Abstract
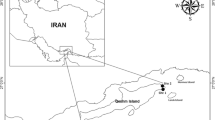
Antarctic benthos has been a main target in Antarctic research, but very few quantitative studies have been carried out in the littoral zone, which may be seasonally covered by macroalgae. In this work, we studied (1) cover and biomass of the macroalgae Iridaea cordata and Adenocystis utricularis, and (2) composition of macrobenthic assemblage associated with these macroalgal species at three locations at King George Island: Mareograph Beach (1 M), Tank’s Bay (2R) and Ardley Bay (3R). Iridaea cordata was collected by completely detaching the algae from the substrate, while A. utricularis was scraped. Adenocystis utricularis covered more than 80 % of the substrate at all locations, while coverage of Iridaea cordata was below 53 % or absent (3R). Fresh biomass of I. cordata was 0.8–61.4 g/individual and 4.7–93.0 g/100 cm2 for A. utricularis. The assemblage associated with both macroalgae differed significantly between sites. The studied fauna was composed mainly of amphipods, gastropods and bivalves. Species diversity was higher in the community associated with A. utricularis. A total of ~27 ind/g DW were found associated with I. cordata, while ~112 ind/g DW were found associated with A. utricularis. The most abundant groups associated with I. cordata were amphipods at 1 M (57 %) and gastropods at 2R (46 %). Both groups were responsible for the dissimilarity between localities (62.50 %). The most abundant groups associated with A. utricularis were the gastropods at all localities reaching up to 82 % at 1 M. This study provides a first baseline on the diversity and abundance of benthic assemblages associated with intertidal macroalgae in the southwest of King George Island.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldea C, Olabarria C, Troncoso JS (2008) Bathymetric zonation and diversity gradient of gastropods and bivalves in West Antarctica from the South Shetland Islands to the Bellingshausen Sea. Deep-Sea Res I 55:350–368
Amsler CD, Rowley RJ, Laur DR, Quetin LB, Ross RM (1995) Vertical distribution of Antarctic peninsular macroalgae: cover, biomass and species composition. Phycologia 34:424–430
Amsler MO, Huang YM, Engl W, McClintock JB, Amsler CD (2015) Abundance and diversity of gastropods associated with dominant subtidal macroalgae from the western Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol. doi:10.1007/s00300-015-1681-4
Arnaud PM, Jazdzewski K, Presler P, Sicinski J (1986) Preliminary survey of benthic invertebrates collected by Polish Antarctic Expeditions in Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). Pol Polar Res 7:7–24
Arntz WE, Brey T, Gallardo VA (1994) Antarctic zoobenthos. In: Ansell AD, Gibson RN, Barnes M (eds) Oceanography and marine biology: an annual review, vol 32. UCL Press, London, pp 241–304
Barnes DKA, Conlan KE (2007) Disturbance, colonization and development of Antarctic benthic communities. Phil Trans R Soc B 362:11–38
Barnes DKA, Rothery P, Clarke A (1996) Colonisation and development in encrusting communities from the Antarctic intertidal and sublittoral. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 196:251–265
Bick A, Arlt G (2013) Description of intertidal macro- and meiobenthic assemblages in Maxwell Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Southern Ocean. Polar Biol 36:673–689
Bone DG (1972) Aspects of the biology of the Antarctic amphipod Bovallia gigantea Pfeffer at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Br Antarc Surv Bull 27:105–122
Boraso A (2013) Elementos para el estudio de las macroalgas de Argentina 1a ed - Comodoro Rivadavia. Universitaria de la Patagonia, Chubut, p 207
Bregazzi PK (1972a) Life cycles and seasonal movements of Cheirimedon femoratus (Pfeffer) and Tryphosella kergueleni (Miers) (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Br Antarct Surv Bull 30:1–34
Bregazzi PK (1972b) Habitat selection by Cheirimedon femoratus (Pfeffer) and Tryphosella kergueleni (Miers) (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Br Antarct Surv Bull 31:21–31
