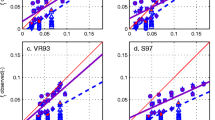
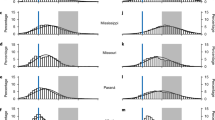
Abstract
Bedforms such as dunes and ripples are ubiquitous in rivers and coastal seas, and commonly described as triangular shapes from which height and length are calculated to estimate hydrodynamic and sediment dynamic parameters. Natural bedforms, however, present a far more complicated morphology; the difference between natural bedform shape and the often assumed triangular shape is usually neglected, and how this may affect the flow is unknown. This study investigates the shapes of natural bedforms and how they influence flow and shear stress, based on four datasets extracted from earlier studies on two rivers (the Rio Paraná in Argentina, and the Lower Rhine in The Netherlands). The most commonly occurring morphological elements are a sinusoidal stoss side made of one segment and a lee side made of two segments, a gently sloping upper lee side and a relatively steep (6 to 21°) slip face. A non-hydrostatic numerical model, set up using Delft3D, served to simulate the flow over fixed bedforms with various morphologies derived from the identified morphological elements. Both shear stress and turbulence increase with increasing slip face angle and are only marginally affected by the dimensions and positions of the upper and lower lee side. The average slip face angle determined from the bed profiles is 14°, over which there is no permanent flow separation. Shear stress and turbulence above natural bedforms are higher than above a flat bed but much lower than over the often assumed 30° lee side angle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JRL (1982) Sedimentary structures: their character and physical basis. Elsevier, New York
Ashley GM (1990) Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at an old problem. J Sediment Res 60:160–172. doi:10.2110/JSR.60.160
Barnard PL, Erikson LH, Kvitek RG (2011) Small-scale sediment transport patterns and bedform morphodynamics: new insights from high-resolution multibeam bathymetry. Geo-Mar Lett 31:227–236. doi:10.1007/s00367-011-0227-1
Bennett SJ, Best JL (1995) Mean flow and turbulence structure over fixed, two-dimensional dunes: implications for sediment transport and bedform stability. Sedimentology 42:491–513. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.1995.tb00386.x
Best J (2005) The fluid dynamics of river dunes: a review and some future research directions. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 110:F04S02. doi:10.1029/2004JF000218
Best J, Kostaschuk R (2002) An experimental study of turbulent flow over a low-angle dune. J Geophys Res Oceans 107:3135. doi:10.1029/2000JC000294
Best J, Simmons S, Parsons D, Oberg K, Czuba J, Malzone C (2010) A new methodology for the quantitative visualization of coherent flow structures in alluvial channels using multibeam echo-sounding (MBES). Geophys Res Lett 37, L06405. doi:10.1029/2009GL041852
Bradley RW, Venditti JG, Kostaschuk R, Church MA, Hendershot M, Allison MA (2013) Flow and sediment suspension events over low-angle dunes: Fraser Estuary, Canada. J Geophys Res 118:1693–1709. doi:10.1002/jgrf.20118
Carling PA (1996) Morphology, sedimentology and palaeohydraulic significance of large gravel dunes, Altai Mountains, Siberia. Sedimentology 43:647–664. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.1996.tb02184.x
Carling PA, Golz E, Orr HG, Radecki-Pawlik A (2000) The morphodynamics of fluvial sand dunes in the River Rhine, near Mainz, Germany. I. Sedimentology and morphology. Sedimentology 47:227–252. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3091.2000.00290.x
Deltares (2011) User manual Delft3D-FLOW. Deltares, Delft, The Netherlands
Engel P (1981) Length of flow separation over dunes. J Hydraul Div 107:1133–1143
Ernstsen VB, Noormets R, Winter C, Hebbeln D, Bartholomae A, Flemming BW, Bartholdy J (2005) Development of subaqueous barchanoid-shaped dunes due to lateral grain size variability in a tidal inlet channel of the Danish Wadden Sea. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 110:F04S08. doi:10.1029/2004JF000180
