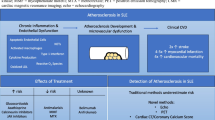
Abstract
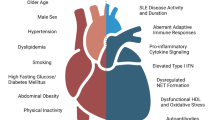
Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by microvascular injury and diffuse fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. While macrovascular disease and higher risk for cardiovascular events are well documented in other systemic rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, the presence and extent of atherosclerosis among patients with SSc is yet to be established. Primary cardiac involvement, due to impairment of coronary microvascular circulation and myocardial fibrosis, considerably affects prognosis and life expectancy of individuals with SSc, representing one of the leading causes of death in this population. On the other hand the existence and prevalence of atherosclerotic coronary disease remains an issue of debate as studies comparing structural and morphological markers of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events between SSc patients and the general population have yielded controversial results. The aim of this review is to summarize recent literature about the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in SSc, review the surrogate markers of CVD that have been evaluated and examine whether common pathogenic mechanisms exist between SSc and macrovascular disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes J, Mayes MD (2012) Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis: incidence, prevalence, survival, risk factors, malignancy, and environmental triggers. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24:165–170
Chifflot H et al (2008) Incidence and prevalence of systemic sclerosis: a systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:223–235
Gabrielli A et al (2009) Scleroderma. N Engl J Med 360:1989–2003
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Karvounis H, Settas L, Kitas GD (2012) Systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary hypertension: unique characteristics and future treatment targets. Curr Pharm Des 18:1457–1464
Cannarile F et al (2015) Cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Ann Transl Med 3:8
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD (2011) Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int 31(11):1409–1417
Sherer Y, Shoenfeld Y (2006) Mechanisms of disease: atherosclerosis in autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2:99–106
Kitas GD, Gabriel SE (2011) Cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art and future perspectives. Ann Rheum Dis 70:8–14
Hollan I et al (2013) Cardiovascular disease in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev 12:1004–1015
Nurmohamed MT, Heslinga M, Kitas GD (2015) Cardiovascular comorbidity in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 11:693–704
Gonzalez A, Maradit Kremers H, Crowson CS, Ballman KV, Roger VL, Jacobsen SJ et al (2008) Cardiovascular risk factors confer the same risk for cardiovascular outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients as in non-rheumatoid arthritis patients? Ann Rheum Dis 67:64–69
Zegos T, Kitas G, Dimitroulas T (2016) Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: assessment, management and next steps. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 8:86–101
Faccini A, Kaski JC, Camici PG (2016) Coronary microvascular dysfunction in chronic nflammatory rheumatoid diseases. Eur Heart J 37:1799–1806
Sharma A, Gopalakrishnan D, Kumar R, Vijayvergiya R, Dogra S (2013) Metabolic syndrome in psoriatic arthritis patients: a cross-sectional study. Int J Rheum Dis 16:667–673
Medina G et al (2003) Increased carotid artery intima-media thickness may be associated with stroke in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 62:607–610
Westlake SL, Colebatch AN, Baird J, Kiely P, Quinn M, Choy E et al (2010) The effect of methotrexate on cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:295–307
Sandoo A, van Zanten JJ, Toms TE, Carroll D, Kitas GD (2012) Anti-TNFα therapy transiently improves high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and microvascular endothelial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:127
Kiortsis DN, Mavridis AK, Vasakos S, Nikas SN, Drosos AA (2005) Effects of infliximab treatment on insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 64:765–766
Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Metsios GS, Panoulas VF, Nightingale P, Koutedakis Y, Kitas GD (2012) Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy improves insulin sensitivity in normal-weight but not in obese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R160
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Cocco G, Kitas GD (2012) Adverse cardiovascular effects of antirheumatic drugs: implications for clinical practice and research. Curr Pharm Des 18:1543–1555
Nurmohamed MT, Kitas G (2011) Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes: how does it compare and when does it start? Annals of the rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 70:881–883
Dimitroulas T, Sarafidis P, Roma V, Karagiannopoulou G, Kapoulas S, Dimitroula H et al (2010) Scleroderma renal crisis accompanied by new-onsetpulmonary arterial hypertension: an acute systemic endothelial injury? Casereport and literature. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 9:313–318