Broitman BR, Navarrete SA, Smith F, Gaines SD (2001) Geographic variation of southeastern Pacific intertidal communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 224:21–34
Cacabelos E, Olabarria C, Incera M, Troncoso JS (2010) Effects of habitat structure and tidal height on epifaunal assemblages associated with macroalgae. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 89:43–52
Castilla JC, Rozbaczylo N (1985) Rocky intertidal assemblages and predation on the gastropod Nacella (Patinigera) concinna at Robert Island, South Shetland, Antarctica. Ser Scient INACH 32:65–73
Chemello R, Milazzo M (2002) Effect of algal architecture on associated fauna: some evidence from phytal molluscs. Mar Biol 140:981–990
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
De Broyer C, Jażdżewska A (2014) Chapter 5.17. Biogeographic patterns of Southern Ocean benthic Amphipods. In: De Broyer C, Koubbi P, Griffiths HJ, Raymond B, Udekem d’Acoz Cd, Van de Putte A, Danis B, David B, Grant S, Gutt J, Held C, Hosie G, Huettmann F, Post A, Ropert-Coudert Y (eds) Biogeographic Atlas of the Southern Ocean. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, Cambridge, pp 155–165
De Broyer C, Koubbi P (2014) Chapter 1.1. The biogeography of the Southern Ocean. In: De Broyer C, Koubbi P, Griffiths HJ, Raymond B, Udekem d’Acoz Cd, Van de Putte A, Danis B, David B, Grant S, Gutt J, Held C, Hosie G, Huettmann F, Post A, Ropert-Coudert Y (eds) Biogeographic Atlas of the Southern Ocean. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, Cambridge, pp 2–9
De Broyer C, Lowry JK, Jazdzewski K, Robert H (2007) Catalogue of the Gammaridean and Corophiidean Amphipoda (Crustacea) of the Southern Ocean with distribution and ecological data. In: De Broyer C (ed) Census of Antarctic Marine Life. Synopsis of the Amphipoda of the Southern Ocean. vol. 1, Part 1. Bull Inst r Sci Nat Belg 77:1–324
Echeverria C, Paiva P (2006) ¿Idiosincrasias del bentos antártico? Oecol Bras 10:165–176
Farías S, Pérez Arisnabarreta S, Vodopivez A, Smichowski P (2002) Levels of essential and potentially toxic trace metals in Antarctic macro algae. Spectrochimica Acta Part B 57:2133–2140
Fortes RR, Absalao RS (2011) Biogeography and connectivity between Western South American and Antarctic marine molluscs. Oecol Aust 15:111–123
Gambi M, Lorenti M, Russo G, Scipione M (1994) Benthic associations of the shallow hard bottoms off Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea: zonation, biomass and population structure. Antarct Sci 6:449–462
Huang YM, McClintock JB, Amsler CD, Peters KJ, Baker BJ (2006) Feeding rates of common Antarctic gammarid amphipods on ecologically important sympatric macroalgae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 329:55–65
Huang YM, McClintock JB, Amsler CD, Baker BJ (2007) Patterns of gammaridean amphipod abundance and species composition associated with dominant subtidal macroalgae from the western Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 30:1417–1430
Ingólfsson A (2005) Community structure and zonation patterns of rocky shores at high latitudes: an interocean comparison. J Biogeogr 32:169–182
Jacobucci GB, Güth AZ, Pereira Leite FP (2008) Experimental evaluation of amphipod grazing over biomass of Sargassum filipendula (Phaeophyta) and its dominant epiphyte. Nauplius 16:65–71
Jazdzewski K, Jurasz W, Kittel W, Presler P, Sicinski J (1986) Abundance and biomass estimates of the benthic fauna in Admiralty Bay, King George Island. Polar Biol 6:5–16
Jazdzewski K, Teodorczyk W, Sicinski J, Kontek B (1991) Amphipod crustaceans as an important component of zoobenthos of the shallow Antarctic sublittoral. Hydrobiologia 223:105–117
Jazdzewski K, De Broyer C, Teodorczyk W, Konopacka A (1992) Survey and distributional patterns of the amphipod fauna of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Pol Polar Res 12:461–472
Jazdzewski K, Weslawski JM, De Broyer C (1995) A comparison of the amphipod faunal diversity in two polar fjords: admiralty Bay, King George Island (Antarctic) and Hornsund, Spitsbergen (Arctic). Pol Arch Hidrobiol 42:367–384
