Abstract
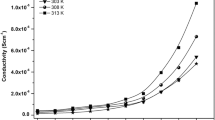
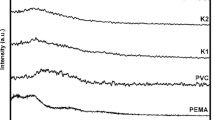
Conducting polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) as a host polymer matrix and polyionic liquid (PIL) hydrophilic/hydrophobic were prepared by solution casting technique and characterized by FTIR, scanning electron microscope (SEM), mechanical, conductivity, dielectric spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. It was found that the presence of PIL affected positively both mechanical and electrical properties of the polymer electrolytes. Polymer electrolytes with PIL-dispersion give the best tensile strength compared to those with PIL-solid. From the results of mechanical properties, it is concluded that PIL-dispersion can act as a plasticizer, whereas PIL-solid can act as traditional filler. The addition of PIL-dispersion significantly increased the permittivity ε′ and dielectric loss ε″ and improved the ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolytes compared to PIL-solid. The ionic conductivity of these polymer electrolytes is greatly increased with doping of PIL-dispersion owing to their strong plasticizing effect. The data of electric modulus M″ are analyzed in terms of Havriliak–Negami function through three relaxation mechanisms. In the temperature range from 50 to 150 °C, three distinct relaxation processes, namely α, αβ and β relaxations were detected in all samples. Polymer electrolytes based on hydrophilic PIL showing ionic conductivities in the range of 10−9–10−5 S/cm are good candidates in construction of electrochemical cells, whereas those based on hydrophobic PIL are suitable for use in liquid membranes.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freemantle M (2009) Introduction to ionic liquids, 1st edn. Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) Publishing, Cambridge
Matsumoto H, Sakaebe H, Tatsumi K, Kikuta M, Ishiko E, Kono M (2006) Fast cycling of Li/LiCoO2 cell with low-viscosity ionic liquids based on bis (fluorosulfonyl) imide [FSI]. J Power Sources 160:1308–1313
Gorlov M, Kloo L (2008) Ionic liquid electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dalton Trans 20:2655–2666
Endres F, El Abedin SZ (2006) Air and water stable ionic liquids in physical chemistry. Phys Chem Phys Chem 8:2101–2116
Yuan J, Antonietti M (2011) Poly(ionic liquid)s: polymers expanding classical property profiles. Polymer 52:1469–1482
Jitendra T, Khushbu K, Balasubramanian KR (2016) The dielectric properties and charge transport mechanism of p-conjugated segments decorated with intrinsic conducting polymer. RSC Adv 6:69733–69742
Sengwa RJ, Sankhla SJ (2007) Dielectric dispersion study of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)–polar solvent solutions in the frequency range 20 Hz–1 MHz. Macromol Sci Part B Phys 46:717–747
Liew C, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2014) Good prospect of ionic liquid based-poly(vinyl alcohol) polymer electrolytes for supercapacitors with excellent electrical, electrochemical and thermal properties. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:2953–2963
Lizhen F, Zhimin D, Ce-Wen N, Ming L (2002) Thermal, electrical and mechanical properties of plasticized polymer electrolytes based on PEO/P(VDF-HFP) blends. Electrochim Acta 48:205–220
Zhenglin T, Li Q, Guitian G (2008) Dynamic mechanical properties of gel polymer electrolytes containing ionic liquid. Solid State Ionics 179:1880–1884
Angulakshmi N, Thomas S, Nahm KS, Manuel Stephan A, Nimma Elizabeth R (2011) Electrochemical and mechanical properties of nanochitin-incorporated PVDF-HFP-based polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Ionics 17:407–414
Gray FM (1991) Fundamentals of technological applications. Wiley, London, pp 149–179
Rajendran S, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2004) Investigations on the effect of various plasticizers in PVA-PMMA solid polymer blend electrolytes. Mater Lett 58:641–649
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2006) Ac impedance, DSC and FT-IR investigations on (x) PVAc-(1 − x) PVdF blends with LiClO4. Mater Chem Phys 98:55–61
West AR (1999) Electrical properties: basic solid state chemistry. Wiley, West Sussex, pp 321–361
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamwa J, Hattori T (2006) Conductivity and thermal studies of blend polymer electrolytes based on PVAc–PMMA. Solid State Ion 177:2679–2682
Sivadevi S, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Sanjeeviraja C, Nithya H, Iwai Y, Kawamura J (2015) Proton- conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA-PAN doped with ammonium thiocyanate. Ionics 21:1017–1029
Xi J, Li X, Tang X, Zhu W, Chen L (2006) PVDF–PEO blends based microporous polymer electrolyte: effect of PEO on pore configurations and ionic conductivity. J Power Sources 157:501–506
Lee L, Park S, Kim S (2013) Effect of nano-sized barium titanate addition on PEO/PVDF blend-based composite polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion 234:19–24
Zhang Y, Lee S, Reddy K, Gopalan A, Lee K (2007) Synthesis and characterization of core-shell SiO2 nanoparticles/poly(3-aminophenylboronic acid) composites. J Appl Polym Sci 104:2743–2750
