, Te Kuiti Group, New Zealand. In: Pedley HM, Carannante G (eds) Cool-water carbonates: depositional systems and palaeoenvironmental controls. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 255:245–268
Anderton R (1976) Tidal-shelf sedimentation: an example from the Scottish Dalradian. Sedimentology 23:429–458
Ashley GM (1990) Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at an old problem: bedforms and bedding structures. J Sed Petrol 60:160–172
Bassetti MA, Jouet G, Dufois F, Berné S, Rabineau M, Taviani M (2006) Sand bodies at the shelf edge in the Gulf of Lions (Western Mediterranean): deglacial history and modern processes. Mar Geol 234:93–109
Belderson RH, Johnson MA, Kenyon NH (1982) Bedforms. In: Stride AH (ed) Offshore tidal sands: processes and deposits. Chapman & Hall, London
Berné S (2003) Offshore sands. In: Middleton GV (ed) Encyclopedia of Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 492–499
Berné S, Auffret JP, Walker P (1988) Internal structure of subtidal sand waves revealed by high-resolution seismic reflection. Sedimentology 35:5–20
Berné S, Vagner P, Guichard F, Lericolais G, Liu Z, Trentesaux A, Yin P, Yi HI (2002) Pleistocene forced regressions and tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea. Mar Geol 188:293–315
Bridges PH (1982) Ancient offshore tidal deposits. In: Stride AH (ed) Offshore tidal sands: processes and deposits. Chapman & Hall, London
Dalrymple RW (1984) The morphology and internal structure of sandwaves in the Bay of Fundy. Sedimentology 31:365–382
Dalrymple RW (1992) Tidal depositional systems. In: Walker HG, James NP (eds) Facies models: response to sea level change, 2nd edn. Geological Association of Canada, St John’s, pp 195–218
Dalrymple RW (2010) Tidal depositional systems. In: James NP, Dalrymple RW (eds) Facies models, vol 4. Geological Association of Canada, St John’s, pp 201–231
Dalrymple RW, Rhodes RN (1995) Estuarine dunes and bars. In: Perillo GME (ed) Geomorphology and sedimentology of estuaries. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Desjardins PR, Buatois LA, Pratt BR, Mángano G (2012) Sedimentological–ichnological model for tide-dominated shelf sandbodies: Lower Cambrian Gog Group of western Canada. Sedimentology 59:1452–1477
Flemming BW (1980) Sand transport and bedform patterns on the continental shelf between Durban and Port Elizabeth (Southeast African continental margin). Sed Geol 26:179–205
Harms JC, Southard JB, Spearing D, Walker R (1975) Depositional environments as interpreted from primary sedimentary structures and stratification sequences. SEPM, Short Course 2
Harris PT, Pattiaratchi CB, Collins MB, Dalrymple RW (1995) What is a bedload parting? In: Flemming BW, Bartholomä A (eds) Tidal signatures in modem and ancient sediments. IAS Spec Publ 24:2–10
Hess H, Ausich WI, Brett CE, Simms MJ (1999) Fossil crinoids. Cambridge University Press, New York
Howell J, Schwarz E, Spalletti L, Veiga G (2005) The Neuquén Basin: an overview. In: Veiga G, Spalletti L, Howell J, Schwarz E (eds) The Neuquén Basin: a case study in sequence stratigraphy and basin dynamics. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 252:1–14
Ikehara K (1993) Modern sedimentation in the shelf to basin areas around southwest Japan, with special reference to the relationship between sedimentation and oceanographic conditions. Bull Geol Surv Japan 44:283–349
Johnson MA, Kenyon NH, Belderson RH, Stride AH (1982) Sand transport. In: Stride AH (ed) Offshore tidal sands, processes and deposits. Chapman & Hall, London
Lazo DG, Concheyro A, Ottone EG, Guler MV, Aguirre-Urreta MB (2009) Bioestratigrafía integrada de la Formación Agrio en su localidad tipo, Cretácico Temprano de la Cuenca Neuquina. Rev Asoc Geol Argentina 65:322–341
Lazo DG, Bressan GS, Schwarz E, Veiga GD (2012) Exceptionally preserved Early Cretaceous stalked crinoids from the Agrio Formation, Neuquén basin, west-central Argentina. In: Res XIII Congr Geológico Chileno, 5–9 August 2012, Antofagasta, Chile, pp 761–763
Legarreta L, Uliana MA (1991) Jurassic-Cretaceous marine oscillations and geometry of backarc basin fill, Central argentine Andes. In: Macdonald DIM (ed) Sedimentation, tectonics and eustasy. Sea level changes at active plate margins. IAS Spec Publ 12:429–450
Levell BK (1980) A Late Precambrian tidal shelf deposit, the lower Sandfjord Formation, Finnmark, North Norway. Sedimentology 27:539–557
Longhitano SG, Mellere D, Steel RJ, Ainsworth RB (2012) Tidal depositional systems in the rock record: a review and new insights. Sed Geol 279:2–22
MacEachern JA, Gingras MK, Bann KL, Pemberton SG, Dafoe LT (2007) Applications of ichnology to high-resolution genetic stratigraphic paradigms. In: McEachern JA, Bann KL, Gingras MK, Pemberton SG (eds) Applied ichnology. SEPM Short Course Notes 52:95–129
McCave IN, Langhorne DN (1982) Sand waves and sediment transport around the end of a tidal sand bank. Sedimentology 29:95–110
Olariu C, Steel RJ, Dalrymple RW, Gingras MK (2012) Tidal dunes versus tidal bars: the sedimentological and architectural characteristics of compound dunes in a tidal seaway, the lower Baronia Sandstone (Lower Eocene), Ager Basin, Spain. Sed Geol 279:134–155
