Abstract
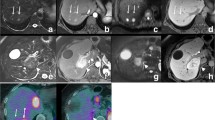
The aim of this study was to compare the diagnostic performance of gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA)-enhanced MR imaging, including dynamic phases and one-hour delayed phase, versus superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-enhanced imaging for detection of liver metastases. Twenty-three patients with 59 liver metastases underwent Gd-BOPTA-enhanced MR imaging (unenhanced, arterial, portal, equilibrium and one-hour delayed phase) using three-dimensional volumetric interpolated imaging and SPIO-enhanced T2-weighted turbo spin–echo and T2*-weighted gradient-echo sequences on a 1.5-T unit. Three observers independently interpreted the three sets of images, i.e. Gd-BOPTA-enhanced dynamic MRI (set 1), delayed phase imaging (set 2) and SPIO-enhanced MRI (set 3). Diagnostic accuracy was evaluated using the alternative-free response receiver operating chracteristic (ROC) analysis. Sensitivity and positive predictive value were also evaluated. The mean accuracy (Az values) and sensitivity of Gd-BOPTA-enhanced delayed phase imaging (0.982, 95.5%) were comparable to those of SPIO-enhanced imaging (0.984, 97.2%). In addition, Az values and sensitivities of both imaging sets were significantly higher than those of Gd-BOPTA-enhanced dynamic images (0.826, 77.4%: p<0.05). There was no significant difference in the positive predictive value among the three image sets. Gd-BOPTA-enhanced delayed phase imaging showed comparable diagnostic performance to SPIO-enhanced imaging for the detection of liver metastases, and had a better diagnostic performance than Gd-BOPTA-enhanced dynamic images.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fusai G, Davidson BR (2003) Management of colorectal liver metastases. Colorectal Dis 5:2–23
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni F, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS (2003) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases in potential candidates for resection: the “test-of-time approach”. Cancer 97:3027–3035
Evrard S, Becouarn Y, Fonck M, Brunet R, Mathoulin-Pelissier S, Picot V (2004) Surgical treatment of liver metastases by radiofrequency ablation, resection, or in combination. Eur J Surg Oncol 30:399–406
Hawksworth J, Geisinger K, Zagoria R, Kavanagh P, Howerton R, Levine EA, Shen P (2004) Surgical and ablative treatment for metastatic adenocarcinoma to the liver from unknown primary tumor. Am Surg 70:512–517
Tanaka K, Shimada H, Ohta M, Togo S, Saitou S, Yamaguchi S, Endo I, Sekido H (2004) Procedures of choice for resection of primary and recurrent liver metastases from colorectal cancer. World J Surg 28:482–487
Soyer P (1996) CT during arterial portography. Eur Radiol 6:349–357
Heiken JP, Weyman PJ, Lee JK, Balfe DM, Picus D, Brunt EM, Flye MW (1989) Detection of focal hepatic masses: prospective evaluation with CT, delayed CT, CT during arterial portography, and MR imaging. Radiology 171:47–51
Ferrucci JT, Stark DD (1990) Iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging of the liver and spleen: review of the first 5 years. AJR Am J Roentgenol155:943–950
Bellin MF, Zaim S, Auberton E, Sarfati G, Duron JJ, Khayat D, Grellet J (1994) Liver metastases: safety and efficacy of detection with superparamagnetic iron oxide MR imaging. Radiology 193:657–663
Ros PR, Freeny PC, Harms SE, Seltzer SE, Davis PL, Chan TW, Stillman AE, Muroff LR, Runge VM, Nissenbaum MA (1995) Hepatic MR imaging with ferumoxides: a multicenter clinical trial of the safety and efficacy in the detection of focal hepatic lesions. Radiology 196:481–488
Hagspiel KD, Neidl KF, Eichenberger AC, Weder W, Marincek B (1995) Detection of liver metastases: comparison of superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced and unenhanced MR imaging at 1.5 T with dynamic CT, intraoperative US, and percutaneous US. Radiology 196:471–478
Soyer P (1996) Will ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging replace CT during arterial portography in the detection of hepatic metastases? Prologue to a promising future. Radiology 200:610–611
Denys A, Arrive L, Servois V, Dubray B, Najmark D, Sibert A, Menu Y (1994) Hepatic tumors: detection and characterization at 1-T MR imaging enhanced with AMI-25. Radiology 193:665–669
Seneterre E, Taourel P, Bouvier Y, Pradel J, Van Beers B, Daures JP, Pringot J, Mathieu D, Bruel JM (1996) Detection of hepatic metastases: ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging versus unenhanced MR imaging and CT during arterial portography. Radiology 200:785–792
Reimer P, Balzer T (2003) Ferucarbotran (Resovist): a new clinically approved RES-specific contrast agent for contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: properties, clinical development, and applications. Eur Radiol 13:1266–1276