Jazdzewski K, De Broyer C, Pudlarz M, Zielinski D (2001) Seasonal fluctuations of vagile benthos in the uppermost sublittoral of a maritime Antarctic fjord. Polar Biol 24:910–917
Kim JH, Jażdżewska A, Choi HG, Kim W (2014) The first report on Amphipoda from Marian Cove, King George Island, Antarctic. Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 43:106–113
Linse K, Griffiths HJ, Barnes DKA, Clarke A (2006) Biodiversity and biogeography of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic mollusca. DeepSea Res 53:985–1008
Macaya EC, Rothäusler E, Thiel M, Molis M, Wahl M (2005) Induction of defenses and within-alga variation of palatability in two brown algae from the northern-central coast of Chile: effects of mesograzers and UV radiation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 325:214–227
Momo FR, Sahade R, Tatián M (2008) Benthic animal communities of Potter Cove (King George Island, Antarctica): observed patterns and explanatory models. Ber Polarforsch Meereforsch 571:162–167
Nedzarek A, Rakusa-Suszczewski S (2004) Decomposition of macroalgae and the release of nutrients in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biosci 17:16–35
Nikula R, Fraser CI, Spencer HG, Waters JM (2010) Circumpolar dispersal by rafting in two subantarctic kelp-dwelling crustaceans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 405:221–230
Oliveira EC, Absher TM, Pellizzari FM, Oliveira MC (2009) The seaweed flora of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctic. Polar Biol 32:1639–1647
Pabis K, Sicinski J (2010) Distribution and diversity of polychaetes collected by trawling in Admiralty Bay—an Antarctic glacial fiord. Polar Biol 33:141–151
Pugh PJA, Davenport J (1997) Colonisation vs. Disturbance: the effects of sustained ice-scouring on intertidal communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 210:1–21
Quartino ML, Zaixso HE, Boraso de Zaixso AL (2008a) Macroalgal assemblages related to abiotic factors in Potter Cove, King George Island (Isla 25 de Mayo), Antarctica. Ber Polarforsch Meereforsch 571:58–67
Quartino ML, Boraso de Zaixso A, Momo FR (2008b) Macroalgal production and the energy cycle of Potter Cove. Ber Polarforsch Meereforsch 571:68–74
Rauschert M (1989) Atylopsis fragilis n. sp. (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Gammaridea, Eusiridae) aus dem Sublitoral von King George (Sud-Shetland-Inseln). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 65:127–138
Rauschert M (1990) Neue Stenothoidae (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Gammaridea) aus dem Sublitoral von King George (Sud-Shetland-Inseln). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 66:3–39
Rauschert M (1991) Ergebnisse der faunistischen Arbeiten im Benthal von King George Island (Südshetlandinseln, Antarktis). Ber Polarforsch 76:1–75
Rauschert M (1994) Gitanopsilis (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Gammaridea), eine neue Amphilochiden-Gattung aus dem Sublitoral der Konig-Georg-Insel (Sudshetlandinseln). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 70:133–156
Rauschert M (1997) Stomacontion bulbus sp. n. (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Gammaridea, Lysianassidae) aus der Maxwell Bay von King George Island (Sudshetlandinseln). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 73:17–25
Rauschert M, Andres HG (1993) Scaphodactylus, eine neue Stenothoiden-Gattung aus dem Sublitoral der Sud-Shetland-Inseln (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Gammaridae). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 69:347–358
Rauschert M, Andres HG (1994) Scaphodactylus simus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Gammaridea), ein weiterer Vertreter der Stenothoiden aus dem Sublitoral der Konig-Georg-Insel (Sud-Shetland-Inseln). Mitt Zool Mus Berl 70:321–330
Ren X, Huang L (1991) Studies on Gammaridea and Caprellidea (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from the northwest waters off the Antarctic Peninsula. Stud Mar Sin 32:185–323
