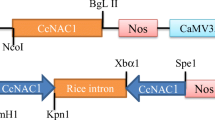
Abstract
The xyloglucan endotransglycosylase gene RcXET of China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.) and the MtDREB1C gene of Medicago truncatula Gaertn. were pyramided into the plant expression vector pBin438 and transformed into China Rose. Southern blot and Northern blot analyses showed that the heterologous gene MtDREB1C was integrated into the genome of surviving transgenic rose plants and expressed at different levels. Real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that robust expression of the congenetic gene RcXET was activated in the five surviving transgenic rose plants. The performance of the five transgenic lines under freezing and drought stress was superior to that of non-transformed controls. Thus, pyramiding of the genes MtDREB1C and RcXET in China Rose was more effective to enhance freezing and drought tolerance than untransformed controls. A positive correlation was observed between the expression of RcXET and the growth rate in contrast to the non-transgenic plants. The physiological assay showed that co-expression had greater effects on EC%, contents of proline, soluble sugar, photosynthesis rate, negative water potential, and turgor loss point than activities of POD and SOD under stress. The study also highlights the utility of a simple and rapid approach to express two or even more genes in one expression vector.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar M, Jaiswal A, Taj G et al (2012) DREB1/CBF transcription factors: their structure, function and role in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. J Genet 91(3):385–395
Bartlett MK, Scoffoni C, Sack L (2012) The determinants of leaf turgor loss point and prediction of drought tolerance of species and biomes: a global meta-analysis. Ecol Lett 15:393–405
Borriss R, Buettner K, Maentsaelae P (1990) Structure of the β-1,3-1,4-glucanase gene of Bacillus macerans: homologies to other β-glucanases. Mol Gen Genet 222:278–283
Campbell P, Braam J (1999) In vitro activities of four xyloglucan endotransglycosylases from Arabidopsis. Plant J 8:371–382
Carins Murphy MR, Jordan GJ, Brodribb TJ (2012) Acclimation to humidity modifies the link between leaf size and the density of veins and stomata. Plant Cell Environ 37(1):124–131
Charity JA, Hughes P, Anderson MA, Bittisnich DJ, Whitecross M, Higgins TJV (2005) Pest and disease protection conferred by expression of barley beta-hordothionin and Nicotiana alata proteinase inhibitor genes in transgenic tobacco. Funct Plant Biol 32:35–44
Chen JR, Liu R, Wang HF (2006) Plant regeneration of transgenic China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.) from organogenic callus. For Stud China 8:92–97
Chen JR, Lü JJ, Wang HF (2008) Rapid and efficient gene splicing using megaprimer-based protocol. Mol Biotechnol 40:224–230
Chen JR, Lü JJ, Wang TX, Chen SY, Wang HF (2009a) Activation of a DRE-binding transcription factor from Medicago truncatula by deleting a Ser/Thr-rich region. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 45:1–11
Chen JR, Xiong XY, Wang TX, Lü JJ, Chen SY, Wang HF (2009b) Rapid construction of a plant RNA interference expression vector for hairpin RNA-mediated targeting using a PCR-based method. DNA Cell Biol 28(12):605–613
Chen JR, Lü JJ, Liu R, Xiong XY, Wang TX, Chen SY, Guo LB, Wang HF (2010) DREB1C from Medicago truncatula enhances freezing tolerance in transgenic M. truncatula and China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.). Plant Growth Regul 60(3):199–211
Chen JR, Deng ZN, Chen YB, Hu BW, Lü JJ, Long YL, Xiong XY (2012) Construction of tandem repeats of DNA fragments by a polymerase chain reaction-based method. DNA Cell Biol 31(4):600–606
Chen JR, Wu L, Hu BW, Yi X, Liu R, Deng ZN, Xiong XY (2014) The influence of plant growth regulators and light quality on somatic embryogenesis in China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.). J Plant Growth Regul 33(2):295–304
