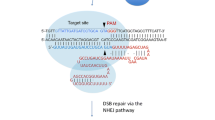
Abstract
RNA-guided endonuclease-mediated targeted mutagenesis using the clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 system has been successful at targeting specific loci for modification in plants. While polyploidy is an evolutionary mechanism enabling plant adaptation, the analysis of gene function in polyploid plants has been limited due to challenges associated with generating polyploid knockout mutants for all gene copies in polyploid plant lines. This study investigated whether CRISPR/Cas9 mediated targeted mutagenesis can generate nulliplex tetraploid mutant lines in Arabidopsis thaliana, while also comparing the relative efficiency of targeted mutagenesis in tetraploid (4x) versus diploid (2x) backgrounds. Using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to generate knockout alleles of the TTG1 gene, we demonstrate that homozygous nulliplex mutants can be directly generated in tetraploid Arabidopsis thaliana plants. CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing now provides a route to more efficient generation of polyploid mutants for improving understanding of genome dosage effects in plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Storme N, Keceli BN, Zamariola L, Angenon G, Geelen D (2016) CENH3-GFP: a visual marker for gametophytic and somatic ploidy determination in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 16:1
Fauser F, Schiml S, Puchta H (2014) Both CRISPR/Cas-based nucleases and nickases can be used efficiently for genome engineering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 79:348–359
Fort A, Ryder P, McKeown PC, Wijnen C, Aarts MG, Sulpice R, Spillane C (2016) Disaggregating polyploidy, parental genome dosage and hybridity contributions to heterosis in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 209:590–599
Walker AR, Davison PA, Bolognesi-Winfield AC, James CM, Srinivasan N, Blundell TL, Esch JJ, Marks MD, Gray JC (1999) The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 Locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein. Plant Cell 11:1337–1349
Wang Z-P, Xing H-L, Dong L, Zhang H-Y, Han C-Y, Wang X-C, Chen Q-J (2015) Egg cell-specific promoter-controlled CRISPR/Cas9 efficiently generates homozygous mutants for multiple target genes in Arabidopsis in a single generation. Genome Biol 16:144
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Chen, Qi-Jun for kindly providing the vector pHEE401 for subsequent vector construction in this study. This work was supported by grant funding from Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) to CS (Principal Investigator Grant 13/IA/1820), and a postdoctoral fellowship from the Irish Research Council (IRC) to MMH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Neal Stewart.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2017_2125_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure S1: Seed morphology of T2 2x and 4x pHEETTG1 lines. A. Col-0 2x; B. pHEETTG1_2x_#1; C. pHEETTG1_2x_#2; D. pHEETTG1_2x_#3; E Col-0 4x; F. pHEETTG1_4x_#1; G. pHEETTG1_4x_#2; White bar = 1 mm. (PDF 2197 KB)
299_2017_2125_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Figure S2: DNA sequencing and multiple sequence alignment for T2 pHEETTG1 2x and 4x lines. DNA extracted and amplified from progeny of selfed T1 pHEETTG1_2x_#1 and pHEETTG1_4x_#1 plants was used for T2 sequencing A. WT TTG1 sequence; B. T2_pHEETTG1_2x_#1_1; C. T2_pHEETTG1_2x_#1_2; D. T2_pHEETTG1_2x_#1_3; E. T2_pHEETTG1_4x_#1_1; F. T2_pHEETTG1_4x_#1_2; G. Multiple alignment of T2 pHEETTG1_2x_#1 and pHEETTG1_4x_#1 lines. Red line signifies the TTG1 sgRNA sequence , while the green line signifies the PAM site. (PDF 443 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryder, P., McHale, M., Fort, A. et al. Generation of stable nulliplex autopolyploid lines of Arabidopsis thaliana using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Plant Cell Rep 36, 1005–1008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2125-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2125-0