Ernstsen VB, Noormets R, Winter C, Hebbeln D, Bartholomä A, Flemming BW, Bartholdy J (2006) Quantification of dune dynamics during a tidal cycle in an inlet channel of the Danish Wadden Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 26:151–163. doi:10.1007/s00367-006-0026-2
Fernandez R, Best J, López F (2006) Mean flow, turbulence structure, and bed form superimposition across the ripple-dune transition. Water Resour Res 42, W05406. doi:10.1029/2005WR004330
Flemming BW (1988) On the classification of subaquatic flow-transverse bedforms (in German). Bochum Geol Geotech Arb 29:44–47
Frings RM (2007) From gravel to sand. Downstream fining of bed sediments in the lower river Rhine. PhD thesis, Utrecht University. Netherlands Geographical Studies 368, Royal Dutch Geographical Society, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Harbor DJ (1998) Dynamics of bedforms in the lower Mississippi River. J Sediment Res 68:750–762. doi:10.2110/jsr.68.750
Holmes RR Jr, Garcia MH (2008) Flow over bedforms in a large sand-bed river: a field investigation. J Hydraul Res 46:322–333. doi:10.3826/jhr.2008.3040
Kornman BA (1995) The effect of changes in the lee shape of dunes on the flow field, turbulence, and hydraulic roughness. Report R 95-1, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Kostaschuk R (2000) A field study of turbulence and sediment dynamics over subaqueous dunes with flow separation. Sedimentology 47:519–531. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3091.2000.00303.x
Kostaschuk R, Villard P (1996) Flow and sediment transport over large subaqueous dunes: Fraser River, Canada. Sedimentology 43:849–863. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.1996.tb01506.x
Kostaschuk R, Shugar D, Best J, Parsons D, Lane S, Hardy R, Orfeo O (2009) Suspended sediment transport and deposition over a dune: Río Paraná, Argentina. Earth Surf Process Landf 34:1605–1611. doi:10.1002/esp.1847
Kwoll E, Becker M, Winter C (2014) With or against the tide: the influence of bedform asymmetry on the formation of macroturbulence and suspended sediment patterns. Water Resour Res 50:7800–7815. doi:10.1002/2013WR014292
Kwoll E, Venditti JG, Bradley RW, Winter C (2016) Flow structure and resistance over subaquaeous high- and low-angle dunes. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 121:545–564. doi:10.1002/2015JF003637
Lefebvre A, Winter C (2016) Predicting bed form roughness: the influence of lee side angle. Geo-Mar Lett 36:121–133. doi:10.1007/s00367-016-0436-8
Lefebvre A, Paarlberg AJ, Winter C (2014a) Flow separation and shear stress over angle of repose bedforms: a numerical investigation. Water Resour Res 50:986–1005. doi:10.1002/2013WR014587
Lefebvre A, Paarlberg AJ, Ernstsen VB, Winter C (2014b) Flow separation and roughness lengths over large bedforms in a tidal environment: a numerical investigation. Cont Shelf Res 91:57–69. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2014.09.001
McLean SR, Nelson JM, Wolfe SR (1994) Turbulence structure over two-dimensional bed forms: implications for sediment transport. J Geophys Res 99:12729–12747. doi:10.1029/94JC00571
McLean SR, Wolfe SR, Nelson JM (1999) Spatially averaged flow over a wavy boundary revisited. J Geophys Res 104:15743–15753. doi:10.1029/1999JC900116
Naqshband S, Ribberink J, Hulscher S (2014) Using both free surface effect and sediment transport mode parameters in defining the morphology of river dunes and their evolution to upper stage plane beds. J Hydraul Eng 140:06014010. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000873
Nelson JM, McLean SR, Wolfe SR (1993) Mean flow and turbulence fields over two-dimensional bed forms. Water Resour Res 29:3935–3953. doi:10.1029/93WR01932
Ogink H (1989) Hydraulic roughness of single and compound bed forms. Part XI. Report on model investigations. Delft Hydraulics Laboratory, Delft, The Netherlands
Omidyeganeh M, Piomelli U (2011) Large-eddy simulation of two-dimensional dunes in a steady, unidirectional flow. J Turbul 12:1–31. doi:10.1080/14685248.2011.609820
Paarlberg AJ, Dohmen-Janssen CM, Hulscher SJMH, Termes P (2007) A parameterization of flow separation over subaqueous dunes. Water Resour Res 43, W12417. doi:10.1029/2006WR005425
