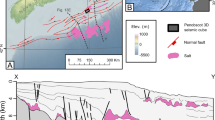
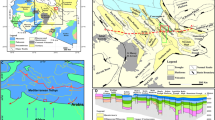
Abstract
Several shore-parallel marine sand bodies lie on the Louisiana continental shelf. They are Trinity Shoal, Ship Shoal, Outer Shoal, and the St. Bernard Shoals. These shoals mark the submerged positions of ancient shorelines associated with abandoned deltas. Three of these shoals are single elongate deposits. The fourth shoal, the St. Bernard Shoals, consists of a group of discrete sand bodies ranging in size from 44 to 0.05 km2, 25 km southeast of the Chandeleur Islands in 15–18 m of water. The St. Bernard Shoals are stratigraphically above the St. Bernard delta complex, which was active 2,500–1,800 years b.p. Understanding the evolution of the St. Bernard Shoals is necessary to reconstruct the Holocene chronology of the St. Bernard delta complex and the eastern Louisiana continental shelf. For this study, 47 vibracores and 400 km of shallow seismic reflection data collected in 1987 across the Louisiana shelf were analyzed. In June 2008, 384 km of higher-resolution seismic reflection data were acquired across the study area and appended to the preexisting datasets. Vibracores were integrated with seismic profiles to identify facies and their regional distribution. Our results demonstrate that the deltaic package stratigraphically below the St. Bernard Shoals is chronologically younger than the northern distributaries, but derived from the same trunk distributary channel (Bayou la Loutre). The river eventually bypassed the northern distributaries, and began to deposit sediment further onto the continental shelf. After abandonment, the overextended delta lobe was rapidly transgressed, creating a transgressive shoreline that eventually coalesced with earlier shorelines in the region to form the Chandeleur Islands. The St. Bernard Shoals formed by the reworking of the relict distributary deposits exposed on the inner to mid shelf during and subsequent to shoreface ravinement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya JP, Giosan L (2003) Wave-influenced deltas: geomorphic implications for facies reconstruction. Sedimentology 50:187–210
Boyd R, Suter J, Penland S (1989) Relation of sequence stratigraphy to modern sedimentary environments. Geology 17:926–929
Brooks GR, Kindinger JL, Penland S, Williams SJ, McBride RA (1995) East Louisiana continental shelf sediments: a product of delta reworking. J Coastal Res 11:1026–1036
Cattaneo A, Steele RJ (2003) Transgressive deposits: a review of their variability. Earth-Sci Rev 62:187–228
Coleman JM, Prior DB (1981) Deltaic sand bodies: a 1981 short course. AAPG Continuing Education Course Notes Series #15
Curray JR, Moore DG (1963) Facies delineation by acoustic-reflection: northern Gulf of Mexico. Sedimentology 2:130–148
Ellis J, Stone GW (2006) Numerical simulation of net longshore sediment transport and granulometry of surficial sediments along Chandeleur Island, Louisiana, USA. Mar Geol 232:115–129
Field ME (1980) Sand bodies on coastal plain shelves: holocene record of the US Atlantic inner shelf off Maryland. J Sediment Petrol 50:505–528
Fisk HN (1944) Geological investigation of the alluvial valley of the Lower Mississippi River. US Army Corps of Engineers, Vicksburg, MS, Mississippi River Commission
Fisk HN, Kolb CR, McFarlan E, Wilbert RJ (1954) Sedimentary framework of the modern Mississippi delta (Louisiana). J Sediment Petrol 24(2):76–99
Frazier DE (1967) Recent deltaic deposits of the Mississippi River: their development and chronology. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 17:287–315
Frazier DE, Osanik A (1969) Recent peat deposits-Louisina coastal plain. In: Dappels EC, Hopkins ME (eds) Environments of coal deposition. Geol Soc Am Spec Publ 114:63–85
