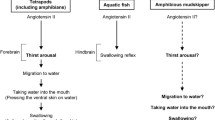
Abstract
The forebrain lamina terminalis has not yet been examined for the role of osmosensing in teleosts, although the thirst center is well known to be present in this vascular permeable forebrain region in mammals. Here, we examined vascular permeability and neuronal responsiveness to dehydration in the lamina terminalis of the mudskipper, a euryhaline goby. Evans blue and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide-biotin both bind to blood proteins, and are impermeable to the blood–brain barrier. Intraperitoneal injection of these probes stained the walls of the preoptic recess (PR) of the third ventricle, indicating increased vascular permeability in this region. When mudskippers kept in isotonic brackish water (ca. 11 psu) were challenged to seawater (ca. 34 psu) for 3 h, body water content showed a 1 % decrease, compared with mudskippers without hypertonic challenge. Simultaneously, the number of immunohistochemically identified cFos-expressing neurons in the anterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPa) of the PR walls increased in a site-specific manner by approximately 1.6-fold compared with controls. Thus, these findings indicate that PPa neurons are activated, following dehydration in mudskippers. Taken together, the vascularly permeable PR walls may be involved in osmosensing, as in the mammalian thirst center.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano M, Mizusawa N, Okubo K, Amiya N, Mizusawa K, Chiba H, Yamamoto N, Takahashi A (2014) Cloning of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) precursor cDNA and immunohistochemical detection of CRH peptide in the brain of the Japanese eel, paying special attention to gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Cell Tissue Res 356:243–251. doi:10.1007/s00441-013-1784-6
Amer S, Brown JA (1995) Glomerular actions of arginine vasotocin in the in situ perfused trout kidney. Am J Physiol 269:R775–R780
Anadón R, Molist P, Rodríguez-Moldes I, López JM, Quintela I, Cerviño MC, Barja P, González A (2000) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in the brain of an elasmobranch, the lesser spotted dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula). J Comp Neurol 420:139–170. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(20000501)420:2<139:AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-T
Anderson WG, Takei Y, Hazon N (2002) Osmotic and volaemic effects on drinking rate in elasmobranch fish. J Exp Biol 205:1115–1122
Ando M, Fujii Y, Kadota T, Kozaka T, Mukuda T, Takase I, Kawahara A (2000a) Some factors affecting drinking behavior and their interactions in seawater-acclimated eels, Anguilla japonica. Zool Sci 17:171–178. doi:10.2108/zsj.17.171
Ando M, Mukuda T, Takase I (2000b) Integrated aspects of osmoregulation in eels acclimated to sea water. Trends Comp Biochem Physiol 6:85–94
Ando M, Mukuda T, Kozaka T (2003) Water metabolism in the eel acclimated to seawater: from mouth to intestine. Comp Biochem Physiol B 136:621–633. doi:10.1016/S1096-4959(03)00179-9
Avella M, Part P, Ehrenfeld J (1999) Regulation of Cl− secretion in seawater fish (Dicentrarchus labrax) gill respiratory cells in primary culture. J Physiol 516:353–363. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0353v.x
Bains JS, Potyok A, Ferguson AV (1992) Angiotensin II actions in paraventricular nucleus: functional evidence for neurotransmitter role in efferents originating in subfornical organ. Brain Res 599:223–229. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(92)90395-P
Balment RJ, Lu W, Weybourne E, Warne JM (2006) Arginine vasotocin a key hormone in fish physiology and behaviour: a review with insights from mammalian models. Gen Comp Endocrinol 147:9–16. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.12.022
Barreiro-Iglesias A, Villar-Cerviño V, Villar-Cheda B, Anadón R, Rodicio MC (2008) Neurochemical characterization of sea lamprey taste buds and afferent gustatory fibers: presence of serotonin, calretinin, and CGRP immunoreactivity in taste bud bi-ciliated cells of the earliest vertebrates. J Comp Neurol 511:438–453. doi:10.1002/cne.21844
Castro A, Becerra M, Anadón R, Manso MJ (2008) Distribution of calretinin during development of the olfactory system in the brown trout, Salmo trutta fario: comparison with other immunohistochemical markers. J Chem Neuroanat 35:306–316. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2008.03.005
Clemente D, Porteros A, Weruaga E, Alonso JR, Arenzana FJ, Aijón J, Arévalo R (2004) Cholinergic elements in the zebrafish central nervous system: histochemical and immunohistochemical analysis. J Comp Neurol 474:75–107. doi:10.1002/cne.20111
