Abstract
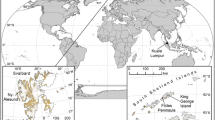
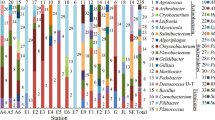
Fungi are known to produce a range of extracellular enzymes and other secondary metabolites. Investment in extracellular enzyme production may be an important element of the survival strategy of these fungi in maritime Antarctic soils. This study focuses on fungi that were isolated from ornithogenic, undisturbed and human-impacted soils collected from the Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctica, during the austral summer in February 2007. We (1) describe fungal diversity based on molecular approaches, (2) describe the thermal characteristics of the fungal isolates, and (3) screen extracellular hydrolase enzyme production (amylase and cellulase) by the isolates. Soil samples were cultured using the Warcup soil plating technique and incubated at 4 and 25 °C to allow basic thermal classification. In total, 101 isolates were obtained. All the isolates were screened at culture temperatures of 4 and 25 °C in order to detect activity of extracellular hydrolase enzymes. At 25 °C, ornithogenic penguin rookery soils recorded the lowest diversity of fungi, with little difference in diversity apparent between the other soils examined. At 4 °C, an undisturbed site recorded the lowest and a human-impacted site the highest diversity of fungi. The majority of the fungi identified in this study were in the mesophilic thermal class. Six strains possessed significant activity for amylase and 13 for cellulase at 25 °C. At 4 °C, four strains showed significant amylase and 22 significant cellulase activity. The data presented increase our understanding of microbial responses to environmental temperature.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams BJ, Bardgett RD, Ayres E, Wall DH, Aislabie J, Bamforth S, Bargagli R, Cary C, Cavacini P, Connell L, Convey P, Fell JW, Frati F, Hogg ID, Newsham KK, O’Donnell A, Russell N, Seppelt RD, Stevens MI (2006) Diversity and distribution of Victoria Land biota. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3003–3018
Ali SH, Alias SA, Siang HY, Smykla J, Pang KL, Guo SY, Convey P (2013) Studies on diversity of soil microfungi in the Horsund area, Spitsbergen. Pol Polar Res 34:39–54
Alias SA, Smykla J, Ming CY, Rizman-Idid M, Convey P (2013) Diversity of microfungi in ornithogenic soils from Beaufort Island, continental Antarctic. Czech Pol Rep 3:44–156
Arenz BE, Blanchette RA (2011) Distribution and abundance of soil fungi in Antarctica at sites on the Peninsula, Ross Sea Region and McMurdo Dry Valleys. Soil Biol Biochem 43:308–315
Arenz BE, Held BW, Jurgens JA, Blanchette RA (2011) Fungal colonization of exotic substrates in Antarctica. Fungal Divers 49:13–22
Azmi OR, Seppelt RD (1997) Fungi of the Windmill Islands, continental Antarctica: effect of temperature, pH and culture media on the growth of selected microfungi. Polar Biol 18:128–134
Azmi OR, Seppelt RD (1998) Broad scale distribution of microfungi in theWindmill Islands, continental Antarctica. Polar Biol 19:92–100
Beyer L, Bolter M (2000) Chemical and biological properties, formation, occurrence and classification of Spodic Cryosols in a terrestrial ecosystem of East Antarctica (Wilkes Land). Catena 39:95–119
Birgisson H, Delgado O, Arroyo LG, Hatti-Kaul R, Mattiasson B (2003) Cold-adapted yeast as producers of cold-active polygalacturonases. Extremophiles 7:185–193
Blackwell M (2011) The fungi: 1, 2, 3 … 5.1 million species? Am J Bot 98:426–438
Block W (1984) Terrestrial microbiology, invertebrates and ecosystems. Antarctic Ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 163–236
Bokhorst S, Huiskes A, Convey P, Aerts R (2007) External nutrient inputs into terrestrial ecosystems of the Falkland Islands and the Maritime Antarctic region. Polar Biol 30:1315–1321
