Abstract
Objectives
To measure the frequency of infraorbital nerve enlargement (IONE) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in European patients suffering from an IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) as compared to patients suffering from non-IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (non-IgG4-ROD).
Methods
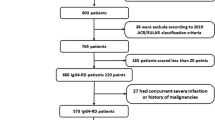
From January 2006 through April 2015, 132 patients were admitted for non-lymphoma, non-thyroid-related orbital inflammation. Thirty-eight had both pre-therapeutic orbital MRI and histopathological IgG4 immunostaining. Fifteen patients were classified as cases of IgG4-ROD and 23 patients as cases of non-IgG4-ROD. Two readers performed blinded analyses of MRI images. The main criterion was the presence of an IONE, defined as the infraorbital nerve diameter being greater than the optic nerve diameter in the coronal section.
Results
IONE was present in 53% (8/15) of IgG4-ROD cases whereas it was never present (0/23) in cases of non-IgG4-ROD (P < 0.0001). IONE was only present in cases where, on MRI, the inflammation of the inferior quadrant was present and in direct contact with the ION canal.
Conclusions
In European patients suffering from orbital inflammation, the presence of IONE on an MRI is a specific sign of IgG4-ROD. Recognition of this pattern may facilitate the accurate diagnosis for clinicians and allow for the adequate management and appropriate care of their patients.
Key points
• IONE on an MRI is a specific sign of IgG4-ROD.
• IONE recognition allows for a quicker diagnosis and appropriate management.
• IONE appears when inflammation is in direct contact with the ION canal.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IgG4-ROD:
-
IgG4-related ophthalmic disease
- non-IgG4-ROD:
-
non-IgG4-related ophthalmic disease
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- ION:
-
Infra-orbital nerve
- IONE:
-
Infra-orbital nerve enlargement
- MIONE:
-
Mild infra-orbital nerve enlargement
References
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A et al (2001) High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 344:732–738
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y et al (2012) A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol Jpn Rheum Assoc 22:1–14
Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C et al (2004) Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease. Scand J Rheumatol 33:432–433
Kitagawa S, Zen Y, Harada K et al (2005) Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration characterizes chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner’s tumor). Am J Surg Pathol 29:783–791
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V (2012) IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 366:539–551
Katsura M, Mori H, Kunimatsu A et al (2012) Radiological features of IgG4-related disease in the head, neck, and brain. Neuroradiology 54:873–882
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y et al (2012) Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol Jpn Rheum Assoc 22:21–30
Wu A, Andrew NH, McNab AA, Selva D (2015) IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: pooling of published cases and literature review. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 15:27
Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Stone JH (2014) Ophthalmic manifestations of IgG4-related disease: single-center experience and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:806–817
McNab AA, McKelvie P (2015) IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Part I: background and pathology. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 31:83–88
Mulholland GB, Jeffery CC, Satija P, Côté DWJ (2015) Immunoglobulin G4-related diseases in the head and neck: a systematic review. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1186/s40463-015-0071-9
Deschamps R, Deschamps L, Depaz R et al (2013) High prevalence of IgG4-related lymphoplasmacytic infiltrative disorder in 25 patients with orbital inflammation: a retrospective case series. Br J Ophthalmol 97:999–1004
Lindfield D, Attfield K, McElvanney A (2012) Systemic immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) disease and idiopathic orbital inflammation; removing “idiopathic” from the nomenclature? Eye 26:623–629
Andrew NH, Sladden N, Kearney DJ, Selva D (2015) An analysis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) among idiopathic orbital inflammations and benign lymphoid hyperplasias using two consensus-based diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD. Br J Ophthalmol 99:376–381
Wallace ZS, Khosroshahi A, Jakobiec FA et al (2012) IgG4-related systemic disease as a cause of “idiopathic” orbital inflammation, including orbital myositis, and trigeminal nerve involvement. Surv Ophthalmol 57:26–33
Katsura M, Morita A, Horiuchi H et al (2011) IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the trigeminal nerve: another component of IgG4-related sclerosing disease? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:E150–E152
Hardy TG, McNab AA, Rose GE (2014) Enlargement of the Infraorbital Nerve. Ophthalmology 121:1297–1303
Sogabe Y, Ohshima K, Azumi A et al (2014) Location and frequency of lesions in patients with IgG4-related ophthalmic diseases. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Für Klin Exp Ophthalmol 252:531–538
Takano K, Yajima R, Seki N et al (2014) A study of infraorbital nerve swelling associated with immunoglobulin G4 Mikulicz’s disease. Mod Rheumatol Jpn Rheum Assoc 24:798–801
Ohshima K-I, Sogabe Y, Sato Y (2012) The usefulness of infraorbital nerve enlargement on MRI imaging in clinical diagnosis of IgG4-related orbital disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol 56:380–382
Tiegs-Heiden CA, Eckel LJ, Hunt CH et al (2014) Immunoglobulin G4-related disease of the orbit: imaging features in 27 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1393–1397
Goto H, Takahira M, Takahira M et al (2015) Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol 59:1–7
R Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 33:363–374
Inoue D, Zen Y, Sato Y et al (2012) IgG4-Related perineural disease. Int J Rheumatol 2012:1–9
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK et al (2012) Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 25:1181–1192
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL et al (2015) International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ 67:1688–1699
Plaza JA, Garrity JA, Dogan A et al (2011) Orbital inflammation with IgG4-positive plasma cells: manifestation of IgG4 systemic disease. Arch Ophthalmol Chic Ill 129:421–428, 1960
Sato Y, Ohshima K, Ichimura K et al (2008) Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology. Pathol Int 58:465–470
Matsuo T, Ichimura K, Sato Y et al (2010) Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive or -negative ocular adnexal benign lymphoid lesions in relation to systemic involvement. J Clin Exp Hematop JCEH 50:129–142
Soussan M, Medjoul A, Badelon I et al (2014) IgG4-related diffuse perineural disease. Neurology 83:1877–1878
Chong VF, Fan YF (1997) Pterygopalatine fossa and maxillary nerve infiltration in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 19:121–125
Nager GT (1984) Neurinomas of the trigeminal nerve. Am J Otolaryngol 5:301–333
Hiwatashi A, Yoshiura T, Togao O et al (2014) Diffusivity of intraorbital lymphoma vs. IgG4-related DISEASE: 3D turbo field echo with diffusion-sensitised driven-equilibrium preparation technique. Eur Radiol 24:581–586
Shah R, Roberson GH, Curé JK (2009) Correlation of MR imaging findings and clinical manifestations in neurosarcoidosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:953–961
Yu W-K, Kao S-C, Yang C-F et al (2015) Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease: clinical features, outcome, and factors associated with response to systemic steroids. Jpn J Ophthalmol 59:8–13
Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A et al (2015) Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1171–1177
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Augustin Lecler, MD. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: retrospective, diagnostic or prognostic study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soussan, J.B., Deschamps, R., Sadik, J.C. et al. Infraorbital nerve involvement on magnetic resonance imaging in European patients with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: a specific sign. Eur Radiol 27, 1335–1343 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4481-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4481-5