Dall W, Milward NE (1969) Water intake, gut absorption and sodium fluxes in amphibious and aquatic fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol 30:247–260. doi:10.1016/0010-406X(69)90808-1
Fitzsimons JT (1998) Angiotensin, thirst, and sodium appetite. Physiol Rev 78:583–686
Fontaine R, Affaticati P, Bureau C, Colin I, Demarque M, Dufour S, Vernier P, Yamamoto K, Pasqualini C (2015) Dopaminergic neurons controlling anterior pituitary functions: anatomy and ontogenesis in zebrafish. Endocrinol 156:2934–2948. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1091
Gibson RN (1986) Intertidal teleosts: life in a fluctuating environment. In: Pitcher PJ (ed) The behaviour of teleost fishes. Springer, New York, pp 388–408
Gómez-Segade P, Segade LA, Anadon R (1991) Ultrastructure of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis in the advanced teleost Chelon labrosus (Risso, 1826). J Hirnforsch 32:69–77
Gonzalez RJ (2012) The physiology of hyper-salinity tolerance in teleost fish: a review. J Comp Physiol B 182:321–329. doi:10.1007/s00360-011-0624-9
Gordon MS, Ng WW, Yip AY (1978) Aspects of the physiology of terrestrial life in amphibious fishes. III. The Chinese mudskipper Periophthalmus cantonensis. J Exp Biol 72:57–75
Hirano T, Hasegawa S (1984) Effects of angiotensins and other vasoactive substances on drinking in the eel, Anguilla japonica. Zool Sci 1:106–113
Hirayama J, Cardone L, Doi M, Sassone-Corsi P (2005) Common pathways in circadian and cell cycle clocks: light-dependent activation of Fos/AP-1 in zebrafish controls CRY-1a and WEE-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:10194–10199. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502610102
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2012.07.019
Hwang PP, Sun CM, Wu SM (1989) Changes of plasma osmolality, chloride concentration and gill Na-K-ATPase activity in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus during seawater acclimation. Marine Biol 100:295–299. doi:10.1007/BF00391142
Hyodo S, Tsukada T, Takei Y (2004) Neurohypophysial hormones of dogfish, Triakis scyllium: structures and salinity-dependent secretion. Gen Comp Endocrinol 138:97–104. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.05.009
Ip YK, Lee CG, Low WP, Lam TJ (1991) Osmoregulation in the mudskipper, Boleophthalmus boddaerti I. Responses of branchial cation activated and anion stimulated adenosine triphosphatases to changes in salinity. Fish Physiol Biochem 9:63–68. doi:10.1007/BF01987612
Jeong JY, Kwon HB, Ahn JC, Kang D, Kwon SH, Park JA, Kim KW (2008) Functional and developmental analysis of the blood-brain barrier in zebrafish. Brain Res Bull 75:619–628. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.10.043
Johnson AK, Cunningham JT, Thunhorst RL (1996) Integrative role of the lamina terminalis in the regulation of cardiovascular and body fluid homeostasis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 23:183–191. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1996.tb02594.x
Kaiya H, Takei Y (1996) Changes in plasma atrial and ventricular natriuretic peptide concentrations after transfer of eels from freshwater to seawater or vice versa. Gen Comp Endocrinol 104:337–345. doi:10.1006/gcen.1996.0179
Kawamoto K, Kawashima S (1986) Effect of glucocorticoids and vasopressin on the regulation of neurohypophyseal hormone-containing axons after hypophysectomy. Zool Sci 3:723–726
Kelly SP, Chow INK, Woo NYS (1999) Haloplasticity of black sea bream (Mylio macrocephalus): hypersaline to freshwater acclimation. J Exp Zool 226:226–241. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990215)283:3<226:AID-JEZ2>3.0.CO;2-8
Knowles WD, Phillips MI (1980) Angiotensin II responsive cells in the organum vasculosum lamina terminalis (OVLT) recorded in hypothalamic brain slices. Brain Res 197:256–259. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(80)90455-2
Konno N, Hyodo S, Yamaguchi Y, Matsuda K, Uchiyama M (2010) Vasotocin/V2-type receptor/aquaporin axis exists in African lungfish kidney but is functional only in terrestrial condition. Endocrinology 151:1089–1096. doi:10.1210/en.2009-1070
Kozaka T, Fujii Y, Ando M (2003) Central effects of various ligands on drinking behavior in eels acclimated to seawater. J Exp Biol 206:687–692. doi:10.1242/jeb.00146
Li Z, Ferguson AV (1993) Subfornical organ efferents to paraventricular nucleus utilize angiotensin as a neurotransmitter. Am J Physiol 265:R302–R309
Ma PM (1994) Catecholaminergic systems in the zebrafish. I. Number, morphology, and histochemical characteristics of neurons in the locus coeruleus. J Comp Neurol 344:242–255
Madsen SS (1990a) Enhanced hypoosmoregulatory response to growth hormone after cortisol treatment in immature rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Fish Physiol Biochem 8:271–279. doi:10.1007/BF00003422