Bradner JR, Gillings M, Nevalainen KHM (1999) Qualitative assessment of hydrolytic activities in Antarctic microfungi grown at different temperatures on solid media. World J Microb Biot 15:131–132
Bridge PD, Spooner BM (2012) Non-lichenized Antarctic fungi: transient visitors or members of a cryptic ecosystem? Fungal Ecol 5:381–394
Brindha RJ, Mohan TS, Immanual G, Jeeva S, Packia Lekshmi NCJ (2011) Studies on amylase and cellulase enzyme activity of the fungal organisms causing spoilage in tomato. Eur J Exp Biol 1:90–96
Broady PA (1996) Diversity, distribution and dispersal of Antarctic terrestrial algae. Biodivers Conserv 5:1307–1335
Brunati M, Rojas JL, Sponga F, Ciciliato I, Losi D, Göttlich E, de Hoog S, Genilloud O, Marinelli F (2009) Diversity and pharmaceutical screening of fungi from benthic mats of Antarctic lakes. Mar Genom 2:43–50
Caretta G, Del Frate G, Mangiarotti AM (1994) A record of Arthrobotrys tortor Jarowaja and Engyodontium album (Limber) de Hoog from Antarctica. Bol Micolog 9:9–13
Carrasco M, Rozas JM, Barahona S, Alcaíno J, Cifuentes V, Baeza M (2012) Diversity and extracellular enzymatic activities of yeasts isolated from King George Island, the sub-Antarctic region. BMC Microbiol 12:251–259
Chown SL, Gaston KJ (2000) Island-hopping invaders hitch a ride with the tourists in South Georgia. Nature 408:905
Chown SL, Hull B, Gaston KJ (2005) Human impacts, energy availability and invasion across Southern Ocean Islands. Global Ecol Biogeogr 14:521–528
Connell L, Redman R, Craig S, Scorzetti G, Iszard M, Rodriguez R (2008) Diversity of soil yeasts isolated from South Victoria Land, Antarctica. Microbial Ecol 56:448–459
Convey P (2013) Antarctic ecosystems. In: Levin SA (ed) Encyclopedia of biodiversity, vol. 1, 2nd edn. San Diego, Elsevier, pp 179–188
Convey P, Smith RIL, Hodgson DA, Peat HJ (2000) The flora of the South Sandwich Islands, with particular reference to the influence of geothermal heating. J Biogeog 27:1279–1295
Convey P, Chown SL, Clarke A, Barnes DKA, Cummings V, Ducklow H, Frati F, Green TGA, Gordon S, Griffiths H, Howard-Williams C, Huiskes AHL, Laybourn-Parry J, Lyons B, McMinn A, Peck LS, Quesada A, Schiaparelli S, Wall D (2014) The spatial structure of Antarctic biodiversity. Ecol Monogr 84:203–244
Cowan DA, Chown SL, Convey P, Tuffin M, Hughes K, Pointing S, Vincent WF (2011) Non-indigenous microorganisms in the Antarctic: assessing the risks. Trends Microbiol 19:540–548
Del Frate G, Caretta G (1990) Fungi isolates from Antarctic material. Polar Biol 11:1–7
Duarte AWF, Dayo-Owoyemi I, Nobre FS, Pagnocca FC, Chaud LCS, Pessoa A, Felipe MGA, Sette LD (2013) Taxonomic assessment and enzymes production by yeasts isolated from marine and terrestrial Antarctic samples. Extremophiles 17:1023–1035
Duncan SM, Farrell RL, Thwaites JM, Held BW, Arenz BE, Jurgens JA, Blanchette RA (2006) Endoglucanase producing fungi isolated from Cape Evans historic expedition hut on Ross Ialsnd, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 8:1212–1219
Duncan SM, Minasaki R, Farrell RL, Thwaites JM, Held BW, Arenz BE, Jurgens JA, Blanchette RA (2008) Screening fungi isolated from historic Discovery Hut on Ross Island, Antarctica for cellulose degradation. Antarct Sci 20:463–470
Egidi E, De Hoog GS, Isola D, Onofri S, Quaedvlieg W, De Vries M, Verkley GJM, Stielow JB, Zucconi L, Selbmann L (2014) Phylogeny and taxonomy of meristematic rock-inhabiting black fungi in the dothideomycetes based on multi-locus phylogenies. Fungal Divers 65:127–165
Farrell RL, Arenz BE, Duncan SM, Held BW, Jurgens JA, Blanchette RA (2011) Introduced and indigenous fungi of the Ross Island historic huts and pristine areas of Antarctica. Polar Biol 34:1669–1677
Fenice M, Selbmann L, Zucconi L, Onofri S (1997) Production of extracellular enzymes by Antarctic fungal strains. Polar Biol 17:275–280
