Abstract
Key message
OsWRKY51 functions as a positive transcriptional regulator in defense signaling against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by direct DNA binding to the promoter of defense related gene, OsPR10a.
Abstract
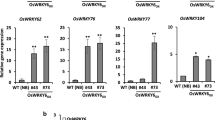
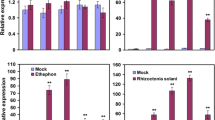
OsWRKY51 in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is induced by exogenous salicylic acid (SA) and inoculation with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). To examine the role of OsWRKY51 in the defense response of rice, we generated OsWRKY51 overexpressing and underexpressing transgenic rice plants. OsWRKY51-overexpressing transgenic rice lines were more resistant to Xoo and showed greater expression of defense-related genes than wild-type (WT) plants, while OsWRKY51-underexpressing lines were more susceptible to Xoo and showed less expression of defense-associated genes than WT plants. Transgenic lines overexpressing OsWRKY51 showed growth retardation compared to WT plants. In contrast, transgenic lines underexpressing OsWRKY51 by RNA interference showed similar plant height with WT plants. Transient expression of OsWRKY51-green fluorescent protein fusion protein in rice protoplasts revealed that OsWRKY51 was localized in the nucleus. OsWRKY51 bound to the W-box and WLE1 elements of the OsPR10a promoter. Based on these results, we suggest that OsWRKY51 is a positive transcriptional regulator of defense signaling and has direct DNA binding ability to the promoter of OsPR10a, although it is reported to be a negative regulator in GA signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruscato P, Nepusz T, Mizzi L, Del Corvo M, Morandini P, Fumasoni I, Michel C, Paccanaro A, Guiderdoni E, Schaffrath U, Morel JB, Piffanelli P, Faivre-Rampant O (2012) OsWRKY22, a monocot WRKY gene, plays a role in the resistance response to blast. Mol Plant Pathol 13:828–841
Bakshi M, Oelmüller R (2014) WRKY transcription factors: jack of many trades in plants. Plant Signal Behav 9:e27700
Banerjee A, Roychoudhury A (2015) WRKY proteins: signaling and regulation of expression during abiotic stress responses. Sci World J 2015:807560
Borun F, Yang S, Du H, Hou X, Zhang J, Liu H, Huang Y (2012) Molecular characterization and functional analysis of plant WRKY genes. Afr J Biotechnol 11:13606–13613
Chen L, Song Y, Li S, Zhang L, Zou C, Yu D (2012) The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant abiotic stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:120–128
Chi Y, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Fan B, Yu JQ, Chen Z (2013) Protein-protein interactions in the regulation of WRKY transcription factors. Mol Plant 6:287–300
Choi C, Hwang SH, Fang IR, Kwon SI, Park SR, Ahn I, Kim JB, Hwang DJ (2015) Molecular characterization of Oryza sativa WRKY6, which binds to W-box-like element 1 of the Oryza sativa pathogenesis-related (PR) 10a promoter and confers reduced susceptibility to pathogens. New Phytol 208:846–859
Chujo T, Takai R, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, Ando S, Minami E, Nagamura Y, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Yasuda M, Nakashita H, Umemura K, Okada A, Okada K, Nojiri H, Yamane H (2007) Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769:497–505
Chujo T, Miyamoto K, Ogawa S, Masuda Y, Shimizu T, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahashi A, Nishizawa Y, Minami E, Nojiri H, Yamane H, Okada K (2014) Overexpression of phosphomimic mutated OsWRKY53 leads to enhanced blast resistance in rice. PLoS One 9:e98737
Ciolkowski I, Wanke D, Birkenbihl RP, Somssich IE (2008) Studies on DNA-binding selectivity of WRKY transcription factors lend structural clues into WRKY-domain function. Plant Mol Biol 68:81–92
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37
Eulgem T (2005) Regulation of the Arabidopsis defense transcriptome. Trends Plant Sci 10:71–78
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Hwang SH, Lee IA, Yie SW, Hwang DJ (2008) Identification of an OsPR10a promoter region responsive to salicylic acid. Planta 227:1141–1150
Hwang SH, Yie SW, Hwang DJ (2011) Heterologous expression of OsWRKY6 gene in Arabidopsis activates the expression of defense related genes and enhances resistance to pathogen. Plant Sci 181:316–323
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsieh SPV, Merca SD (1973) An improved technique for evaluating resistance to rice varieties of Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep 57:537–541
Lee H, Ko YJ, Cha JY, Park SR, Ahn I, Hwang DJ (2013) The C-terminal region of OsWRKY30 is sufficient to confer enhanced resistance to pathogen and activate the expression of defense-related genes. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7:221–230
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331
Liu XQ, Bai XQ, Wang XJ, Chu CC (2007) OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response. J Plant Physiol 164:969–979
Maeo K, Tomiya T, Hayashi K, Akaike M, Morikami A, Ishiguro S, Nakamura K (2001) Sugar-responsible elements in the promoter of a gene for beta-amylase of sweet potato. Plant Mol Biol 46:627–637