Madsen SS (1990b) The role of cortisol and growth hormone in seawater adaptation and development of hypoosmoregulatory mechanisms in sea trout parr (Salmo trutta trutta). Gen Comp Endocrinol 79:1–11. doi:10.1016/0016-6480(90)90082-W
Martemyanov VI (2013) Use of body-water content to assess the physiological state of roach Rutilus rutilus L. in nature condition. Inland Water Biol 3:246–248. doi:10.1134/S1995082913030103
McKinley MJ, Johnson AK (2004) The physiological regulation of thirst and fluid intake. News Physiol Sci 19:1–6. doi:10.1152/nips.01470.2003
McKinley MJ, Badoer E, Oldfield BJ (1992) Intravenous angiotensin II induces Fos-immunoreactivity in circumventricular organs of the lamina terminalis. Brain Res 594:295–300. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(92)91138-5
McKinley MJ, Hards DK, Oldfield BJ (1994) Identification of neural pathways activated in dehydrated rats by means of Fos-immunohistochemistry and neural tracing. Brain Res 653:305–314. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)90405-7
McKinley MJ, Mathai ML, Pennington G, Rundgren M, Vivas L (1999) Effect of individual or combined ablation of the nuclear groups of the lamina terminalis on water drinking in sheep. Am J Physiol 276:R673–R683
Mukuda T, Ando M (2003) Medullary motor neurones associated with drinking behaviour of Japanese eels. J Fish Biol 62:1–12. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00002.x
Mukuda T, Ando M (2010) Central regulation of the pharyngeal and upper esophageal reflexes during swallowing in the Japanese eel. J Comp Physiol A 196:111–122. doi:10.1007/s00359-009-0498-4
Mukuda T, Matsunaga Y, Kawamoto K, Yamaguchi K, Ando M (2005) “Blood-contacting neurons” in the brain of the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. J Exp Zool A 303:366–376. doi:10.1002/jez.a.134
Mukuda T, Hamasaki S, Koyama Y, Takei Y, Kaidoh T, Inoué T (2013) A candidate of organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis with neuronal connections to neurosecretory preoptic nucleus in eels. Cell Tissue Res 353:525–538. doi:10.1007/s00441-013-1663-1
Nelson DO (1989) Altered angiotensin II sensitivity of neurons in the organum vasculosum lamina terminalis region of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Brain Res 444:46–52. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(88)90911-0
Nobata S, Ando M (2013) Regulation of drinking. In: Trischitta F, Takei Y, Sébert P (eds) Eel physiology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 225–248
Nobata S, Takei Y (2011) The area postrema in hindbrain is a central player for regulation of drinking behavior in Japanese eels. Am J Physiol 300:R1569–R1577. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00056.2011
Nobata S, Ando M, Takei Y (2013) Hormonal control of drinking behavior in teleost fishes; insights from studies using eels. Gen Comp Endocrinol 192:214–221. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.05.009
O’Connell LA, Matthews BJ, Hofmann HA (2012) Isotocin regulates paternal care in a monogamous cichlid fish. Horm Behav 61:725–733. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.03.009
Okuya S, Inenaga K, Kaneko T, Yamashita H (1987) Angiotensin II sensitive neurons in the supraoptic nucleus, subfornical organ and anteroventral third ventricle of rats in vitro. Brain Res 402:58–67. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)91047-X
Oldfield BJ, Bicknell RJ, McAllen RM, Weisinger RS, McKinley MJ (1991) Intravenous hypertonic saline induces Fos immunoreactivity in neurons throughout the lamina terminalis. Brain Res 561:151–156. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(91)90760-S
Pérez SE, Yáñez J, Marín O, Anadón R, González A, Rodríguez-Moldes I (2000) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunoreactivity in the brain of the adult trout and tract-tracing observations on the connections of the nuclei of the isthmus. J Comp Neurol 428:450–474. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20001218)428:3<450:AID-CNE5>3.0.CO;2-T
Pombal MA, Marín O, González A (2001) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive structures in the lamprey brain. J Comp Neurol 431:105–126. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20010226)431:1<105:AID-CNE1058>3.0.CO;2-P
Roberts BL, Meredith GE, Maslam S (1989) Immunocytochemical analysis of the dopamine system in the brain and spinal cord of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. Anat Embryol (Berl) 180:401–412. doi:10.1007/BF00311171
Rodriguez-Gömez FJ, Rendön-Unceta MC, Sarasquete C, Muñoz-Cueto JA (2000) Localization of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactivity in the brain of the Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis. J Chem Neuroanat 19:17–32. doi:10.1016/S0891-0618(00)00047-8