Cho SK, Kim JE, Park J, Eom TJ, Kim WT (2006) Constitutive expression of abiotic stress-inducible hot pepper CaXTH3, which encodes a xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase homolog, improves drought and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. FEBS Lett 580:3136–3144
Choi JY, Seo YS, Kim SJ, Kim WT, Shin JS (2011) Constitutive expression of CaXTH3, a hot pepper xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase, enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stresses without phenotypic defects in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Dotaerang). Plant Cell Rep 30(5):867–877
Cui J, Luo J, van der Werf W, Ma Y, Xia J (2011) Effect of pyramiding Bt and CpTI genes on resistance of cotton to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae) under laboratory and field conditions. J Econ Entomol 104:673–684
de Silva J, Jarman CD, Arrowsmith S, Stronach MS, Chengappa S, Sidebottom C, Reid JSG (1993) Molecular characterization of a xyloglucan-specific endo-(1-4)-β-d-glucanase (xyloglucan endotransglycosylase) from nasturtium seeds. Plant J 3:701–711
Dunse KM, Stevens JA, Lay FT et al (2010) Coexpression of potato type I and II proteinase inhibitors gives cotton plants protection against insect damage in the field. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15011–15015
Faize M, Faize L, Burgos L (2010) Using quantitative real-time PCR to detect chimeras in transgenic tobacco and apricot and to monitor their dissociation. BMC Biotechnol 10(1):53
Geisler M (2010) Transcription and signaling factors in the drought response regulatory network. In: Matthew AJ, Andrew JW (eds) Genes for plant abiotic stress. Wiley, Singapore, p 60
Gilmour SJ, Zarka DG, Stockinger EJ, Salazar MP, Houghton JM, Thomashow MF (1998) Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J 16:433–442
Golmirizaie A, Zhang DP, Nopo L et al (1997) Enhanced resistance to West Indian sweet potato weevil (Euscepes postfaciatus) in transgenic ‘Jewel’ sweet potato with cowpea trypsin inhibitor and snowdrop lectin. Hortic Sci 32:435
Gutha LR, Reddy AR (2008) Rice DREB1B promoter shows distinct stress-specific responses, and the over-expression of cDNA in tobacco confers improved abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 68:533–555
Han Y, Wang W, Sun J, Wang RR, Zhang X, Han F, Hu Z (2013) Populus euphratica XTH overexpression enhances salinity tolerance by the development of leaf succulence in transgenic tobacco plants. J Exp Bot 64(14):4225–4238
Hsieh TH, Lee JT, Yang PT, Chiu LH, Charng YY, Wang YC, Chan MT (2002) Heterology expression of the Arabidopsis C-repeat/dehydration response element binding factor 1 gene confers elevated tolerance to chilling and oxidative stresses in transgenic tomato. Plant Physiol 129(3):1086–1094
Jaglo-Ottosen KR, Gilmour SJ, Zarka DG, Schabenberger O, Thomashow MF (1998) Arabidopsis CBF1 over-expression induces COR genes and enhances freezing tolerance. Sci 280:104–106
Johansson P, Brumer H, Baumann MJ, Kallas AM, Henriksson H, Dennan SE, Teeri TT, Jones A (2004) Crystal structures of a poplar xyloglucan endotransglycosylase reveal details of transglycosylation acceptor binding. Plant Cell Online 16(4):874–886
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Improving drought, salt and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat Biotech 17:287–291
Kim CK, Chung JD, Park SH, Burrell AM, Kamo KK, Byrne DH (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Rosa hybrida using the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 78:107–111
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Medina J, Catalá R, Salinas J (2001) Developmental and stress regulation of RCI2A and RCI2B, two cold-inducible genes of Arabidopsis encoding highly conserved hydrophobic proteins. Plant Physiol 125:1655–1656
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 15:473–497