Simeón-Aznar CP, Fonollosa-Plá V, Tolosa-Vilella C, Espinosa-Garriga G, Campillo-Grau M, Ramos-Casals M et al Spanish Scleroderma Study Group (SSSG); Autoimmune Diseases Study Group (GEAS); Spanish Society of Internal Medicine (SEMI) (2015) Registry of the Spanish Network for systemic sclerosis: survival, prognostic factors, and causes of death. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e1728
Nussinovitch U, Shoenfeld Y (2011) Atherosclerosis and macrovascular involvement in systemic sclerosis: myth or reality. Autoimmun Rev 10:259–266
Psarras A et al (2014) Giant cell arteritis and systemic sclerosis: a rare overlap syndrome. Rheumatol Rep 6:1
Hupp SL (1989) Giant cell arteritis associated with progressive systemic sclerosis. J Clin Neuroophthalmol 9:126–130
Jacobsen S et al (1998) Mortality and causes of death of 344 Danish patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Br J Rheumatol 37:750–755
Hesselstrand R et al (1998) Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 57:682–686
Tyndall AJ et al (2010) Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1809–1815
Dave AJ et al (2014) Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in hospitalized patients with systemic sclerosis: higher mortality than patients with lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 66:323–327
Man A et al (2013) The risk of cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1188–1193
Ngian GS et al (2012) Prevalence of coronary heart disease and cardiovascular risk factors in a national cross-sectional cohort study of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1980–1983
Ngian GS et al (2011) Cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis–an emerging association? Arthritis Res Ther 13:237
Aviña-Zubieta JA, Man A, Yurkovich M, Huang K, Sayre EC, Choi HK (2016) Early cardiovascular disease after the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis. Am J Med 129:324–331
D’Angelo WA et al (1969) Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am J Med 46:428–440
Youssef P et al (1995) Limited scleroderma is associated with increased prevalence of macrovascular disease. J Rheumatol 22:469–472
Komocsi A et al (2010) Overlap of coronary disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:202–205
Derk CT, Jimenez SA (2007) Acute myocardial infarction in systemic sclerosis patients: a case series. Clin Rheumatol 26:965–968
Khurma V et al (2008) A pilot study of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis: coronary artery calcification in cases and controls. Arthritis Rheum 59:591–597
Tarek G et al (2006) Coronary angiographic findings in asymptomatic systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 25:487–490
Lekakis J et al (1998) Short-term estrogen administration improves abnormal endothelial function in women with systemic sclerosis and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Am Heart J 136:905–912
Sherer Y et al (2007) Early atherosclerosis and autoantibodies to heat-shock proteins and oxidized LDL in systemic sclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:259–267
Bartoli F et al (2007) Angiotensin-converting enzyme I/D polymorphism and macrovascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:772–775
Bartoli F et al (2007) Flow-mediated vasodilation and carotid intima-media thickness in systemic sclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:283–290
Kaloudi O et al (2007) Circulating levels of Nepsilon-(carboxymethyl)lysine are increased in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:412–416
Kumar U, Verma N, Kumar AK, Hari S, Yadav R, Sreenivas V et al (2010) Endothelial dysfunction in Indian patients with systemic sclerosis[abstract]. Ann Rheum Dis 69(Suppl 3):692
Tsifetaki N et al (2010) Subclinical atherosclerosis in scleroderma patients. Scand J Rheumatol 39:326–329
Hettema ME, Zhang D, de Leeuw K, Stienstra Y, Smit AJ, Kallenberg CG, Bootsma H (2008) Early atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis and its relation to disease or traditional risk factors. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R49
Roustit M et al (2008) Discrepancy between simultaneous digital skin microvascular and brachial artery macrovascular post-occlusive hyperemia in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 35:1576–1583
Piccione MC et al (2011) Early identification of vascular damage in patients with systemic sclerosis. Angiology 62:338–343
Liu J et al (2011) Preferential macrovasculopathy in systemic sclerosis detected by regional pulse wave velocity from wave intensity analysis: comparisons of local and regional arterial stiffness parameters in cases and controls. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:579–587
Ho M et al (2000) Macrovascular disease and systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 59:39–43
Schiopu E et al (2014) Prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis is increased in systemic sclerosis and is associated with serum proteins: a cross-sectional, controlled study of carotid ultrasound. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:704–713
Ozen G, Inanc N, Unal AU, Korkmaz F, Sunbul M, Ozmen M et al (2016) Subclinical Atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis: not less frequent than rheumatoid arthritis and not detected with cardiovascular risk indices. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2016 Feb 11 [Epub ahead of print]
Szucs G et al (2007) Endothelial dysfunction precedes atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis–relevance for prevention of vascular complications. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:759–762
