Abstract
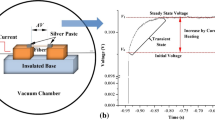
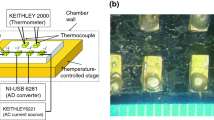
This work reports on the development of a Johnson noise electro-thermal (JET) technique to directly characterize the thermal conductivity of one-dimensional micro-/nanoscale materials. In this technique, the to-be-measured micro-/nanoscale sample is connected between two electrodes and is subjected to steady-state Joule heating. The average temperature rise of the sample is evaluated by simultaneously measuring the Johnson noise over it and its electrical resistance. The system’s Johnson noise measurement accuracy is evaluated by measuring the Boltzmann constant (k B). Our measured k B value (1.375 × 10−23 J/K) agrees very well with the reference value of 1.381 × 10−23 J/K. The temperature measurement accuracy based on Johnson noise is studied against the resistance temperature detector method, and sound agreement (4 %) is obtained. The thermal conductivity of a glass fiber with a diameter of 8.82 μm is measured using the JET technique. The measured value 1.20 W/m K agrees well with the result using a standard technique in our laboratory. The JET technique provides a very compelling way to characterize the thermophysical properties of micro-/nanoscale materials without calibrating the sample’s resistance–temperature coefficient, thereby eliminating the effect of resistance drift/change during measurement and calibration. Since JET technique does not require resistance–temperature correlation, it is also applicable to semi-conductive materials which usually have a nonlinear I–V relation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Yi, L. Lu, D.L. Zhang, Z.W. Pan, S.S. Xie, Phys. Rev. B 59, R9015 (1999)
T. Choi, D. Poulikakos, J. Tharian, U. Sennhauser, Nano Lett. 6, 1589 (2006)
P. Kim, L. Shi, A. Majumdar, P.L. McEuen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 215502 (2001)
P. Kim, L. Shi, A. Majumdar, P.L. McEuen, Physica B 323, 67 (2002)
L. Shi, D. Li, C. Yu, W. Jang, D. Kim, Z. Yao, P. Kim, A. Majumdar, J. Heat Transf. 125, 881 (2003)
J. Hou, X. Wang, L. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 152504 (2006)
J. Guo, X. Wang, D.B. Geohegan, G. Eres, C. Vincent, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 113505 (2008)
X. Feng, X. Wang, X. Chen, Y. Yue, Acta Mater. 59, 1934 (2011)
J. Guo, X. Wang, T. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 063537 (2007)
J.B. Johnson, Phys. Rev. 32, 97 (1928)
H. Nyquist, Phys. Rev. 32, 110 (1928)
R. Kisner, C. L. Britton, U. Jagadish, J. B. Wilgen, M. Roberts, T. V. Blalock, D. Holcomb, M. Bobrek, M. N. Ericson, Aerosp. Conf. Proc. 2586 (2004)
M.G. Pepper, J.B. Brown, J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 12, 31 (1979)
S.P. Benz, J.M. Martinis, P.D. Dresselhaus, S.W. Nam, IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 52, 545 (2003)
S.W. Nam, S.P. Benz, P.D. Dresselhaus, C.J. Burroughs, W.L. Tew, D.R. White, J.M. Martinis, IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 54, 653 (2005)
S.P. Benz, J.F. Qu, H. Rogalla, D.R. White, P.D. Dresselhaus, W.L. Tew, S.W. Nam, IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 58, 884 (2009)
S. P. Benz, J. M. Martinis, S. W. Nam, W. L. Tew, D. R. White, in Proceedings Tempmeko 2001: 8th International Symposium on Temperature and Thermal Measurement in Industry and Science, Vol 1 & 2, 37 (2002)
C.J. Borkowski, T.V. Blalock, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 45, 151 (1974)
K.C. Fong, K.C. Schwab, Phys. Rev. X 2, 031006 (2012)
R.H. Dicke, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 17, 268 (1946)
L. Spietz, K.W. Lehnert, I. Siddiqi, R.J. Schoelkopf, Science 300, 1929 (2003)
H. Brixy, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 97, 75 (1971)
C.P. Pickup, Metroloogia 11, 151 (1975)
L. Crovini, A. Actis, R. Galleano, IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 42, 391 (1993)
V.A. Khlus, Sov. Phys. JETP 66, 2179 (1987)
M. Reznikov, M. Heiblum, H. Shtrikman, D. Mahalu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3340 (1995)
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 5th edn. (Wiley, New York, 1976)
H. Lin, S. Xu, X.W. Wang, N. Mei, Small 9, 2585 (2013)
D.F. Santavicca, J.D. Chudow, D.E. Prober, M.S. Purewal, P. Kim, Nano Lett. 10, 4538 (2010)
F. Völklein, H. Reith, T.W. Cornelius, M. Rauber, R. Neumann, Nanotechnology 20, 325706 (2009)
G.Q. Liu, S. Xu, T.T. Cao, H. Lin, Y.Q. Zhang, X.W. Wang, Biopolymers 101, 2019 (2014)
D.R. Lide, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2015, 95th edn. (Boca Raton, 2014)
Acknowledgments
Support of this work by the Army Research Office (W911NF-12-1-0272), Office of Naval Research (N000141210603) and National Science Foundation (CBET1235852, CMMI1264399) is gratefully acknowledged. We are grateful to MO-SCI Corporation for providing the glass fiber samples used in this work. X.W thanks the partial support of the “Taishan Scholar” Program of Shandong, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wang, X. Characterization of thermal transport in one-dimensional microstructures using Johnson noise electro-thermal technique. Appl. Phys. A 119, 871–879 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9056-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9056-9