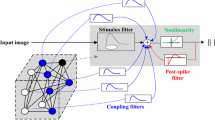
Abstract
The biological networks have been widely reported to present small-world properties. However, the effects of small-world network structure on population’s encoding performance remain poorly understood. To address this issue, we applied a small world-based framework to quantify and analyze the response dynamics of cell assemblies recorded from rat primary visual cortex, and further established a population encoding model based on small world-based generalized linear model (SW-GLM). The electrophysiological experimental results show that the small world-based population responses to different topological shapes present significant variation (t test, p < 0.01; effect size: Hedge’s g > 0.8), while no significant variation was found for control networks without considering their spatial connectivity (t test, p > 0.05; effect size: Hedge’s g < 0.5). Furthermore, the numerical experimental results show that the predicted response under SW-GLM is more accurate and reliable compared to the control model without small-world structure, and the decoding performance is also improved about 10 % by taking the small-world structure into account. The above results suggest the important role of the small-world neural structure in encoding visual information for the neural population by providing electrophysiological and theoretical evidence, respectively. The study helps greatly to well understand the population encoding mechanisms of visual cortex.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCH:
-
Cross-correlation histogram
- FNF:
-
Full network-based framework
- MEA:
-
Microelectrode array
- PSTH:
-
Post-stimulus time histogram
- RF:
-
Receptive field
- SWF:
-
Small world-based framework (for quantifying population response)
- SW-GLM:
-
Small world-based generalized linear model
- V1:
-
The primary visual cortex
References
Achard S, Salvador R, Whitcher B, Suckling J, Bullmore E (2006) A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J Neurosci 26(1):63–72. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3874-05.2006
Aertsen AM, Gerstein GL, Habib MK, Palm G (1989) Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of “effective connectivity”. J Neurophysiol 61(5):900–917
Andersen P, Borgan O, Gill R, Keiding N (1992) Statistical models based on counting processes. Springer, New York
Bassett D, Bullmore E (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12(6):512–523. doi:10.1177/1073858406293182
Berens P, Ecker A, Gerwinn S, Tolias A, Bethge M (2011) Reassessing optimal neural population codes with neurometric functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(11):4423–4428. doi:10.1073/pnas.1015904108
Bialek W, Rieke F, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Warland D (1991) Reading a neural code. Science 252(5014):1854–1857
Bishop C (2007) Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer, Berlin
Bock DD, Lee WC, Kerlin AM, Andermann ML, Hood G, Wetzel AW, Yurgenson S, Soucy ER, Kim HS, Reid RC (2011) Network anatomy and in vivo physiology of visual cortical neurons. Nature 471(7337):177–182. doi:10.1038/nature09802
Eckhorn R, Bauer R, Jordan W, Brosch M, Kruse W, Munk M, Reitboeck HJ (1988) Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex? Multiple electrode and correlation analyses in the cat. Biol Cybern 60(2):121–130
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2010) Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 33(1):1–22
Fritz CO, Morris PE, Richler JJ (2012) Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. J Exp Psychol Gen 141(1):2–18. doi:10.1037/a0024338
Gerhard F, Pipa G, Lima B, Neuenschwander S, Gerstner W (2011) Extraction of network topology from multi-electrode recordings: is there a small-world effect? Front Comput Neurosci 5:4. doi:10.3389/fncom.2011.00004
Gray CM, Singer W (1989) Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(5):1698–1702
Gupta D, Ossenblok P, van Luijtelaar G (2011) Space-time network connectivity and cortical activations preceding spike wave discharges in human absence epilepsy: a MEG study. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(5):555–565. doi:10.1007/s11517-011-0778-3
Haslinger R, Pipa G, Lewis L, Nikolic D, Williams Z, Brown E (2013) Encoding through patterns: regression tree-based neuronal population models. Neural Comput 25(8):1953–1993. doi:10.1162/NECO_a_00464
Jones JP, Stepnoski A, Palmer LA (1987) The two-dimensional spectral structure of simple receptive fields in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol 58(6):1212–1232
Kaiser M (2008) Mean clustering coefficients: the role of isolated nodes and leafs on clustering measures for small-world networks. New J Phys. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/10/8/083042
Laurent G, Naraghi M (1994) Odorant-induced oscillations in the mushroom bodies of the locust. J Neurosci 14(5 Pt 2):2993–3004
Leergaard TB, Hilgetag CC, Sporns O (2012) Mapping the connectome: multi-level analysis of brain connectivity. Front Neuroinformatics 6:14. doi:10.3389/fninf.2012.00014
Loffler G (2008) Perception of contours and shapes: low and intermediate stage mechanisms. Vision Res 48(20):2106–2127. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2008.03.006
Matsui T, Ohki K (2013) Target dependence of orientation and direction selectivity of corticocortical projection neurons in the mouse V1. Front Neural Circuits 7:143. doi:10.3389/fncir.2013.00143
