Abstract
Purpose
To assess the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging (DWI) for prostate cancer detection, using different b-values.
Methods
A total of 201 patients who underwent MR imaging before total prostatectomy were evaluated. MR images were independently assessed by three radiologists. Three combinations of sequences were separately evaluated, as follows: group 1 [T2-weighted images (T2WI) alone], group 2 (T2WI and DWI with a b-value of 1,000 s/mm2), group 3 (T2WI and DWI with a b-value of 2,000 s/mm2). Whole-mount-section histopathological examination was the reference standard. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUCs) and diagnostic performance parameters were determined.
Results
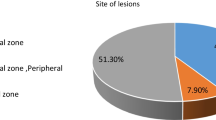
The sensitivity, specificity, and AUC for the detection of prostate cancer were as follows: 52.2%, 80.7%, and 0.694 in group 1; 61.2%, 82.6%, and 0.755 in group 2; 73.2%, 89.7%, and 0.842 in group 3. Group 3 achieved the highest diagnostic performance, followed by group 2 (P < 0.05). In the transition zone, the specificity was lower (P < 0.001) for group 2 (82.2%) than for group 1 (86.2%).
Conclusion
The addition of diffusion-weighted images with a b-value of 2,000 s/mm2 to T2WI can improve the diagnostic performance of MR imaging in prostate cancer detection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley DL, Roberts C, Parker GJM, Logue JP, Hutchnson CE (2004) Prostate cancer: evaluation of vascular characteristics with dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR imaging-initial experience. Radiology 233:709–715
Engelbrecht MR, Huisman HF, Laheiji RJF et al (2003) Discrimination of prostate cancer from normal peripheral zone and central gland tissue by using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 229:248–254
Turnbull LW, Buckley DL, Turnbull LS, Liney GP, Knowles AJ (1999) Differentiation of prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia:correlation between dynamic Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging and histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:311–316
Kim JK, Hong SS, Choi YJ et al (2005) Wash-in rate on the basis of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: usefulness for prostate cancer detection and localization. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:639–646
Li H, Sugimura K, Kaji Y et al (2006) Conventional MRI capabilities in the diagnosis of prostate cancer in the transition zone. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:729–742
Lim HK, Kim JK, Kim KA, Cho KS (2009) Prostate cancer: apparent diffusion coefficient map with T2-weighted images for detection—a multireader study. Radiology 250:145–151
Tanimoto A, Nakashima J, Kohno H et al (2007) Prostate cancer screening: the clinical value of diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic MR imaging in combination with T2-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:146–152
Shimofusa R, Fujimoto H, Akamata H et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:149–153
Hosseinzadah K, Schwarz S (2004) Endorectal diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer to differentiate malignant and benign peripheral zone tissue. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:654–661
Kim CK, Par BK, Lee HM, Kwon GY (2007) Value of diffusion-weighted imaging for the prediction of prostate cancer location at 3 T using a phased-array coil. Invest Radiol 42:842–847
Kim JH, Kim JK, Par BW, Kim N, Cho KS (2008) Apparent diffusion coefficient: prostate cancer versus noncancerous tissue according to anatomical region. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:1173–1179
Kim CK, Par BK, Han JJ, Kang TW, Lee HM (2007) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate at 3 T for differentiation of malignant and benign tissue in transition and peripheral zones: preliminary results. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31:449–454
Lichy MP, Aschoff P, Plathow C et al (2007) Tumor detection by diffusion-weighted MRI and ADC-mapping- initial clinical experiences in comparison to PET-CT. Invest Radiol 42:605–613
Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M (2004) Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 22:275–282
Ichikawa T, Erturk SM, Motosugi U et al (2006) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MRI in colorectal cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:181–184
Ichikawa T, Erturk SM, Motosugi U et al (2007) High-b-value diffusion-weighted MRI for detecting pancreatic adenocarcinoma: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:409–414
Hricak H, Choyke PL, Eberhardt SC, Leibel S, Scardino PT (2007) Imaging prostate cancer: a multidisciplinary perspective. Radiology 243:28–53
Yu KK, Scheidler J, Hricak H et al (1999) Prostate cancer: prediction of extracapusular extension with endorectal MR imaging and three-dimentional proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 213:481–488
Bloch BN, Furman-Haran E, Helbich TH (2007) Prostate cancer: accurate determination of extracapsular extension with high-spatial-resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced and T2-weighted MR imaging—initial results. Radiology 245:176–185
Wang L, Mullerad M, Chen H et al (2004) Prostate cancer: incremental value of endorectal MR imaging findings for prediction of extracapsular extension. Radiology 232:133–139
Sala E, Akin O, Moskowitz C et al (2006) Endorectal MR imaging in the evaluation of seminar vesicle invastion: diagnostic accuracy and multivariate feature analysis. Radiology 238:929–937
Wang L, Hricak H, Kattan M et al (2007) Prediction of seminar vesicle invasion in prostate cancer: incremental value of adding endorectal MR imaging to the Kattan nomogram. Radiology 242:182–188
Schiebler ML, Tomaszewski JE, Bezzi M et al (1989) Prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlation of high-resolution MR and histopathologic findings. Radiology 172:131–137
Turnbull LW, Buckley DL, Turnbull LS, Liney GP, Knowles AJ (1999) Differentiation of prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlation between dynamic Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging and histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:311–316
Kim CK, Park BK, Kim B (2010) High-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 T to detect prostate cancer: comparisons between b values of 1,000 and 2,000 s/mm2. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:W33–W37
Roehl KA, Anterior JAV, Catalona WJ (2002) Serial biopsy results in prostate cancer screening study. J Urol 167:2435–2439
Wefer AE, Hricak H, Vigneron DB et al (2000) Sextant localization of prostate cancer: comparison of sextant biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectoroscopic imaging with step section histology. J Urol 164:400–404
Haider MA, van der Kwast TH, Tanguay J et al (2007) Combined T2-Weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI for Localization of prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:323–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katahira, K., Takahara, T., Kwee, T.C. et al. Ultra-high-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging for the detection of prostate cancer: evaluation in 201 cases with histopathological correlation. Eur Radiol 21, 188–196 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1883-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1883-7