Richardson MG, Whitaker TM (1979) An Antarctic fast-ice food chain: observations on the interaction of the amphipod Pontogeneia antarctica Chereux with ice-associated micro-algae. Br Antarct Surv Bul 47:107–115
Rothäusler E, Macaya EC, Molis M, Wahl M, Thiel M (2005) Laboratory experiments examining inducible defense show variable responses of temperate brown and red macroalgae. Rev Chil Hist Nat 78:603–614
Saiz JI, Anadon N, Cristobo J, Garcia-Alvarez O, Garcia-Castrillo G, Lopez E, Palacin C, Troncoso JS, Ramos A (2013) Enhancement of the benthic communities around an isolated island in the Antarctic Ocean. Acta Oceanol 32:47–55
Shabica SV (1972) Tidal zone ecology at Palmer Station. Antarct J US 7:184–185
Sicinski J, Jazdzewski K, De Broyer C, Presler P, Ligowski R, Nonato EF, Corbisier TN, Petti MAV, Brito TAS, Lavrado HP, Bazewicz-Paszkowycz M, Pabis K, Jazdzewska A, Campos LS (2011) Admiralty Bay Benthos Diversity - a census of a complex polar ecosystem. Deep-Sea Res II 58:30–48
Stockton W (1973) An intertidal assemblage at Palmer Station. Antarct J US 8:305–307
Thurston MH (1974) Crustacea Amphipoda from Graham Land and the Scotia Arc, collected by Operation Tabarin and the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1944–59. Sci Rep Br Antarc Surv 85:1–89
Torres AC, Veiga P, Rubal M, Sousa-Pinto I (2015) The role of annual macroalgal morphology in driving its epifaunal assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 462:96–106
Veiga P, Rubal M, Sousa-Pinto I (2014) Structural complexity of macroalgae influences epifaunal assemblages associated with native and invasive species. Mar Env Res 101:115–123
Wakabara Y, Tararam A, Valério-Berardo M, Ogihara R (1990) Records of Amphipoda collected during I and III Brazilian Antarctic Expeditions Relat. Int Inst Oceanogr Univ S Paulo 30:1–9
Waller CL (2008) Variability in intertidal communities along a latitudinal gradient in the Southern Ocean. Pol Biol 31:809–816
Waller CL, Barnes DKA, Convey P (2006) Ecological contrasts across an Antarctic land-sea interface. Austral Ecol 31:656–666
Wessels H, Hagen W, Molis M, Wiencke C, Karsten U (2006) Intra- and interspecific differences in palatability of Arctic macroalgae from Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen) for two benthic sympatric invertebrates. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 329:20–33
Weykam G, Goméz I, Wiencke C, Ikenka K, Kloset H (1996) Photosynthetic characteristics and C: N ratios of macroalgae from King George Island (Antarctica). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 204:1–22
Wiencke C, Clayton MN, Gómez I, Iken K, Lunder UH, Amsler CD, Karsten U, Hanelt D, Bischof K, Dunton K (2007) Life strategy, ecophysiology and ecology of seaweeds in polar waters. Rev Env Sci Biotechnol 6:95–126
Zielinski K (1990) Bottom macro-algae of Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctic). Pol Polar Res 11:95–131
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Venezuelan Scientific Antarctic Program, through the 2009 exploration campaign carried out by the Ministerio del Poder Popular para Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación (MCTI) and the Armada Nacional Bolivariana, with the collaboration of the Instituto Antártico Uruguayo. Special thanks to Manuel Caballer and Nelsy Rivero, who helped in the fieldwork. We also wish to thank Sandra López, Humberto Camisotti and Emiliana Mendoza, students at Universidad Simón Bolívar in Caracas, Venezuela for their laboratory assistance and Emanuel Valero for his assistance with the figures. We extend our gratitude to the four anonymous reviewers who provided invaluable comments and literature to significantly improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín, A., Miloslavich, P., Díaz, Y. et al. Intertidal benthic communities associated with the macroalgae Iridaea cordata and Adenocystis utricularis in King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol 39, 207–220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1773-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-015-1773-1