Ferrari BC, Zhang CD, Dorst J (2011) Recovering greater fungal diversity from pristine and diesel fuel contaminated sub-Antarctic soil through cultivation using both a high and a low nutrient media approach. Front Microbiol 2:1–14
Gamundi IJ, Spinedi HA (1988) Ascomycotina from Antarctica. New species and interesting collections from Danco Coast, Antarctic Peninsula. Mycotaxon 33:467–482
German DP, Weintraub MN, Grandy AS, Lauber CL, Rinkes ZL, Allison SD (2011) Optimization of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme methods for ecosystem studies. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1387–1397
Gesheva V, Vasileva-Tonkova E (2012) Production of enzymes and antimicrobial compounds by halophilic Antarctic Nocardioides sp. grown on different carbon sources. World J Microb Biot 28:2069–2076
Greenfield LG (1992) Precepitation nitrogen at Maritime Signy Island and Continental Cape-Bird, Antarctica. Polar Biol 11:649–653
Guminska B, Heinrich Z, Olech M (1994) Macromycetes of the South Shetland Islands (Antarctica). Pol Polar Res 15:103–109
Jongmans AG, Van Breemen N, Lundstrom U, Van Hees PAW, Finlay RD, Srinivasan M, Unestam T, Giesler R, Melkerud PA, Olsson M (1997) Rock-eating fungi. Nature 389:682–683
Kappen L (1993) Lichens in the Antarctic region. Antarctic microbiology. Wiley, New York, pp 433–490
Kasieczka-Burnecka M, Kuc K, Kalinowska H, Knap M, Turkiewicz M (2007) Purification and characterization of two cold-adapted extracellular tannin acyl hydrolases from an Antarctic strain Verticillium sp. P9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:77–89
Kerry E (1990) Microorganisms colonizing plants and soil subject to different degrees of human activity, including petroleum contamination in the Vestfold Hills and MacRobertson Land, Antarctica. Polar Biol 10:423–430
Krishnan A, Alias SA, Michael Wong CVL, Pang KL, Convey P (2011) Extracellular hydrolase enzyme production by soil fungi from King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol 4:1535–1542
Loperena L, Soria V, Varela H, Lupo S, Bergalli A, Guigou M, Pellegrino A, Bernardo A, Calviño A, Rivas F, Batista S (2012) Extracellular enzymes produced by microorganisms isolated from maritime Antarctica. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2249–2256
Margesin R, Miteva V (2011) Diversity and ecology of psychrophilic microorganisms. Res Microbiol 162:346–361
Margesin R, Gander S, Zacke G, Gounot AM, Schinner F (2003) Hydrocarbon degradation and enzyme activities of cold-adapted bacteria and yeasts. Extremophiles 7:451–458
Margesin R, Neuner G, Storey KB (2007) Cold-loving microbes, plants, and animals—fundamental and applied aspects. Naturwissenschaften 94:77–99
Marshall WA (1998) Aerial transport of keratinaceous substrate and distribution of the fungus Geomyces pannorum in Antarctic soils. Microbial Ecol 36:212–219
Mercantini R, Marsella R, Moretto D, Finotti E (1993) Keratinophilic fungi in the Antarctic environment. Mycopathologia 169:169–175
Moller C, Dreyfuss MM (1996) Microfungi from Antarctic lichens, mosses and vascular plants. Mycologia 88:922–933
Montemartini Corte A (1991) Funghi di ambienti acquatici. In: Proceedings of the 1st meeting on ‘Biology in Antarctica’ (English summaries). Rome: Scienza e Cultura, Edizioni Universitarie Patavine, pp 67–76
Montemartini Corte A, Caretta G, Del Frate G (1993) Notes on Thelebolus microsporus isolated in Antarctica. Mycotaxon 48:343–358
Newsham KK (2010) The biology and ecology of the liverwort Cephaloziella varians in Antarctica. Antarct Sci 22:131–143
Newsham KK, Bridge PD (2010) Sebacinales are associates of the leafy liverwort Lophozia excisa in the southern maritime Antarctica. Mycorrhiza 20:307–313
Nichols DS, Sanderson K, Buia A, Kamp JV, Holloway P, Bowman JP, Smith M, Nichols CM, Nichols PD, McMeekin DA (2002) Bioprospecting and biotechnology in Antarctica. In: Jabour-Green J, Haward M (eds) The Antarctic: past, present and future, Antarctic CRC research report 28. Hobart, pp 85–103