Novillo F, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Salinas J (2004) CBF2/DREB1C is a negative regulator of CBF1/DREB1B and CBF3/DREB1A expression and plays a central role in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(11):3985–3990
Okazawa K, Sato Y, Nakagawa T, Asada K, Kato I, Tomita E, Nishitani K (1993) Molecular cloning and cDNA sequencing of endoxyloglucan transferase, a novel class of glycosyltransferase that mediates molecular grafting between matrix polysaccharides in plant cell walls. J Biol Chem 268:25364–25368
Potter I, Fry S (1993) Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase activity in pea internodes. Plant Physiol 103:235–241
Purugganan MM, Braam J, Fry SC (1997) The Arabidopsis TCH4 xyloglucan endotransglycosylase. Substrate specificity, pH optimum, and cold tolerance. Plant Physiol 115:181–190
Ravikumar G, Manimaran P, Voleti SR, Subrahmanyam D, Sundaram RM, Bansal KC, Viraktamath BC, Balachandran SM (2014) Stress-inducible expression of AtDREB1A transcription factor greatly improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic indica rice. Transgenic Res 23(3):421–439
Santamaria ME, Cambra I, Martinez M, Pozancos C, González-Melendi P, Grbic V, Castañera P, Ortego F, Diaz I (2012) Gene pyramiding of peptidase inhibitors enhances plant resistance to the spider mite Tetranychus urticae. PLoS One 7(8):e43011
Senthilkumar R, Cheng CP, Yeh KW (2010) Genetically pyramiding protease-inhibitor genes for dual broad-spectrum resistance against insect and phytopathogens in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biotech J 8:65–75
Shen YG, Zhang WK, Yan DQ, Du BX, Zhang JS, Liu Q, Chen SY (2003) Characterization of a DRE-binding transcription factor from a halophyte Atriplex hortensis. Theor Appl Genet 107:155–161
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Smith RC, Fry SC (1991) Endotransglycosylation of xyloglucans in plant cell suspension cultures. Biochem J 279:529–535
Stockinger EJ, Gilmour SJ, Thomashow MF (1997) Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1035–1040
Thompson JE, Fry SC (2001) Restructuring of wall-bound xyloglucan by transglycosylation in living plant cells. Plant J 26(1):23–34
Vergne P, Maene M, Gabant G, Chauvet A, Debener T, Bendahmane M (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and transformation of the diploid Rosa chinensis cv Old Blush. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100:73–81
Wang JJ, Mo WP, Jia WS, Liu GJ (2013) The relationship of grape leaf stomatal conductance and water potential with leaf position under drought conditions. Sci Agric Sinica 46(10):2151–2158
Xu W, Purugganan MM, Polisensky DH, Antosiewicz DM, Fry SC, Braam J (1995) Arabidopsis TCH4, regulated by hormones and the environment, encodes a xyloglucan endotransglycosylase. Plant Cell 7:1555–1567
Xu W, Campbell P, Vargheese AK, Braam J (1996) The Arabidopsis XET-related gene family: environmental and hormonal regulation of expression. Plant J 9(6):879–889
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264
Yang W, Liu XD, Chi XJ, Wu CA, Li YZ, Song LL, Liu XM, Wang YF, Wang FW, Zhang C, Liu Y, Zong JM, Li HY (2011) Dwarf apple MbDREB1 enhances plant tolerance to low temperature, drought, and salt stress via both ABA-dependent and ABA-independent pathways. Planta 233:219–229
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31071826, 31272208), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 20100471215 and 201104473), and Hunan innovation fund for graduates (CX2015B271). English-language editing was supplied by Edanz Editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ji-Ren Chen, Yan-Bin Chen, and Monika Ziemiańska have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JR., Chen, YB., Ziemiańska, M. et al. Co-expression of MtDREB1C and RcXET Enhances Stress Tolerance of Transgenic China Rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.). J Plant Growth Regul 35, 586–599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9564-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9564-z