Abstract
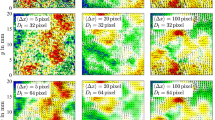
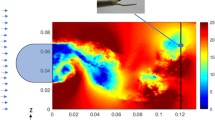
Influences of evaluation bias of the correlation-based interrogation algorithm on particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurement of turbulent flow are investigated. Experimental tests in the Iowa Institute of Hydraulic Research towing tank with a towed PIV system and a surface-piercing flat plate and simulations demonstrate that the experimentally determined mean velocity and Reynolds stress components are affected by the evaluation bias and the gradient of the evaluation bias, respectively. The evaluation bias and gradient of the evaluation bias can both be minimized effectively by using Gaussian digital masks on the interrogation window, so that the measurement uncertainty can be reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 September 1999/Accepted: 7 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, L., Longo, J. & Stern, F. Biases of PIV measurement of turbulent flow and the masked correlation-based interrogation algorithm. Experiments in Fluids 30, 27–35 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000131
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000131