Abstract
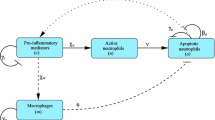
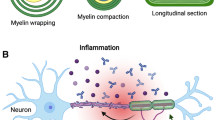
In this paper we derive a reaction-diffusion-chemotaxis model for the dynamics of multiple sclerosis. We focus on the early inflammatory phase of the disease characterized by activated local microglia, with the recruitment of a systemically activated immune response, and by oligodendrocyte apoptosis. The model consists of three equations describing the evolution of macrophages, cytokine and apoptotic oligodendrocytes. The main driving mechanism is the chemotactic motion of macrophages in response to a chemical gradient provided by the cytokines. Our model generalizes the system proposed by Calvez and Khonsari (Math Comput Model 47(7–8):726–742, 2008) and Khonsari and Calvez (PLos ONE 2(1):e150, 2007) to describe Baló’s sclerosis, a rare and aggressive form of multiple sclerosis. We use a combination of analytical and numerical approaches to show the formation of different demyelinating patterns. In particular, a Turing instability analysis demonstrates the existence of a threshold value for the chemotactic coefficient above which stationary structures develop. In the case of subcritical transition to the patterned state, the numerical investigations performed on a 1-dimensional domain show the existence, far from the bifurcation, of complex spatio-temporal dynamics coexisting with the Turing pattern. On a 2-dimensional domain the proposed model supports the emergence of different demyelination patterns: localized areas of apoptotic oligodendrocytes, which closely fit existing MRI findings on the active MS lesion during acute relapses; concentric rings, typical of Baló’s sclerosis; small clusters of activated microglia in absence of oligodendrocytes apoptosis, observed in the pathology of preactive lesions.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banati RB, Newcombe J, Gunn RN, Cagnin A, Turkheimer F, Heppner F, Price G, Wegner F, Giovannoni G, Miller DH, Perkin GD, Smith T, Hewson AK, Bydder G, Kreutzberg GW, Jones T, Cuzner ML, Myers R (2000) The peripheral benzodiazepine binding site in the brain in multiple sclerosis. Brain 123(11):2321–2337
Barnett MH, Parratt JDE, Pollard JD, Prineas JW (2009) MS: is it one disease? Int MS J 16(2):57–65
Barnett M, Prineas J (2004) Relapsing and remitting multiple sclerosis: pathology of the newly forming lesion. Ann Neurol 55(4):458–468
Barresi R, Bilotta E, Gargano F, Lombardo MC, Pantano P, Sammartino M (2016) Wavefront invasion for a chemotaxis model of multiple sclerosis. Ricerche di Matematica 65(2):423–434
Beaudoin A, Huberson S, Rivoalen E (2003) Simulation of anisotropic diffusion by means of a diffusion velocity method. J Comput Phys 186(1):122–135
Bilotta E, Pantano P, Vena S (2011) Artificial micro-worlds part I: a new approach for studying life-like phenomena. Int J Bifurc Chaos 21(2):373–398
Bilotta E, Pantano P (2005) Emergent patterning phenomena in 2D cellular automata. Artif Life 11(3):339–362
Bilotta E, Pantano P (2011) Artificial micro-worlds part II: cellular automata growth dynamics. Int J Bifurc Chaos 21(3):619–645
Boche D, Perry V, Nicoll J (2013) Review: activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39(1):3–18
Bø L, Esiri M, Evangelou N, Kuhlmann T (2013) Demyelination and remyelination in multiple sclerosis, vol 290. Springer US, pp XIV
Bozzini B, Gambino G, Lacitignola D, Lupo S, Sammartino M, Sgura I (2015) Weakly nonlinear analysis of Turing patterns in a morphochemical model for metal growth. Comput Math Appl 70(8):1948–1969
Breij E, Brink B, Veerhuis R, Van Den Berg C, Vloet R, Yan R, Dijkstra C, Van Der Valk P, Bø L (2008) Homogeneity of active demyelinating lesions in established multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 63(1):16–25
Burger M, Di Francesco M, Dolak-Struss Y (2006) The Keller-Segel model for chemotaxis with prevention of overcrowding: linear vs. nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J Math Anal 38(4):1288–1315
Calvez V, Corrias L (2008) The parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel model in \(\mathbb{R}^2\). Commun Math Sci 6(2):417–447
Calvez V, Khonsari R (2008) Mathematical description of concentric demyelination in the human brain: self-organization models, from Liesegang rings to chemotaxis. Math Comput Model 47(7–8):726–742
Cerasa A, Bilotta E, Augimeri A, Cherubini A, Pantano P, Zito G, Lanza P, Valentino P, Gioia M, Quattrone A (2012) A cellular neural network methodology for the automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neurosci Methods 203(1):193–199
Chalmers A, Cohen A, Bursill C, Myerscough M (2015) Bifurcation and dynamics in a mathematical model of early atherosclerosis: how acute inflammation drives lesion development. J Math Biol 71(6–7):1451–1480
Chen CJ, Chu NS, Lu CS, Sung CY (1999) Serial magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Balo’s concentric sclerosis: natural history of lesion development. Ann Neurol 46(4):651–656
Chen X, Hao J, Wang X, Wu Y, Zhang Y (2014) Stability of spiky solution of Keller-Segel’s minimal chemotaxis model. J Differ Equ 257(9):3102–3134