Rollando D et al (2010) Brachial artery endothelial-dependent flow-mediated dilation identifies early-stage endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis and correlates with nailfold microvascular impairment. J Rheumatol 37:1168–1173
Stucker M et al (2000) Macroangiopathy of the upper extremities in progressive systemic sclerosis. Eur J Med Res 5:295–302
Trostle DC et al (1988) Renal vascular histology and morphometry in systemic sclerosis. A case-control autopsy study. Arthritis Rheum 31:393–400
Stafford L et al (1998) Distribution of macrovascular disease in scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis 57:476–479
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Karvounis H, Garyfallos A, Settas L, Kitas GD (2014) Micro- and macro-vascular treatment targets in scleroderma heart disease. Curr Pharm 20:536–544
Zakopoulos NA et al (2003) Systemic sclerosis is not associated with clinical or ambulatory blood pressure. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21:199–204
Zeng Y et al (2012) Macrovascular involvement in systemic sclerosis: evidence of correlation with disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30(2 Suppl 71):S76–S80
Lippi G et al (2006) Lipoprotein[a] and the lipid profile in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin ChimActa 364(1–2):345–348
Borba EF et al (2005) Lipoprotein profile in limited systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Int 25:379–383
Abraham DJ, Distler O (2007) How does endothelial cell injury start? The role of endothelin in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 9(Suppl 2):S2
Abraham DJ, Krieg T, Distler O (2009) Overview of pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford)48(Suppl 3):iii3-7
Assaly R et al (2001) Initial evidence of endothelial cell apoptosis as a mechanism of systemic capillary leak syndrome. Chest 120:1301–1308
Muro Y et al (2009) An evaluation of the efficacy of the toe brachial index measuring vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis and other connective tissue diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27(3 Suppl 54):26–31
Sgonc R et al (2000) Endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis is induced by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity via CD95. Arthritis Rheum 43:2550–2562
Fernández-Codina A, Simeón-Aznar CP, Pinal-Fernandez I, Rodríguez-Palomares J, Pizzi MN, Hidalgo CE (2015) Cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis: differences between clinical subsets and influence on survival. Rheumatol Int 2015 Oct 25 [Epub ahead of print]
Muresan L, Petcu A, Pamfil C, Muresan C, Rinzis M, Mada RO (2016) Cardiovascular profiles of scleroderma patients arrhythmias and conduction disorders. Acta Reumatol Port 41:26–39
Cannarile F, Valentini V, Mirabelli G, Alunno A, Terenzi R, Luccioli F (2015) Cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Ann Transl Med 3:8
Fernandes F et al (2003) Cardiac remodeling in patients with systemic sclerosis with no signs or symptoms of heart failure: an endomyocardial biopsy study. J Card Fail 9:311–317
Lekakis J, Mavrikakis M, Emmanuel M, Prassopoulos V, Papazoglou S, Papamichael C et al (1997) Cold-induced coronary Raynaud’s phenomenon in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 16:135–140
Gustafsson R, Kazzam E, Mannting F, Waldenström A, Hällgren R (1989) Cold-induced reversible myocardial ischaemia in systemic sclerosis. The Lancet 334:475–479
Long A, Duffy G, Bresnihan B (1986) Reversible myocardial perfusion defects during cold challenge in scleroderma. Rheumatology 25:158–161
Mueller KA, Mueller II, Eppler D, Zuern CS, Seizer P, Kramer U (2015) Clinical and histopathological features of patients with systemic sclerosis undergoing endomyocardial biopsy. PLoS ONE 10:e0126707
Kahan A, Nitenberg A, Foult JM, Amor B, Menkes CJ, Devaux JY et al (1985) Decreased coronary reserve in primary scleroderma myocardial disease. Arthritis Rheum 28:637–646
Follansbee WP, Curtiss EI, Medsger TA Jr, Steen VD, Uretsky BF, Owens GR (1984) Rodnan GP (1984) Physiologic abnormalities of cardiac function in progressive systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. NEJM 310:142–148
Desai CS, Lee DC, Shah SJ (2011) Systemic sclerosis and the heart: current diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:545–554
Can I, Onat AM, Aytemir K, Akdogan A, Ureten K, Kiraz S et al (2009) Detecting subclinical biventricular impairment in scleroderma patients by use of pulsed-wave tissue Doppler imaging. Tex Heart Inst J 1:36
Schattke S, Knebel F, Grohmann A, Dreger H, Kmezik F, Riemekasten G et al (2010) Early right ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with systemic sclerosis without pulmonary hypertension: a Doppler Tissue and Speckle Tracking echocardiography study. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 8:1
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Papadopoulou K, Karvounis H, Dimitroula H, Koliakos G et al (2010) Early detection of cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis assessed by tissue-Doppler echocardiography: relationship with neurohormonal activation and endothelial dysfunction. J Rheumatol 37:993–999