O’Brien A, Sharp R, Russel NJ, Roller S (2004) Antarctic bacteria inhibit growth of food-borne microorganisms at low temperatures. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:157–167
Miller Jr. OK (2002) Basidiomycetes in Arctic tundra in North America. In: Abstract in seventh international mycological congress proceedings, p 18
Onofri S, Tosi S (1992) Arthrobotrys ferox sp. nov. a springtail-capturing hyphomycete from continental Antarctica. Mycotaxon 44:445–451
Onofri S, Rambelli A, Maggi O, Persiani AM, Riess S, Tosi S, Grasselli E (1991) Micologia del Suolo. In: Battaglia B, Bisol PM, Varotto V (eds) Proceedings of the 1st meeting on Biology in Antarctica (English summaries), Rome CNR, 22–23 June 1989. Scienza e Cultura. Edizioni Universitarie Patavine, Padua, pp 55–65
Onofri S, Pagano S, Zucconi L, Tosi L (1999) Friedmanniomyces endolithicus (Fungi, Hyphomycetes), anam.-gen. and sp. nov., from continental Antarctica. Nova Hedwigia 68:175–181
Onofri S, Fenice M, Cicalini AR, Tosi S, Magrino A, Pagano S, Selbmann L, Zucconi L, Vishniac HS, Ocampo-Friedmann R, Friedmann EI (2000) Ecology and biology of microfungi from Antarctic rocks and soils. Ital J Zool 67:163–167
Onofri S, Zucconi L, Tosi S (2007a) Continental Antarctic fungi. ECHING bei Munchen: IHW-Verlag, ISBN: 978-3-930167-67-8, pp 1–247
Onofri S, Selbmann L, de Hoog GS, Grube M, Barreca D, Ruisi S, Zucconi L (2007b) Evolution and adaptation of fungi at the boundaries of life. Adv Space Res 40:1657–1664
Peck LS, Convey P, Barnes DKA (2006) Environmental constraints on life histories in Antarctic ecosystems: tempos, timings and predictability. Biol Rev 81:75–109
Pegler DN, Spooner BM, Smith RIL (1980) Higher fungi of Antarctica, the subantarctic zone and Falkland Islands. Kew Bull 35:499–562
Pickard J, Seppelt RD (1984) Phytogeography of Antarctica. J Biogeogr 11:83–102
Quanfu W, Yanhua H, Yu D, Peisheng Y (2012) Purification and biochemical characterization of a cold-active lipase from Antarctic sea ice bacteria Pseudoalteromonas sp. NJ 70. Mol Biol Rep 39:9233–9238
Read DJ, Perez-Moreno J (2003) Mycorrhizas and nutrient cycling in ecosystems: a journey towards relevance? New Phytol 157:475–492
Ruisi S, Barreca D, Selbmann L, Zucconi L, Onofri S (2007) Fungi in Antarctica. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 5:127–141
Selbmann L, de Hoog GS, Mazzaglia A, Friedmann EI, Onofri S (2005) Fungi at the edge of life: cryptoendolithic black fungi from Antarctic deserts. Stud Mycol 51:1–32
Selbmann L, Isola D, Zucconi L, Onofri S (2011) Resistance to UV-B induced DNA damage in extreme-tolerant cryptoendolithic Antarctic fungi: detection by PCR assays. Fungal Biol 115:937–944
Selbmann L, Isola D, Fenice M, Zucconi L, Sterflinger K, Onofri S (2012) Potential extinction of Antarctic endemic fungal species as a consequence of global warming. Sci Total Environ 438:127–134
Selbmann L, Grube M, Onofri S, Isola D, Zucconi L (2013) Antarctic epilithic lichens as niches for black meristematic fungi. Biology 2:784–797
Singh PN, Singh SK, Sharma PK (2013) Pigment, fatty acid and extracellular enzyme analysis of a fungal strain Thelebolus microsporus from Larsemann Hills, Antarctica. Polar Rec 50:31–36
Smith RIL (1984) Terrestrial plant biology of the Sub-Antarctic and Antarctic. Antarctic Ecology. Academic Press, London, pp 61–162
Smith RIL (1994) Species-diversity and resource relationships of South Georgian fungi. Antarct Sci 6:45–52
Strauss SL, Garcia-Pichel F, Day TA (2012) Soil microbial carbon and nitrogen transformations at a glacial foreland on Anvers Island, Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 35:1459–1471
Tatur A, Myrcha A, Niegodzisz J (1997) Formation of abandoned penguin rookery ecosystems in the Maritime Antarctic. Polar Biol 17:405–417
