Abstract
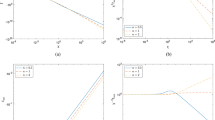
We describe the downstream flow developing at the corner of a partially immersed flat plate, placed perpendicular to a uniform stream. As the flow converges toward the plate centerline, a steady wave, which remains attached to the corner of the plate, develops downstream. Both the amplitude and slope of the wave increase with the downstream distance until the wave either gently spills or plunges depending on the flow conditions. We show that this “corner wave” can be used as a prototypical flow to study the breaking process of two-dimensional deep-water surface waves allowing for the application of a variety of measurement techniques to characterize their evolution. We propose a criterion, based on the Froude number, to determine the transition from spilling to plunging for two-dimensional surface gravity waves consistent with a large set of experimental observations obtained in this flow configuration.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliseda A, Lasheras JC (2006) Effect of buoyancy on the dynamics of a turbulent boundary layer laden with microbubbles. J Fluid Mech 559:307–334
Banner ML, Peregrine DH (1993) Wave breaking in deep water. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 25:373–397
Bonmarin P, Ramamonjiarisoa A (1985) Deformation to breaking of deep water gravity waves. Exp Fluids 3:11–16
Chows VT (1959) Open-channel hydraulics. Mcgraw-Hill, New York, pp 00701–07769
Cokelet ED (1977) Breaking waves. Nature 267:769–774
Drazen D, Melville WK, Lenain L (2008) Inertial scaling of dissipation in unsteady breaking waves. J Fluid Mech 611:307–332
Duncan JH (1981) An experimental investigation of breaking waves produced by a towed hydrofoil. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A Math Phys Sci 377(1770):331–348
Duncan JH (2001) Spilling breakers. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 33:519–547
Duncan JH, Philomin V, Behres M, Kimmel J (1994) The formation of spilling breaking water waves. Physics of Fluids 6(8):2558–2560
Duncan JH, Qiao H, Philomin V, Wenz A (1999) Gentle spilling breakers: crest profile evolution. J Fluid Mech 379:191–222
Fontaine E, Tulin MP (1998) On the prediction of nonlinear free-surface flows past slender hulls using 2D+T theory: the evolution of an idea. RTO MP-15
Galvin, Jr CJ (1968) Breaker type on three laboratory beaches. J Geophys Res 73:3651–3659
Hager WH, Mazumder SK (1992) Supercritical flow at abrupt expansions. Proc Inst Civ Eng Water Marit Energy 96:153–166
Hager WH, Yasuda Y (1997) Unconfined expansion of supercritical water flow. J Eng Mech 123:451–457
Iafrati A, Broglia R (2010) Comparisons between 2D+T potential flow models and 3D RANS for planing hull hydrodynamics. In: Proceedings 25th international workshop on water waves and floating bodies, pp 65–69
Richter JP (1970) The notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci. Dover Publications Inc., ISBN 0-486-22573-9
Kiger KT, Duncan JH (2011) Air-entrainment mechanisms in plunging jets and breaking waves. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 44:563–596
Kim D-G (2007) Numerical analysis of free flow past a sluice gate. KSCE J Civ Eng 11(2):127–132
Longuet-Higgins M (1995) On the disintegration of the jet in a plunging breaker. J Phys Oceanogr 25:2458–2462
Martínez-Legazpi P (2011) Corner waves downstream from a partially submerged vertical plate. PhD thesis, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
Martínez-Legazpi P, Rodríguez-Rodríguez J, Korobkin A, Lasheras JC (2012) Formation of corner waves in the wake of a partially submerged bluff body. J Fluid Mech (submitted to)
Mauer BD, Bolster DT, Linden PF (2010) Intrusive gravity currents between two stably stratified fluids. J Fluid Mech 647:53–69
Melville WK (1996) The role of surface-wave breaking in air–sea interaction. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 28:279–321
Melville WK, Rapp JH (1988) The surface velocity field in steep and breaking waves. J Fluid Mech 189:1–22
Molland A (2008) The maritime engineering reference book. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, p 599. ISBN: 978-0-7506-8987-8
Montes JS (1997) Irrotational flow and real fluid effects under planar sluice gates. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 123:219–232
Munk MM (1924) The aerodynamic forces on airship hulls. NACA report 184
Newman JN (1977) Marine hydrodynamics. MIT Press, Cambridge, p 29. ISBN 0-262-14026-8
Oh S, et al (2005) Experimental investigation of breaking criteria of deep water wind waves under strong wind action. Appl Ocean Res 27:235–250
Rapp JH, Melville WK (1990) Laboratory measurements of deep-water breaking waves. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 331:735–800
Rodríguez-Rodríguez J, Marugán-Cruz C, Aliseda A, Lasheras JC (2011) Dynamics of large turbulent structures in a steady breaker. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 35:301–310
Roth A, Hager WH (1999) Underflow of a standard sluice gate. Exp Fluids 27:339–350
Schultz WW, Huh J, Griffin OM (1994) Potential energy in steep and breaking waves. J Fluid Mech 278:201–228
Shakeri M, Maxeiner E, Fu T, Duncan JH (2009) An experimental examination of the 2D+T approximation. J Ship Res 53:59–67
Shakeri M, Tavakolinejad M, Duncan JH (2009) An experimental investigation of divergent bow waves simulated by a 2D+T technique. J Fluid Mech 634:217–243
Sumer BM, Fredsoe J (1997) Hydrodynamics around cylindrical structures. World Scientific, Singapore, p 129. ISBN: 981022898
Tulin MP (1957) Theory of slender surface planing at high speeds. Schiffstechnik 4, Heft 21, pp 125–133
Tulin MP, Wu M (1997) Divergent bow waves. In: Proceedings of the 21st symposium on naval hydrodynamics, pp 661–669
Wagner H (1932) Über Stoβ und Gleitvorgänge ander Oberfläche von Flüssigkeiten. ZAMM 12:193–215
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the ONR under contract N00014-05-1-0121 and the Spanish Ministry of Science through grant: DPI2011-28356-C03-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Legazpi, P., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J., Marugán-Cruz, C. et al. Plunging to spilling transition in corner surface waves in the wake of a partially submerged vertical plate. Exp Fluids 54, 1437 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1437-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1437-7