Pandey SP, Somssich IE (2009) The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Plant Physiol 150:1648–1655
Peng X, Hu Y, Tang X, Zhou P, Deng X, Wang H, Guo Z (2012) Constitutive expression of rice WRKY30 gene increases the endogenous jasmonic acid accumulation, PR gene expression and resistance to fungal pathogens in rice. Planta 236:1485–1498
Ricachenevsky FK, Sperotto RA, Menguer PK, Fett JP (2010) Identification of Fe-excess-induced genes in rice shoots reveals a WRKY transcription factor responsive to Fe, drought and senescence. Mol Biol Rep 37:3735–3745
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16:1139–1149
Ross CA, Liu Y, Shen QJ (2007) The WRKY gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). J Integr Plant Biol 49:827–842
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–258
Ryu HS, Han M, Lee SK, Cho JI, Ryoo N, Heu S, Lee YH, Bhoo SH, Wang GL, Hahn TR, Jeon JS (2006) A comprehensive expression analysis of the WRKY gene superfamily in rice plants during defense response. Plant Cell Rep 25:836–847
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J et al (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Shimono M, Sugano S, Nakayama A, Jiang CJ, Ono K, Toki S, Takatsuji H (2007) Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance. Plant Cell 19:2064–2076
Shimono M, Koga H, Akagi A, Hayashi N, Goto S, Sawada M, Kurihara T, Matsushita A, Sugano S, Jiang CJ, Kaku H, Inoue H, Takatsuji H (2012) Rice WRKY45 plays important roles in fungal and bacterial disease resistance. Mol Plant Pathol 13:83–94
Tao Z, Liu H, Qiu D, Zhou Y, Li X, Xu C, Wang S (2009) A pair of allelic WRKY genes play opposite roles in rice-bacteria interactions. Plant Physiol 151:936–948
Tao Z, Kou Y, Liu H, Li X, Xia J, Wang S (2011) OsWRKY45 alleles play different roles in abscisic acid signalling and salt stress tolerance but similar roles in drought and cold tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 62:4863–4874
Ülker B, Somssich IE (2004) WRKY transcription factors: from DNA binding towards biological function. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:491–498
Wang H, Hao J, Chen X, Hao Z, Wang X, Lou Y, Peng Y, Guo Z (2007) Overexpression of rice WRKY89 enhances ultraviolet B tolerance and disease resistance in rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 65:799–815
Wang H, Meng J, Peng X, Tang X, Zhou P, Xiang J, Deng X (2015) Rice WRKY4 acts as a transcriptional activator mediating defense responses toward Rhizoctonia solani, the causing agent of rice sheath blight. Plant Mol Biol 89:157–171
Wu X, Shiroto Y, Kishitani S, Ito Y, Toriyama K (2009) Enhanced heat and drought tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings overexpressing OsWRKY11 under the control of HSP101 promoter. Plant Cell Rep 28:21–30
Xie Z, Zhang ZL, Zou X, Huang J, Ruas P, Thompson D, Shen QJ (2005) Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 137:176–189
Xie Z, Zhang ZL, Zou X, Yang G, Komatsu S, Shen QJ (2006) Interactions of two abscisic-acid induced WRKY genes in repressing gibberellin signaling in aleurone cells. Plant J 46:231–242
Yang B, Jiang Y, Rahman MH, Deyholos MK, Kav NN (2009) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in canola (Brassica napus L.) in response to fungal pathogens and hormone treatments. BMC Plant Biol 9:68
Yu S, Ligang C, Liping Z, Diqiu Y (2010) Overexpression of OsWRKY72 gene interferes in the abscisic acid signal and auxin transport pathway of Arabidopsis. J Biosci 35:459–471
Zhang ZL, Xie Z, Zou X, Casaretto J, Ho TH, Shen QJ (2004) A rice WRKY gene encodes a transcriptional repressor of the gibberellin signaling pathway in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 134:1500–1513
Zhang ZL, Shin M, Zou X, Huang J, Ho TH, Shen QJ (2009) A negative regulator encoded by a rice WRKY gene represses both abscisic acid and gibberellins signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Mol Biol 70:139–151
Zhang Y, Su J, Duan S, Ao Y, Dai J, Liu J, Wang P, Li Y, Liu B, Feng D, Wang J, Wang H (2011) A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 7:30
Zhou QY, Tian AG, Zou HF, Xie ZM, Lei G, Huang J, Wang CM, Wang HW, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008) Soybean WRKY-type transcription genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21 and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6(5):486–503
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant PJ01087001 from the National Institute of Agricultural Sciences and Grant PJ01109104 from the Next-Generation BioGreen21 Program to Dr. Duk-Ju Hwang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by H. S. Judelson.
S.-H. Hwang and S. I. Kwon contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, SH., Kwon, S.I., Jang, JY. et al. OsWRKY51, a rice transcription factor, functions as a positive regulator in defense response against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae . Plant Cell Rep 35, 1975–1985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2012-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2012-0