Abstract
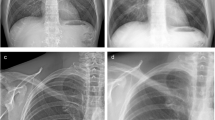
The purpose of this retrospective study was to intra-individually compare the image quality of computed radiography (CR) and low-dose linear-slit digital radiography (LSDR) for supine chest radiographs. A total of 90 patients (28 female, 62 male; mean age, 55.1 years) imaged with CR and LSDR within a mean time interval of 2.8 days ± 3.0 were included in this study. Two independent readers evaluated the image quality of CR and LSDR based on modified European Guidelines for Quality Criteria for chest X-ray. The Wilcoxon test was used to analyse differences between the techniques. The overall image quality of LSDR was significantly better than the quality of CR (9.75 vs 8.16 of a maximum score of 10; p < 0.001). LSDR performed significantly better than CR for delineation of anatomical structures in the mediastinum and the retrocardiac lung (p < 0.001). CR was superior to LSDR for visually sharp delineation of the lung vessels and the thin linear structures in the lungs. We conclude that LSDR yields better image quality and may be more suitable for excluding significant pathological features of the chest in areas with high attenuation compared with CR.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Douglas TS, Sanders V, Pitcher R, van As AB (2008) Early detection of fractures with low-dose digital X-ray images in a pediatric trauma unit. J Trauma 65(1):E4–E7
Lodox Homepage http://www.lodox.com/html/specs.html Last updated: November 27, 2007
Mulligan ME, Flye CW (2006) Initial experience with Lodox Statscan imaging system for detecting injuries of the pelvis and appendicular skeleton. Emerg Radiol 13:129–133
Pitcher RD, van As AB, Sanders V, Douglas TS, Wieselthaler N, Vlok A, Paverd S, Kilborn T, Rode H, Potgieter H, Beningfield SJ (2008) A pilot study evaluating the “STATSCAN” digital X-ray machine in paediatric polytrauma. Emerg Radiol 15:35–42
Maree GJ, Irving BJ, Hering ER (2007) Paediatric dose measurement in a full-body digital radiography unit. Pediatr Radiol 37:990–997
Samei E, Saunders RS, Lo JY, Dobbins JT 3rd, Jesneck JL, Floyd CE, Ravin CE (2004) Fundamental imaging characteristics of a slot-scan digital chest radiographic system. Med Phys 31:2687–2698
McAdams HP, Samei E, Dobbins J 3rd, Tourassi GD, Ravin CE (2006) Recent advances in chest radiography. Radiology 241:663–683
Irving BJ, Maree GJ, Hering ER, Douglas TS (2008) Radiation dose from a linear slit scanning X-ray machine with full-body imaging capabilities. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 130:482–489
Boffard KD, Goosen J, Plani F, Degiannis E, Potgieter H (2006) The use of low dosage X-ray (Lodox/Statscan) in major trauma: comparison between low dose X-ray and conventional x-ray techniques. J Trauma 60:1175–1181 discussion 1181-1173
Gruber M, Uffmann M, Weber M, Prokop M, Balassy C, Schaefer-Prokop C (2006) Direct detector radiography versus dual reading computed radiography: feasibility of dose reduction in chest radiography. Eur Radiol 16:1544–1550
Bacher K, Smeets P, Bonnarens K, De Hauwere A, Verstraete K, Thierens H (2003) Dose reduction in patients undergoing chest imaging: digital amorphous silicon flat-panel detector radiography versus conventional film-screen radiography and phosphor-based computed radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:923–929
Sandborg M, Tingberg A, Dance DR, Lanhede B, Almen A, McVey G, Sund P, Kheddache S, Besjakov J, Mattsson S, Mansson LG, Alm Carlsson G (2001) Demonstration of correlations between clinical and physical image quality measures in chest and lumbar spine screen-film radiography. Br J Radiol 74:520–528
European guidelines on quality criteria for diagnostic radiographic images (1996). In: EUR 16260 EN. European Commission, Brussels
Irving BJ, Maree GJ, Hering ER, Douglas TS (2007) Radiation dose from a linear slit scanning x-ray machine with full body imaging capabilities. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 0:1–5
Quality Criteria for Diagnostic Radiographic Images (1990). In: Working Document XII/173/90. Commission of the European Communities (CEC), Brussels
Exadaktylos AK, Benneker LM, Jeger V, Martinolli L, Bonel HM, Eggli S, Potgieter H, Zimmermann H (2008) Total-body digital X-ray in trauma. An experience report on the first operational full body scanner in Europe and its possible role in ATLS. Injury 39:525–529
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szucs-Farkas, Z., Vock, P. Image quality of supine chest radiographs: intra-individual comparison of computed radiography and low-dose linear-slit digital radiography. Eur Radiol 19, 2156–2162 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1412-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1412-8