Georgiou IY, Schindler J (2009) Numerical simulations of waves and sediment transport along a transgressive barrier island. In: An evaluation of the resilience of the Breton National Wildlife Refuge. US Geol Surv Open-File Rep (in press)
Gerdes RG (1985) The Caminada-Moreau Beach Ridge Plain. In: Penland S, Boyd R (eds) Transgressive depositional environments of the Mississippi River delta plain. A guide to the barrier islands, beaches, and shoals in Louisiana. Louisiana Geol Surv Guidebook Series 3:125–140
Hampson GJ, Rodriguez AB, Storms JEA, Johnson HD, Meyer CT (2008) Geomorphology and high-resolution stratigraphy of progradational wave-dominated shoreline deposits: impact on reservoir-scale architecture. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 90:117–142
Hayes MO, Nairn RB (2004) Natural maintenance of sand ridges and linear shoals on the U.S. Gulf and Atlantic continental shelves and the potential impacts of dredging. J Coastal Res 20:138–148
Huthnance JM (1982) On one mechanism forming linear sand banks. Estuarine Mar Coastal Sci 14:79–99
Jol HM, Smith DG, Meyers R (1996) Digital ground penetrating radar (GPR): a new geophysical tool for coastal barrier research (examples from the Atlantic Gulf and Pacific Coasts, USA). J Coastal Res 12:960–968
Keen TR, Furukawa Y, Bentley SJ, Slingerland RL, Teague WJ, Dykes JD, Rowley CD (2006) Geological and oceanographic perspectives on event bed formation during Hurricane Katrina. Geophys Res Lett 33:23, L23614. doi:10.1029/2006GL027981
Kesel RH (2008) A revised Holocene geochronology for the lower Mississippi Valley. Geomorphology 101:78–89
Kindinger JL, Miller RJ, Stelting CE, Bouma AH (1982) Depositional history of the Louisiana-Mississippi outer continental shelf. US Geol Surv Open-File Rep 82–1077
Kindinger JL, Penland S, Williams SJ, Suter JR (1989) Inner shelf deposits of the Louisiana-Mississippi-Alabama region, Gulf of Mexico. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 39:413–420
Kolb CR, Van Lopik JR (1958) Geology of the Mississippi River deltaic plain southeastern Louisiana. US Army Corps Eng Tech Rep 3–483
Kulp MA, Howell P, Adiau S, Penland S, Kindinger JL, Williams SJ (2002) Latest Quaternary stratigraphic framework of the Mississippi delta region. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 52:573–582
Kulp M, FitzGerald D, Penland S (2005) Sand-rich lithosomes of the Holocene Mississippi River delta plain. In: Bhattacharya JP, Giosan L (eds) River deltas—concepts, models, and examples. Soc Econ Mineral Paleontol Spec Publ 83:277–291
Ludwick JC (1964) Sediments in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. In: Miller RL (ed) Papers in marine geology, shepard commemorative volume. Macmillan, New York, pp 204–238
McBride RA, Moslow TF (1991) Origin evolution and distribution of shoreface sand ridges; Atlantic inner shelf, USA. Mar Geol 97:57–85
McBride RA, Anderson LC, Tudoran A, Roberts HH (1999) Holocene stratigraphic architecture of a sand-rich shelf and the origin of linear shoals. Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 64:95–126
Mitchum RM Jr, Vail PR, Sangree JB (1977) Stratigraphic interpretation of seismic reflection patterns in depositional sequences in seismic stratigraphy — applications to hydrocarbon exploration. In: Payton EC (ed) Seismic stratigraphy — applications to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Mem 26:117–134
Moore LJ, Jol HM, Kruse S, Vanderburgh S, Kaminsky GM (2004) Annual layers revealed by GPR in the subsurface of a prograding coastal barrier, southwest Washington, SA. J Sediment Res 74:690–696
Niedoroda AW, Swift DJP, Figueiredo AG, Freeland GL (1985) Barrier island evolution, middle Atlantic shelf, U.S.A. Part II: evidence from the shelf floor. Mar Geol 63:363–396
Otvos EG, Giardino MJ (2004) Interlinked barrier chain and delta lobe development, northern Gulf of Mexico. Sediment Geol 169:47–73