Rowland NE (1998) Brain mechanisms of mammalian fluid homeostasis: insights from use of immediate early gene mapping. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:49–63. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(97)00068-7
Sakamoto T, Yokota S, Ando M (2000) Rapid morphological oscillation of mitochondrion-rich cell in estuarine mudskipper following salinity changes. J Exp Zool 286:666–669
Sakamoto T, Kozaka T, Takahashi A, Kawauchi H, Ando M (2001) Medaka (Oryzias latipes) as a model for hypoosmoregulation of euryhaline fishes. Aquaculture 193:347–354. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00471-3
Sakamoto T, Nishiyama Y, Ikeda A, Takahashi H, Hyodo S, Kagawa N, Sakamoto H (2015) Neurohypophysial hormones regulate amphibious behaviour in the mudskipper goby. PLoS One 10:e0134605. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134605
Sladek CD, Johnson AK (1983) Effect of anteroventral third ventricle lesions on vasopressin release by organ-cultured hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal explants. Neuroendocrinol 37:78–84. doi:10.1159/000123519
Sueiro C, Carrera I, Rodríguez-Moldes I, Molist P, Anadón R (2003) Development of catecholaminergic systems in the spinal cord of the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula (Elasmobranchs). Brain Res Dev Brain Res 142:141–150. doi:10.1016/S0165-3806(03)00062-2
Sunn N, McKinley MJ, Oldfield BJ (2003) Circulating angiotensin II activates neurones in circumventricular organs of the lamina terminalis that project to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neuroendocrinol 15:725–731. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.00969.x
Takei Y, Hirano T, Kobayashi H (1979) Angiotensin and water intake in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Gen Comp Endocrinol 38:466–475. doi:10.1016/0016-6480(79)90155-2
Takei Y, Okubo J, Yamaguchi K (1988) Effects of cellular dehydration on drinking and plasma angiotensin II level in the eel, Anguilla japonica. Zool Sci 5:43–51
Thrasher TN, Simpson JB, Ramsay DJ (1982) Lesions of the subfornical organ block angiotensin-induced drinking in the dog. Neuroendocrinology 35:68–72
Tsukada T, Nobata S, Hyodo S, Takei Y (2007) Area postrema, a brain circumventricular organ, is the site of antidipsogenic action of circulatin atrial natriuretic peptide in eels. J Exp Biol 210:3970–3978. doi:10.1242/jeb.010645
Tsuneki K (1986) A survey of occurrence of about seventeen circumventricular organs in brains of various vertebrates with special reference to lower groups. J Hirnforsch 27:441–470
Uyama O, Okamura N, Yanase M, Narita M, Kawabata K, Sugita M (1988) Quantitative evaluation of vascular permeability in the gerbil brain after transient ischemia using Evans blue fluorescence. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:282–284. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1988.59
Wai MS, Lorke DE, Webb SE, Yew DT (2006) The pattern of c-fos activation in the CNS is related to behavior in the mudskipper, Periophthalmus cantonensis. Behav Brain Res 167:318–327. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2005.09.018
Warne JM, Bond H, Weybourne E, Sahajpal V, Lu W, Balment RJ (2005) Altered plasma and pituitary arginine vasotocin and hypothalamic provasotocin expression in flounder (Platichthys flesus) following hypertonic challenge and distribution of vasotocin receptors within the kidney. Gen Comp Endocrinol 144:240–247. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.06.007
Watanabe Y, Sakihara T, Mukuda T, Ando M (2007) Antagonistic effects of vasotocin and isotocin on the upper esophageal sphincter muscle of the eel acclimated to seawater. J Comp Physiol B 177:867–873. doi:10.1007/s00360-007-0184-1
Zucker DK, Wooten GF, Lothman EW (1983) Blood-brain barrier changes with kainic acid-induced limbic seizures. Exp Neurol 79:422–433. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(83)90223-6
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Y. Furukawa (Hiroshima University) and Dr. M. Ando for valuable suggestions. We also thank Y. Koyama and M. Matsuura for their technical support. The study was supported, in part, by a Women Researchers Grant from Hiroshima University to S.H. and by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI to T.M. (No. 25840118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamasaki, S., Mukuda, T., Kaidoh, T. et al. Impact of dehydration on the forebrain preoptic recess walls in the mudskipper, Periophthalmus modestus: a possible locus for the center of thirst. J Comp Physiol B 186, 891–905 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1005-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1005-1