Abstract
Objectives
Our aim was to retrospectively evaluate the occurrence of respiratory motion artefacts in patients undergoing dynamic liver magnetic resonance (MR) either with gadoxetate disodium or gadobutrol.
Methods
Two hundred and thirty liver MR studies (115 with gadobutrol, 115 with gadoxetate disodium) were analysed. Respiratory motion artefacts on dynamic 3D T1-weighted MR images (pre-contrast, arterial, venous, and late-dynamic phase) were assessed using a five-point rating scale. Severe motion was defined as a score ≥ 4. Mean motion scores were compared with the Mann-Whitney-U-test. The chi-squared-test was used for dichotomous comparisons.
Results
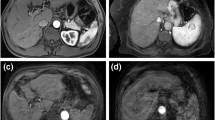
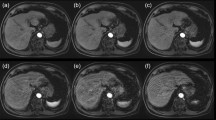
Mean motion scores for gadoxetate disodium and gadobutrol showed no relevant differences for each phase of the dynamic contrast series (pre-contrast: 1.85 ± 0.70 vs. 1.88 ± 0.57, arterial: 1.85 ± 0.81 vs. 1.87 ± 0.74, venous: 1.82 ± 0.67 vs. 1.74 ± 0.64, late-dynamic: 1.75 ± 0.62 vs. 1.79 ± 0.63; p = 0.469, 0.557, 0.382 and 0.843, respectively). Severe motion artefacts had a similar incidence using gadoxetate disodium and gadobutrol (11/460 [2.4 %] vs. 7/460 [1.5 %]; p = 0.341).
Conclusions
Gadoxetate disodium is associated with equivalent motion scores compared to gadobutrol in dynamic liver MRI. In addition, both contrast agents demonstrated a comparable and acceptable rate of severe respiratory motion artefacts.
Key Points
• Gadobutrol and gadoxetate disodium showed comparable motion scores in dynamic phase imaging.
• The incidence of severe motion artefacts was pronounced in arterial phase imaging.
• Adverse respiratory side effects were not recorded in 115 examinations with gadoxetate disodium.


Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42:1208–1236
Bruix J, Sherman M (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology 53:1020–1022
Willatt JM, Hussain HK, Adusumilli S, Marrero JA (2008) MR Imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: challenges and controversies. Radiology 247:311–330
Clavien PA, Lesurtel M, Bossuyt PM, Gores GJ, Langer B, Perrier A (2012) Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an international consensus conference report. Lancet Oncol 13:e11–e22
Albiin N (2012) MRI of Focal Liver Lesions. Curr Med Imaging Rev 8:107–116
Grazioli L, Morana G, Kirchin MA, Schneider G (2005) Accurate differentiation of focal nodular hyperplasia from hepatic adenoma at gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging: prospective study. Radiology 236:166–177
Hammerstingl R, Huppertz A, Breuer J et al (2008) Diagnostic efficacy of gadoxetic acid (Primovist)-enhanced MRI and spiral CT for a therapeutic strategy: comparison with intraoperative and histopathologic findings in focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 18:457–467
Huppertz A, Haraida S, Kraus A et al (2005) Enhancement of focal liver lesions at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging: correlation with histopathologic findings and spiral CT–initial observations. Radiology 234:468–478
Raman SS, Leary C, Bluemke DA et al (2010) Improved characterization of focal liver lesions with liver-specific gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: a multicenter phase 3 clinical trial. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:163–172
Denecke T, Steffen IG, Agarwal S et al (2012) Appearance of hepatocellular adenomas on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol 22:1769–1775
Fujita N, Nishie A, Kubo Y et al (2014) Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical significance of signal heterogeneity in the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3349-9
Davenport MS, Viglianti BL, Al-Hawary MM et al (2013) Comparison of acute transient dyspnea after intravenous administration of gadoxetate disodium and gadobenate dimeglumine: effect on arterial phase image quality. Radiology 266:452–461
Stenver D (2009) Pharmacovigilance: when to report adverse reactions. In: Thomsen H, Webb J (eds) Contrast media safety issues and ESUR guidelines. Springer, Berlin
Davenport MS, Caoili EM, Kaza RK, Hussain HK (2014) Matched within-patient cohort study of transient arterial phase respiratory motion-related artifact in MR imaging of the liver: gadoxetate disodium versus gadobenate dimeglumine. Radiology. doi:10.1148/radiol.14132269:132269
Pietryga JA, Burke LM, Marin D, Jaffe TA, Bashir MR (2014) Respiratory motion artifact affecting hepatic arterial phase imaging with gadoxetate disodium: examination recovery with a multiple arterial phase acquisition. Radiology 271:426–434
Bergmann K, Agris J, Balzer T (2013) Does intravenous administration of gadoxetate disodium have any effect on breath-hold times. Radiology 268:926–927
Davenport MS, Bashir MR, Pietryga JA, Weber JT, Khalatbari S, Hussain HK (2014) Dose-toxicity relationship of gadoxetate disodium and transient severe respiratory motion artifact. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:796–802
Bashir MR, Castelli P, Davenport MS et al (2014) Respiratory motion artifact affecting hepatic arterial phase mr imaging with gadoxetate disodium is more common in patients with a prior episode of arterial phase motion associated with gadoxetate disodium. Radiology. doi:10.1148/radiol.14140386:140386
Holland AE, Goldfarb JW, Edelman RR (1998) Diaphragmatic and cardiac motion during suspended breathing: preliminary experience and implications for breath-hold MR imaging. Radiology 209:483–489
Huppertz A, Balzer T, Blakeborough A et al (2004) Improved detection of focal liver lesions at MR imaging: multicenter comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR images with intraoperative findings. Radiology 230:266–275
Tanimoto A, Lee JM, Murakami T, Huppertz A, Kudo M, Grazioli L (2009) Consensus report of the 2nd International Forum for Liver MRI. Eur Radiol 19(Suppl 5):S975–S989
Haradome H, Grazioli L, Tsunoo M et al (2010) Can MR fluoroscopic triggering technique and slow rate injection provide appropriate arterial phase images with reducing artefacts on gadoxetic acid-DTPA (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced hepatic MR imaging? J Magn Reson Imaging 32:334–340
Ringe KI, Husarik DB, Sirlin CB, Merkle EM (2010) Gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI of the liver: part 1, protocol optimization and lesion appearance in the noncirrhotic liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:13–28
Agrawal MD, Spincemaille P, Mennitt KW et al (2013) Improved hepatic arterial phase MRI with 3-second temporal resolution. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:1129–1136
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Guido M. Kukuk. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luetkens, J.A., Kupczyk, P.A., Doerner, J. et al. Respiratory motion artefacts in dynamic liver MRI: a comparison using gadoxetate disodium and gadobutrol. Eur Radiol 25, 3207–3213 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3736-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3736-x