Vogl TJ, Schwarz W, Blume S, Pietsch M, Shamsi K, Franz M, Lobeck H, Balzer T, del Tredici K, Neuhaus P, Felix R, Hammerstingl RM (2003) Preoperative evaluation of malignant liver tumors: comparison of unenhanced and SPIO (Resovist)-enhanced MR imaging with biphasic CTAP and intraoperative US. Eur Radiol 13:262–272
Kettritz U, Schlund JF, Wilbur K, Eisenberg LB, Semelka RC (1996) Comparison of gadolinium chelates with manganese-DPDP for liver lesion detection and characterization: preliminary results. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:1185–1190
Vogl TJ, Pegios W, McMahon C et al (1992) Gadobenate dimeglumine—a new contrast agent for MR imaging: preliminary evaluation in healthy volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 158:887–892
Kirchin MA, Pirovano G, Spinazzi A (1998) Gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA): an overview. Invest Radiol 33:798–809
Cavagna FM, Maggioni F, Castelli PM, Dapra M, Imperatori LG, Lorusso V, Jenkins BG (1997) Gadolinium chelates with weak binding to serum proteins. A new class of high-efficiency, general purpose contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 32:780–796
Caudana R, Morana G, Pirovano G, Nicoli N, Portuese A, Spinazzi A, Di Rito R, Pistolesi GF (1996) Focal malignant hepatic lesions: MR imaging enhanced with gadolinium benzyloxypropionictetra-acetate (BOPTA)—preliminary results of phase II clinical application. Radiology 199:513–520
Pirovano G, Vanzulli A, Marti-Bonmati L, Grazioli L, Manfredi R, Greco A, Holzknecht N, Daldrup-Link HE, Rummeny E, Hamm B, Arneson V, Imperatori L, Kirchin MA, Spinazzi A (2000) Evaluation of the accuracy of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175:1111–1120
del Frate C, Bazzocchi M, Mortele KJ, Zuiani C, Londero V, Como G, Zanardi R, Ros PR (2002) Detection of liver metastases: comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced and ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging examinations. Radiology 225:766–772
Kim YK, Lee JM, Kim JS, Lee YH (2004) Gadobenate dimeglumine–enhanced liver MR imaging: value of delayed imaging for the characterization and detection of focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 14:5–13
Rofsky NM, Lee VS, Laub G, Pollack MA, Krinsky GA, Thomasson D, Ambrosino MM, Weinreb JC (1999) Abdominal MR imaging with a volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination. Radiology 212:876–884
Chakraborty DP, Winter LH (1990) Free-response methodology: alternate analysis and a new observer-performance experiment. Radiology 74:873–881
Spinazzi A, Lorusso V, Pirovano G, Taroni P, Kirchin M, Davies A (1998) MultiHance clinical pharmacology: biodistribution and MR enhancement of the liver. Acad Radiol 5(Suppl 1):S86–S89
Schima W, Saini S, Petersein J, Weissleder R, Harisinghani M, Mayo-Smith W, Hahn PF (1999) MR imaging of the liver with Gd-BOPTA: quantitative analysis of T1-weighted images at two different doses. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:80–83
Runge VM, Kenney CM (2000) Phase II. Double-blind, dose-ranging clinical evaluation of gadobenate dimeglumine in focal liver lesions: with analysis of liver and kidney signal change on early and delayed imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:655–664
Sheafer DH, Frederick MG, Paulson EK, Keogan MT, DeLong DM, Nelson RC (1999) Comparison of unenhanced, hepatic arterial-dominant and portal venous-dominant phase helical CT for the detection of liver metastases in women with breast carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:961–968
Ch’en IY, Ktz DS, Jeffrey RB Jr, Daniel BL, Li KC, Beaulieu CF, Mindelzun RE, Yao D, Olcott EW (1997) Do arterial phase helical CT images improve detection or characterization of colorectal liver metastases? J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:391–397
Peterson MS, Baron RL, Marsh JW Jr, Oliver JH III, Confer SR, Hunt LE (2000) Pretransplantation surveillance for possible hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: epidemiology and CT-based tumor detection rate in 430 cases with surgical pathologic correlation. Radiology 217:743–749
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Bonnie Hami for her editorial assistance in the manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.K., Lee, J.M., Kim, C.S. et al. Detection of liver metastases: gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced three-dimensional dynamic phases and one-hour delayed phase MR imaging versus superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol 15, 220–228 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2570-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-004-2570-3