Li Z, Ye M, Han A, Du H (2016) Preparation, characterization and microwave absorption properties of NiFe2O4 and its composites with conductive polymer. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:1031–1043
Tayfun U, Dogan M (2016) Improving the dyeability of poly(lactic acid) fiber using organoclay during melt spinning. Polym Bull 73:1581–1593
Xin H, Xue T, Xu C (2015) Conductive properties and mechanisms of different polymers doped by carbon nanotube/polypyrrole 1D hybrid nanotubes. RSC Adv 5:61383–61389
Reddy KR, Sin BC, Ryu KS, Kim JC, Chung H, Lee Y (2009) Conducting polymer functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes with noble metal nanoparticles: synthesis, morphological characteristics and electrical properties. Synth Met 159:595–603
Hassan M, Haque E, Faisal SN, Ghasemi S, Minett A, Gomes VG (2014) Hierarchical assembly of graphene/polyaniline nanostructures to synthesize free-standing supercapacitor electrode. Compos Sci Tech 98:1–8
Reddy KR, Lee KP, Gopalan AI (2007) Self-assembly directed synthesis of poly(orthotoluidine)- metal (gold and palladium) composite nanospheres. J Nanosci Nanotech 7:3117–3125
Yi Yang, Sun N, Sun P, Zheng L (2016) Effect of the bis-imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid) on the Microstructure and the properties of AAEMs based on polyvinyl alcohol. RSC Adv 6:25311
Rozik N, Antonietti M, Yuan J, Tauer K (2013) Polymerized ionic liquid as stabilizer in aqueous emulsion polymerization enables a hydrophilic-hydrophobic transition during film formation. Macromol Rapid Commun 34:665–671
Rozik N, Abd El-Messieh S L (2017) Polyionic liquid incorporated PS/PANI-based polymer electrolytes: electrical and dielectric properties. Polym Bull. doi:10.1007/s00289-017-1904-7
Pimentel GC, McClellan AL (1960) The hydrogen bond. Freeman, San Francisco, pp 348–363
Çavuş S, Durgun E (2016) Poly(vinyl alcohol) based polymer gel electrolytes: investigation on their conductivity and characterization. Acta Physica Polonica A 129:621–624
Kumar R, Subramania A, Sundaram NTK, Kumar GV, Baskaran I (2007) Effect of MgO nanoparticles on ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte. J Membr Sci 300:104–110
Saroj AI, Singh RK (2012) Thermal, dielectric and conductivity studies on PVA/Ionic liquid [EMIM][EtSO4] based polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem Solids 73:162–168
Every H, Bishop AG, Forsyth M, MacFarlane DR (2000) Ion diffusion in molten salt mixtures. Electrochim Acta 45:1279–1284
Anderson JL, Armstrong DW, Wei G (2006) Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. Anal Chem 78:2893–2902
Nassar MA, Ward AA, Abdel Baseer R (2013) Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline nanocomposites. KGK-kautschuk Gummi Kunststoffe 66:39–46
Bhargav PB, Mohan Sharma VM et al (2009) Investigations on electrical properties of (PVA:NaF) polymer electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. Current Appl Phys 9:165–171
Kremer F, Arntt M (1997) Dielectric spectroscopy of polymeric materials. American chemical Society, Washington DC
El-Houssiny AS, Ward AAM, Mansour SH, Abd- El- Messieh SL (2012) Biodegradable blends based on polyvinyl pyrrolidone for insulation purposes. J Appl Polym Sci 124:3879–3891
Havriliak S, Negami S (1966) A complex plane analysis of α-dispersions in some polymer systems. J Polym Sci Part C Poly Symp 14:99–117
Mc Crum NG, Read BE, Williams G (1967) Anelastic and dielectric effects in polymeric solids. Wiley, London
von Hippel AR (1995) Dielectrics and waves. Artech House, Boston
Wilkes JS, Levisky JA, Wilson RA, Hurrey CL (1982) Dialkyimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: a new class of room- temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorg Chem 21:1263–1264
Boroglu, Celik SU, Bozkurt A, Boz I (2103) Proton-conducting blend membranes of crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) sulfosuccinic acid ester and poly(1-vinyl-1,2,4-triazole) for high temperature fuel cells. Polym Eng Sci 53:153–158
Ayesh AI, Mohsin MA, Haik MY, Haik Y (2012) Investigations on electrical properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) doped with 1-methyl-3-n-decyl-imidazolium bromide ionic liquid. Curr Appl Phys 12:1223–1228
Thayumanasundaram S, Rangasamy VS, Greef ND, Seo JW, Locquet JP (2015) Hybrid polymer electrolytes based on a poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) blend and a pyrrolidinium-based ionic liquid for lithium-ion batteries. Eur J Inorg Chem 7:1290–1299
Yang JM, Chiang CY, Wang HZ, Yang CC (2009) Two step modification of poly(vinyl alcohol) by UV radiation with 2 -hydroxyl ethyl methacrylate and sol-gel process for the application of polymer electrolyte membrane. J Membr Sci 341:186–194
Acknowledgements
Nehad N. Rozik would like to thank Dr J. Y. Yuan for introducing the synthesis of PIL dispersion and Dr. K. Tauer for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozik, N.N., Ward, A.A. A novel approach on poly(ionic liquid)-based poly(vinyl alcohol) as a hydrophilic/hydrophobic conductive polymer electrolytes. Polym. Bull. 75, 267–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2027-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2027-x