Posamentier HW (2002) Ancient shelf ridges—A potentially significant component of the transgressive systems tract: case study from offshore northwest Java. Bull Am Assoc Petrol Geol 86:75–106
Pugh DT (1987) Tides, surges and mean sea-level; a handbook for engineers and scientists. Wiley, Chichester
Pugh D, Woodworth P (2014) Sea-level science. Understanding tides, surges, tsunamis and mean sea level. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Reynaud J-Y, Dalrymple RW (2012) Shallow-marine tidal deposits. In: Davis RA, Dalrymple RW (eds) Principles of tidal sedimentology. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 335–369
Reynaud J-Y, Ferrandini M, Ferrandini L, Santiago M, Thinon I, André J-P, Barthet Y, Guennoc P, Tessier B (2013) From non-tidal shelf to tide-dominated strait: the Miocene Bonifacio Basin, Southern Corsica. Sedimentology 60:599–623
Schwarz E (2012) Sharp-based marine sandstone bodies in the Mulichinco Formation (Lower Cretaceous), Neuquén Basin, Argentina: remnants of transgressive offshore sand ridges. Sedimentology 59:1478–1508
Schwarz E, Buatois LA (2012) Substrate-controlled ichnofacies along a marine sequence boundary: the Intra-Valanginian Discontinuity in central Neuquén Basin (Argentina). Sed Geol 277–278:72–87
Schwarz E, Spalletti LA, Howell JA (2006) Sedimentary response to a tectonically-induced sea-level fall in a shallow back-arc basin: the Mulichinco Formation (Lower Cretaceous), Neuquén Basin, Argentina. Sedimentology 53:55–81
Schwarz E, Spalletti LA, Veiga GD (2011) La Formación Mulichinco (Cretácico Temprano) en la Cuenca Neuquina. In: Leanza HA, Arregui C, Carbone O, Danielli JC, Vallés JM (eds) Geología y recursos naturales del Neuquén. Rel XVIII Congr Geológico Argentino, pp 131–144
Snedden JW, Dalrymple RW (1999) Modern shelf sand bodies: from historical perspective to a unified theory for sand body genesis and evolution. In: Bergman KM, Snedden JD (eds) Isolated shallow marine sand bodies: sequence stratigraphic analysis and sedimentologic interpretation. SEPM Spec Publ 64:13–28
Spalletti LA, Franzese JR, Matheos SD, Schwarz E (2000) Sequence stratigraphy of a tidally dominated carbonate–siliciclastic ramp; the Tithonian–Early Berriasian of the Southern Neuquén Basin, Argentina. J Geol Soc 157:433–446
Spalletti LA, Poiré D, Pirrie D, Matheos S, Doyle P (2001) Respuesta sedimentológica a cambios de nivel de base en una secuencia mixta clástica – carbonática del Cretácico de la Cuenca Neuquina, Argentina. Rev Soc Geol España 14:57–74
Spalletti LA, Veiga GD, Schwarz E (2011) La Formación Agrio (Cretácico Temprano) en la Cuenca Neuquina. In: Leanza HA, Arregui C, Carbone O, Danielli JC, Vallés JM (eds) Geología y recursos naturales del Neuquén. Rel XVIII Congr Geológico Argentino, pp 145–160
Stride AH (1988) Preservation of marine sand wave structures. In: de Boer PL, van Gelder A, Nio SD (eds) Tide-influenced sedimentary environments and facies. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp 13–22
Stride AH, Belderson RH, Kenyon NH, Johnson MA (1982) Offshore tidal deposits: sand sheet and sand bank facies. In: Stride AH (ed) Offshore tidal sands: processes and deposits. Chapman & Hall, London
Suter JR (2006) Facies models revisited: clastic shelves. ln: Posamentier HW, Walker RG (eds) Facies models revisited. SEPM Spec Publ 84:339–397
Taylor AM, Goldring R (1993) Description and analysis of bioturbation and ichnofabric. J Geol Soc Lond 150:141–148
Testa V, Bosence DWJ (1999) Physical and biological controls on the formation of carbonate and siliciclastic bedforms on the north-east Brazilian shelf. Sedimentology 46:279–301
Veiga GD, Spalletti LA, Schwarz E (2011) El Miembro Avilé de la Formación Agrio (Cretácico Temprano). In: Leanza HA, Arregui C, Carbone O, Danielli JC, Vallés JM (eds) Geología y recursos naturales del Neuquén. Rel XVIII Congr Geológico Argentino, pp 161–173
Vergani GD, Tankard AJ, Belotti HJ, Welsink HJ (1995) Tectonic evolution and paleogeography of the Neuquén Basin, Argentina. In: Tankard AJ, Suarez-Soruco R, Welsink HJ (eds) Petroleum basins of South America. AAPG Memoir 62:383–402
Zeller M, Verwer K, Eberli GP, Massaferro JL, Schwarz E, Spalletti L (2015) Depositional controls on mixed carbonate–siliciclastic cycles and sequences on gently inclined shelf profiles. Sedimentology 62:2009–2037
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank CONICET (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas), Universidad Nacional de La Plata and YPF S.A. for financial support of this project. Gabriel Giacommone, Gastón Álvarez Trentini and José Luis Burini are thanked for field and laboratory assistance. The article benefited from fruitful discussions through some years and, for that, Luis Spalletti is also thanked. M. Gugliotta and an anonymous reviewer provided useful comments that considerably improved the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with third parties.
Additional information
Responsible guest editor: J.I. Cuitiño
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veiga, G.D., Schwarz, E. Facies characterization and sequential evolution of an ancient offshore dunefield in a semi-enclosed sea: Neuquén Basin, Argentina. Geo-Mar Lett 37, 411–426 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-016-0467-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-016-0467-1