Mavrogeni S, Sfikakis PP, Dimitroulas T, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Karabela G, Katsifis G et al (2015) Imaging patterns of cardiovascular involvement in mixed connective tissue disease evaluated by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 4:111–116
Barison A et al (2015) Early myocardial and skeletal muscle interstitial remodelling in systemic sclerosis: insights from extracellular volume quantification using cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16:74–80
Ntusi NA, Piechnik SK, Francis JM, Ferreira VM, Rai AB, Matthews PM et al (2014) Subclinical myocardial inflammation and diffuse fibrosis are common in systemic sclerosis—a clinical study using myocardial T1-mapping and extracellular volume quantification. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 16:21
Mavrogeni S, Bratis K, Karabela G et al (2015) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging clarifies cardiac pathophysiology in early, asymptomatic diffuse systemic sclerosis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 14:29–36
Mavrogeni SI, Kitas GD, Dimitroulas T, Sfikakis PP, Seo P, Gabriel S et al (2016) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in rheumatology: current status and recommendations for use. Int J Cardiol 217:135–148
Hachulla E, Gressin V, Guillevin L et al (2005) Early detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: a French nationwide prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum 52:3792–3800
Hunzelmann N, Genth E, Krieg T et al (2008) The registry of the German Network for Systemic Scleroderma: frequency of disease subsets and patterns of organ involvement. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:1185–1192
Avouac J, Airò P, Meune C et al (2010) Prevalence of pulmonary hyper- tension in systemic sclerosis in European Caucasians and metaana- lysis of 5 studies. J Rheumatol 37:2290–2298
Phung S, Strange G, Chung LP et al (2009) Prevalence of pulmonary arterial hypertension in an Australian scleroderma population: screening allows for earlier diagnosis. Intern Med J 39:682–691
Sanz J, Kariisa M, Dellegrottaglie S, Prat-Gonzalez S, Garcia MJ, Fuster V, Rajagopalan S (2009) Evaluation of pulmonary artery stiffness in pulmonary hypertension with cardiac magnetic resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 2:286–295
Fisher MR, Mathai SC, Champion HC et al (2006) Clinical differences between idiopathic and scleroderma-related pulmonary hypertension. Arthritis Rheum 54:3043–3050
Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Papadopoulou K et al (2010) Left atrial volume and N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide are associated with elevated pulmonary artery pressure in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 29:957–964
Tongers J, Schwerdtfeger B, Klein G et al (2007) Incidence and clinical relevance of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias in pulmonary hypertension. Am Heart J 153:127–132
Mathai SC, Bueso M, Hummers LK et al (2010) Disproportionate elevation of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in scleroderma-related pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 35:95–104
Allanore Y, Meune C, Vonk MC et al (2010) Prevalence and factors associated with left ventricular dysfunction in the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research group (EUSTAR) database of systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 69:218–221
Aversa A, Greco E, Bruzziches R, Pili M, Rosano G, Spera G (2007) Relation-ship between chronic tadalafil administration and improvement of endothelial function in men with erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Int J Impot Res 19:200–207
Koka S, Das A, Salloum FN, Kukreja RC (2013) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil attenuates oxidative stress and protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic mice. Free Radic Biol Med 60:80–88
Varma A, Das A, Hoke NN, Durrant DE, Salloum FN, Kukreja RC (2012) Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects of tadalafil in diabetic mice. PLoS One7:e45243
Metsios G, Lahart IM (2015) Exercise as medicine in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediterr J Rheumatol 26:54–61
John H, Carroll D, Kitas GD (2011) Cardiovascular education for people with rheumatoid arthritis: what can existing patient education programmes teach us? Rheumatology (Oxford) 50:1751–1759
Domsic RT, Dezfulian C, Shoushtari A, Ivanco D, Kenny E, Kwoh CK et al (2014) Endothelial dysfunction is present only in the microvasculature and microcirculation of early diffuse systemics clerosis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(6 Suppl 86):S-154-60
Turiel M, Gianturco L, Ricci C, Sarzi-Puttini P, Tomasoni L, Colonna Vde G et al (2013) Silent cardiovascular involvement in patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis: a controlled cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2013(65):274–280
Authors contributions
Review concept and design: Antonios Psarras, Theodoros Dimitroulas. Drafting of the manuscript: Antonios Psarras, Stergios Soulaidopoulos. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: George Kitas, Alexandros Garyfallos, Theodoros Dimitroulas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Psarras, A., Soulaidopoulos, S., Garyfallos, A. et al. A critical view on cardiovascular risk in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Int 37, 85–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3530-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3530-3