Abstract
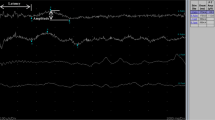
This study was performed to determine the utility of sympathetic skin response (SSR) in evaluating the sympathetic function and to follow up the effects of sympathetic blockade in reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD). Thirty patients having RSD with upper extremity involvement were randomly divided into two groups. Besides medical therapy and exercise, physical therapy agents were applied to both the groups. In addition to this treatment protocol, stellar ganglion blockade was done by diadynamic current in Group II. The normal sides of the patients were used for the control group. SSRs were measured in all the patients before and after the therapy. The amplitude was found to be increased and the latency was found to be decreased in the affected side in both the groups before the therapy. After the therapy, the amplitude was decreased and latency was increased in both the groups. But, the differences in amplitude (P=0.001) and latency (P=0.002) before and after the therapy were significantly higher in Group II. (Before the treatment, SSRs were significantly different between the normal and the affected sides in both the groups. The observed change in SSRs after the treatment was higher in Group II.) It was concluded that, SSR can be a useful and noninvasive method in diagnosing the sympathetic dysfunction in RSD and can be used for evaluating the response to sympathetic blockade and other treatment modalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doury P, Dequeker J (1994) Regional bone disease: algodystrophy/reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. In: Klippel JH, Dieppe RA (eds) Rheumatology. Mosby, St Louis, pp. 7.38.1–7.38.7
Kozin F (1993) Painful shoulder and the reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. In: McCarty DJ, Koopman WJ (eds) Arthritis and allied conditions, 12th edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp. 1663–1676
Gellman H (1992) Reflex sympathetic dysrophy. In: Nickel VL, Botte MJ (eds) Orthopaedic rehabilitation, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 645–657
Kozin F (1992) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome: a review. Clin Exp Rheumatol 10:401–409
Gordon N (1996) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (Abst.). Brain Dev 18(4):257–262
Lankford LL (1990) Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. In: Hunter JM, Schneider LH, Mackin EJ et al (eds) Rehabilitation of the hand, 3rd edn. The CV Mosby Company, St Louis, pp 763–786
Clinchot DM, Lorch F (1996) Sympathetic skin response in patients with reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 75:252–256
Shahani BT, Days TS, Cros D et al (1990) R–R interval variation and the sympathetic skin response in the assesment of autonomic function in peripheral neuropathy. Arch Neurol 47:659–664
Ide J, Yamaga M, Kıtamura T et al (1997) Quantitative evaluation of sympathetic nervous system dysfunction in patients with reflex sympathetic dystrophy. J Hand Surg 22B(1):102–106
Drory VE, Korczyn AD (1995) The sympathetic skin response in reflex sympathetic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 128:92–95
Oh SJ (1993) Uncommon nerve conduction studies. Clinical electromyography, vol. 11, 2nd edn. Willams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp. 267–270
Ba-M’Hamed S, Clancia B, Delerm B et al (1985) Influence of skin temperature on latency and amplitude of skin potential responses in the cat. Biol Psychol 22:59–67
Aisen ML, Stallman J, Aisen PS (1995) The sympathetic skin response in the shoulder–hand syndrome complicating tetraplegie. Paraplegia 33:602–605
Rommel O, Tegenthoff M, Pern U et al (1995) Sympathetic skin response in patients with reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Clin Auton Res 5:205–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolel, K., Hizmetli, S. & Akyüz, A. Sympathetic skin responses in reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Rheumatol Int 26, 788–791 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-005-0081-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-005-0081-4