Thomas AR, Hill EC (1976) Aspergillus fumigatus and supersonic aviation. I. Growth of A. fumigatus. Int Biodeterior 12:87–94
Tortella GR, Rubilar O, Gianfreda L, Valenzuela E, Diez MC (2008) Enzymatic characterization of Chilean native wood-rotting fungi for potential use in the bioremediation of polluted environments with chlorophenols. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2805–2818
Tosi S, Casado B, Gerdol R, Caretta G (2002) Fungi isolated from Antarctic mosses. Polar Biol 25:262–268
Tosi S, Onofri S, Brusoni M, Zucconi L, Vishniac H (2005) Response of the Antarctic soil fungal assemblages to the experimental warming and reduction of UV radiation. Polar Biol 28:470–482
Upson R, Read DJ, Newsham KK (2007) Widespread association between the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Rhizoscyphus ericae and a leafy liverwort in the maritime and sub-Antarctic. New Phytol 176:460–471
Upson R, Newsham KK, Read DJ (2008) Root-fungal associations of Colobanthus quitensis and Deschampsia antarctica in the maritime and sub-Antarctic. Arct Antarct Alp Res 40:592–599
Vega K, Villena GK, Sarmiento VH, Ludeña Y, Vera N, Gutiérrez-Correa M (2012) Production of alkaline cellulase by fungi isolated from an undisturbed rain forest of Peru. Biotechnol Res Int. doi:10.1155/2012/934325
Vishniac HS, Onofri S (2002) Cryptococcus antarcticus var. circumpolaris var. nov., a basidiomycetous yeast from Antarctica. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83:233–235
Warcup JH (1950) The soil plate method for isolation of fungi from soil. Nature 166:117–118
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and application. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Williams PG, Roser DJ, Seppelt RD (1994) Mycorrhizas of hepatics in continental Antarctica. Mycol Res 98:34–36
Wong CMVL, Tam HK, Alias SA, Gonzalez M, Gonzalez-Rocha G, Dominguez-Yevenes M (2011) Pseudomonas and Pedobacter isolates from King George Island (Antarctica) inhibited the growth of foodborne pathogens. Pol Polar Res 32:3–14
Yergeau E, Kang S, He Z, Zhou J, Kowalchuck GA (2007) Functional microarray analysis of nitrogen and carbon cycling genes across and Antarctic latitudinal transect. ISME J 1:163–179
Zucconi L, Pagano S, Fenice M, Selbmann L, Tosi S, Onofri S (1996) Growth temperature preferences of fungal strains from Victoria Land, Antarctica. Polar Biol 16:53–61
Zucconi L, Ripa C, Selbmann L, Onofri S (2002) Effects of UV on the spores of the fungal species Arthrobotrys oligospora and A. ferox. Polar Biol 25:500–505
Acknowledgments
We thank the Malaysian Antarctic Research Program and the University of Malaya for support and the provision of research facilities, and the Academy of Sciences Malaysia, Sultan Mizan Antarctica Research Award, Postgraduate Research Fund PG041-2013A, UMRG RG007-2012C and the Instituto Antarctico Chileno for logistics and support of the fieldwork. PC is supported by NERC core funding to the BAS core ‘Ecosystems’ programme and also by a Visiting Professorship to the University of Malaya. We thank anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and Peter Fretwell, British Antarctic Survey for providing South Shetland Islands map. This paper also contributes to the SCAR ‘Antarctic Thresholds—Ecosystem Resilience and Adaptation’ research programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited contribution on Life in Antarctica: Boundaries and Gradients in a Changing Environment as the main theme of the XIth SCAR Biology Symposium. J. -M. Gili and R. Zapata Guardiola (Guest Editors).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, A., Convey, P., Gonzalez-Rocha, G. et al. Production of extracellular hydrolase enzymes by fungi from King George Island. Polar Biol 39, 65–76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1606-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-014-1606-7