Parsons DR, Best JL, Orfeo O, Hardy RJ, Kostaschuk R, Lane SN (2005) Morphology and flow fields of three-dimensional dunes, Rio Paraná, Argentina: results from simultaneous multibeam echo sounding and acoustic Doppler current profiling. J Geophys Res 110:F04S03. doi:10.1029/2004JF000231
Peakall J, Ashworth PJ, Best JL (1996) Physical modelling in fluvial geomorphology: principles, applications and unresolved issues. In: Rhoads BL, Thorne CE (eds) The scientific nature of geomorphology. Wiley, New York, pp 221–253
Piomelli U, Omidyeganeh M (2013) Large-eddy simulations in dune-dynamics research. In: Van Lancker V, Garlan T (eds) MARID 2013 4th Int Conf Marine and River Dune Dynamics, Bruges, Belgium. VLIZ Spec Publ 65, pp 15–22
Roden JE (1998) The sedimentology and dynamics of mega-dunes, Jamuna River, Bangladesh. PhD thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK
Schindler RJ, Parsons DR, Ye L, Hope JA, Baas JH, Peakall J, Manning AJ, Aspden RJ, Malarkey J, Simmons S, Paterson DM, Lichtman ID, Davies AG, Thorne PD, Bass SJ (2015) Sticky stuff: redefining bedform prediction in modern and ancient environments. Geology 43:399–402. doi:10.1130/G36262.1
Smith JD, McLean SR (1977) Spatially averaged flow over a wavy surface. J Geophys Res 84:1735–1746. doi:10.1029/JC082i012p01735
Stoesser T, Braun C, García-Villalba M, Rodi W (2008) Turbulence structures in flow over two-dimensional dunes. J Hydraul Eng 134:42–55. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:1(42)
Uittenbogaard R, van Kester J, Stelling G (1992) Implementation of three turbulence models in 3D-TRISULA for rectangular grids. Tech Rep Z81, WL. Delft Hydraulics, Delft, The Netherlands
Van der Mark CF, Blom A (2007) A new and widely applicable tool for determining the geometric properties of bedforms. University of Twente, Enschede
Van der Mark CF, Blom A, Hulsher SJMH (2008) Quantification of variability in bedform geometry. J Geophys Res 113, F03020. doi:10.1029/2007JF000940
Van Rijn LC (1993) Principles of sediment transport in rivers, estuaries and coastal seas. Aqua Publications, Amsterdam
Venditti JG (2003) Initiation and development of sand dunes in river channels. PhD thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Venditti JG (2007) Turbulent flow and drag over fixed two- and three-dimensional dunes. J Geophys Res 112, F04008. doi:10.1029/2006JF000650
Venditti JG (2013) Bedforms in sand-bedded rivers. In: Shroder J, Wohl E (eds) Treatise on geomorphology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 137–162. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-374739-6.00235-9
Venditti JG, Bennett SJ (2000) Spectral analysis of turbulent flow and suspended sediment transport over fixed dunes. J Geophys Res 105:22035–22047. doi:10.1029/2000JC900094
Villard P, Kostaschuk R (1998) The relation between shear velocity and suspended sediment concentration over dunes: Fraser Estuary, Canada. Mar Geol 148:71–81. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00015-2
Wilbers AWE, Ten Brinke WBM (2003) The response of subaqueous dunes to floods in sand and gravel bed reaches of the Dutch Rhine. Sedimentology 50:1013–1034. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3091.2003.00585.x
Acknowledgements
This study was funded through the DFG Research Center/Cluster of Excellence “The Ocean in the Earth System”. Alice Lefebvre is appreciative of the support provided by GLOMAR – Bremen International Graduate School for Marine Sciences. The authors wish to thank Roy M. Frings and Daniel R. Parsons for providing the multibeam echosounder data used in the analysis. Eva Kwoll is also thanked for giving helpful suggestions on the structure of the discussion. Three reviewers are acknowledged for comments on an earlier version of the article, as well as the journal editors for other suggestions. Data are available through the Publishing Network for Geoscientific & Environmental Data (PANGAEA, http://www.pangaea.de).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with third parties.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lefebvre, A., Paarlberg, A.J. & Winter, C. Characterising natural bedform morphology and its influence on flow. Geo-Mar Lett 36, 379–393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-016-0455-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-016-0455-5