Neuenschwander S, Singer W (1996) Long-range synchronization of oscillatory light responses in the cat retina and lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature 379(6567):728–732. doi:10.1038/379728a0
Niell CM, Stryker MP (2008) Highly selective receptive fields in mouse visual cortex. J Neurosci 28(30):7520–7536. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0623-08.2008
Okatan M, Wilson MA, Brown EN (2005) Analyzing functional connectivity using a network likelihood model of ensemble neural spiking activity. Neural Comput 17(9):1927–1961. doi:10.1162/0899766054322973
Paninski L (2004) Maximum likelihood estimation of cascade point-process neural encoding models. Network 15(4):243–262
Pantev C, Makeig S, Hoke M, Galambos R, Hampson S, Gallen C (1991) Human auditory evoked gamma-band magnetic fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(20):8996–9000
Partzsch J, Schüffny R (2012) Developing structural constraints on connectivity for biologically embedded neural networks. Biol Cybern 106(3):191–200. doi:10.1007/s00422-012-0489-3
Pernice V, Staude B, Cardanobile S, Rotter S (2011) How structure determines correlations in neuronal networks. PLoS Comput Biol 7(5):e1002059. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002059
Pernice V, Deger M, Cardanobile S, Rotter S (2013) The relevance of network micro-structure for neural dynamics. Front Comput Neurosci 7:72. doi:10.3389/fncom.2013.00072
Pillow JW, Shlens J, Paninski L, Sher A, Litke AM, Chichilnisky EJ, Simoncelli EP (2008) Spatio-temporal correlations and visual signalling in a complete neuronal population. Nature 454(7207):995–999. doi:10.1038/nature07140
Quiroga RQ, Nadasdy Z, Ben-Shaul Y (2004) Unsupervised spike detection and sorting with wavelets and superparamagnetic clustering. Neural Comput 16(8):1661–1687. doi:10.1162/089976604774201631
Ringach DL, Bredfeldt CE, Shapley RM, Hawken MJ (2002) Suppression of neural responses to nonoptimal stimuli correlates with tuning selectivity in macaque V1. J Neurophysiol 87(2):1018–1027
Samonds JM, Zhou Z, Bernard MR, Bonds AB (2006) Synchronous activity in cat visual cortex encodes collinear and cocircular contours. J Neurophysiol 95(4):2602–2616. doi:10.1152/jn.01070.2005
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1994) Noise, neural codes and cortical organization. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4(4):569–579
Sporns O, Zwi JD (2004) The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics 2(2):145–162. doi:10.1385/NI:2:2:145
Supek S, Magjarevic R (2011) Neurodynamic measures of functional connectivity and cognition. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(5):507–509. doi:10.1007/s11517-011-0779-2
Toyama K, Kimura M, Tanaka K (1981) Cross-correlation analysis of interneuronal connectivity in cat visual cortex. J Neurophysiol 46(2):191–201
Trousdale J, Hu Y, Shea-Brown E, Josić K (2012) Impact of network structure and cellular response on spike time correlations. PLoS Comput Biol 8(3):e1002408. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002408
Trousdale J, Hu Y, Shea-Brown E, Josić K (2013) A generative spike train model with time-structured higher order correlations. Front Comput Neurosci 7:84. doi:10.3389/fncom.2013.00084
Truccolo W, Eden UT, Fellows MR, Donoghue JP, Brown EN (2005) A point process framework for relating neural spiking activity to spiking history, neural ensemble, and extrinsic covariate effects. J Neurophysiol 93(2):1074–1089. doi:10.1152/jn.00697.2004
Ungerleider L, Mishkin M (1982) Two cortical visual systems. Analysis of visual behavior. MIT, Cambridge, pp 549–586
Wang Z, Shi L, Wan H, Niu X (2011) An information integration model of the primary visual cortex under grating stimulations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 413(1):5–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.120
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442. doi:10.1038/30918
Yu S, Huang D, Singer W, Nikolic D (2008) A small world of neuronal synchrony. Cereb Cortex 18(12):2891–2901. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn047
Zhao Q, Meng Y, XU Z (2012) L1/2 regularized logistic regression. Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 25:721–728
Zheng Y, Wang Q, Danca MF (2014) Noise induced complexity: patterns and collective phenomena in a small-world neuronal network. Cogn Neurodyn 8(2):143–149. doi:10.1007/s11571-013-9257-x
Zhou Z, Bernard MR, Bonds AB (2008) Deconstruction of spatial integrity in visual stimulus detected by modulation of synchronized activity in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci 28(14):3759–3768. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4481-07.2008
Zhu Y, Yao H (2013) Modification of visual cortical receptive field induced by natural stimuli. Cereb Cortex 23(8):1923–1932. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs178
Acknowledgments
These experiments with their associated surgical procedures followed the guidelines of National Institutes of Health and were approved by the Research Ethics Committee and the Animal Care and Use Committee of Zhengzhou University. This study was supported by Grants (U1304602) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and a Grant (122102210102) from the key scientific and technological project of Henan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Niu, X. & Wan, H. Effect of the small-world structure on encoding performance in the primary visual cortex: an electrophysiological and modeling analysis. J Comp Physiol A 201, 471–483 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-0996-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-0996-5