Penland S, Boyd R, Suter JR (1988) Transgressive depositional systems of the Mississippi delta plain: a model for barrier shoreline and shelf sand development. J Sediment Petrol 58:932–949
Penland S, Suter JR, McBride RA, Williams SJ, Kindinger JL, Boyd R (1989) Holocene sand shoals offshore of the Mississippi River delta plain. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 39:471–480
Pope D, Conner P Jr, Penland S (1993) Stratigraphical assessment of the mineral aggregate resources in the St. Bernard Shoal, offshore Louisiana. US Minerals Management Service Prof Pap
Posamentier HW, Vail PR (1988) Eustatic controls on clastic deposition II. Sequence and system tract models. In: Wilgus CK, Ross CA, Posamentier HW, Hastings BK, Kendall CG (eds) Sea-level change: an integrated approach. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Edn 42:109–124
Roberts HH (1997) Dynamic changes of the Holocene Mississippi River delta plain: the delta cycle. J Coastal Res 13:605–627
Rodriguez AB, Meyer CT (2006) Sea-level variation during the Holocene deduced from the morphologic and stratigraphic evolution of Morgan Peninsula, Alabama, USA. J Sediment Res 76:257–269
Savage RP (1959) Notes on the formation of beach-ridges. Bull Beach Erosion Board 13:31–35
Smith DG, Meyers RA, Jol HM (1999) Sedimentology of an upper-mesotidal (3.7 m) Holocene barrier, Willapa Bay, SW Washington, USA. J Sediment Res 69:1290–1296
Snedden JW, Dalrymple RW (1999) Modern shelf sand ridges: from historical perspective to a unified hydrodynamic and evolutionary model. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 64:13–28
Snedden JW, Kreisa RP, Thillman RK, Culver SJ, Schweller WJ (1999) An expanded model for modern shelf sand ridge genesis and evolution on the New Jersey, Atlantic shelf. In: Bergman KM, Snedden JW (eds) Isolated shallow marine sand bodies: sequence stratigraphic analysis and sedimentological interpretation. SEPM Spec Publ 64:147–164
Suter JR, Penland S, Williams SJ, Kindinger JL (1988) Transgressive evolution of the Chandeleur Islands, Louisiana. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 38:315–322
Taylor M, Stone GW (1996) Beach ridges: a review. J Coastal Res 12(3):612–621
Teague WJ, Jarosz E, Keen TR, Wang DW, Hulbert MS (2006) Bottom scour observed under Hurricane Ivan. Geophys Res Lett 33:3, L07607. doi:10.1029/2005GL025281
Teague WJ, Jarosz E, Wang DW, Mitchell DA (2007) Observed oceanic response over upper continental slope and outer shelf during Hurricane Ivan. J Phys Oceanogr 37:2181–2206
Thieler ER, Pilkey OH Jr, Cleary WJ, Schwab WC (2001) Modern sedimentation of the shoreface and inner continental shelf at Wrightsville Beach, North Carolina, U.S.A. J Sediment Res 71:958–970
Törnqvist TE, Kidder TR, Autin WJ, van der Borg K, de Jong AFM, Klerks CJW, Snijders EMA, Storms JEA, van Dam RL, Wiemann MC (1996) A revised chronology for Mississippi River subdeltas. Science 273:1693–1696
Twichell D, Pendleton E, Baldwin W, Flocks J (2009) Subsurface control on seafloor erosional processes offshore of the Chandeleur Islands, Louisiana. Geo-Mar Lett SI (in press). doi:10.1007/s00367-009-0150-x
Vail PR, Mitchum RM, Todd RG (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes in sea-level. In: Payton CE (ed) Seismic stratigraphy — applications to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Mem 26:49–212
Van Heteren S, Fitzgerald DM, McKinlay PA, Buynevich IV (1998) Radar facies of paraglacial barrier systems: coastal New England, USA. Sedimentology 45:181–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogers, B.E., Kulp, M.A. & Miner, M.D. Late Holocene chronology, origin, and evolution of the St. Bernard Shoals, Northern Gulf of Mexico, USA. Geo-Mar Lett 29, 379–394 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-009-0162-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-009-0162-6