Chertock A, Kurganov A (2006) On a practical implementation of particle methods. Appl Numer Math 56(10-11 SPEC. ISS.):1418–1431
Childress S, Percus J (1981) Nonlinear aspects of chemotaxis. Math Biosci 56(3–4):217–237
Cruywagen G, Maini P, Murray J (1997) Biological pattern formation on two-dimensional spatial domains: a nonlinear bifurcation analysis. SIAM J Appl Math 57(6):1485–1509
De Groot C, Bergers E, Kamphorst W, Ravid R, Polman C, Barkhof F, Van Der Valk P (2001) Post-mortem mri-guided sampling of multiple sclerosis brain lesions: increased yield of active demyelinating and (p)reactive lesions. Brain 124(8):1635–1645
Degond P, Mustieles FJ (1990) A deterministic approximation of diffusion equations using particles. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 11(2):293–310
Dolak Y, Schmeiser C (2006) The Keller-Segel model with logistic sensitivity function and small diffusivity. SIAM J Appl Math 66(1):286–308
Edelstein-Keshet L, Spiros A (2002) Exploring the formation of Alzheimer’s disease senile plaques in silico. J Theor Biol 216(3):301–326
El Khatib N, Genieys S, Kazmierczak B, Volpert V (2012) Reaction-diffusion model of atherosclerosis development. J Math Biol 65(2):349–374
Fischer M, Wimmer I, Höftberger R, Gerlach S, Haider L, Zrzavy T, Hametner S, Mahad D, Binder C, Krumbholz M, Bauer J, Bradl M, Lassmann H (2013) Disease-specific molecular events in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 136(6):1799–1815
Galiano G, Selgas V (2015) Deterministic particle method approximation of a contact inhibition cross-diffusion problem. Appl Numer Math 95:229–237
Gambino G, Lombardo M, Sammartino M (2009) A velocity-diffusion method for a Lotka-Volterra system with nonlinear cross and self-diffusion. Appl Numer Math 59(5):1059–1074
Gambino G, Lombardo M, Sammartino M (2012) Turing instability and traveling fronts for a nonlinear reaction-diffusion system with cross-diffusion. Math Comput Simul 82(6):1112–1132
Gambino G, Lombardo M, Sammartino M (2013a) Pattern formation driven by cross-diffusion in a \(2\)D domain. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 14(3):1755–1779
Gambino G, Lombardo M, Sammartino M, Sciacca V (2013b) Turing pattern formation in the Brusselator system with nonlinear diffusion. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 88(4):042925
Gambino G, Lombardo M, Sammartino M (2014) Turing instability and pattern formation for the Lengyel-Epstein system with nonlinear diffusion. Acta Applicandae Mathematicae 132(1):283–294
Goodhill G (1997) Diffusion in axon guidance. Eur J Neurosci 9(7):1414–1421
Guttmann C, Ahn S, Hsu L, Kikinis R, Jolesz F (1995) The evolution of multiple sclerosis lesions on serial MR. Am J Neuroradiol 16(7):1481–1491
Herald M (2010) General model of inflammation. Bull Math Biol 72(4):765–779
Hidalgo A, Tello L, Toro E (2014) Numerical and analytical study of an atherosclerosis inflammatory disease model. J Math Biol 68(7):1785–1814
Hillen T, Zielinski J, Painter K (2013) Merging-emerging systems can describe spatio-temporal patterning in a chemotaxis model. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser B 18(10):2513–2536
Hillen T, Painter K (2001) Global existence for a parabolic chemotaxis model with prevention of overcrowding. Adv Appl Math 26(4):280–301
Hillen T, Painter KJ (2009) A user’s guide to PDE models for chemotaxis. J Math Biol 58(1–2):183–217
Hohlfeld R, Wekerle H (2004) Autoimmune concepts of multiple sclerosis as a basis for selective immunotherapy: from pipe dreams to (therapeutic) pipelines. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(SUPPL. 2):14599–14606
Jensen O, Pannbacker V, Mosekilde E, Dewel G, Borckmans P (1994) Localized structures and front propagation in the Lengyel-Epstein model. Phys Rev E 50(2):736–749
Kang K, Kolokolnikov T, Ward M (2007) The stability and dynamics of a spike in the 1D Keller-Segel model. IMA J Appl Math (Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications) 72(2):140–162
Keller E, Segel L (1970) Initiation of slime mold aggregation viewed as an instability. J Theor Biol 26(3):399–415
Keller E, Segel L (1971) Model for chemotaxis. J Theor Biol 30(2):225–234
Khonsari R, Calvez V (2007) The origins of concentric demyelination: self-organization in the human brain. PLos ONE 2(1):e150
Kolokolnikov T, Ward M, Wei J (2014a) The stability of steady-state hot-spot patterns for a reaction-diffusion model of urban crime. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser B 19(5):1373–1410
Kolokolnikov T, Wei J, Alcolado A (2014b) Basic mechanisms driving complex spike dynamics in a chemotaxis model with logistic growth. SIAM J Appl Math 74(5):1375–1396
Kumar R, Clermont G, Vodovotz Y, Chow C (2004) The dynamics of acute inflammation. J Theor Biol 230(2):145–155
Kumar N, Horsthemke W (2010) Turing bifurcation in a reaction-diffusion system with density-dependent dispersal. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 389(9):1812–1818
Kutzelnigg A, Lassmann H (2014) Chapter 2—pathology of multiple sclerosis and related inflammatory demyelinating diseases. In: Goodin DS (ed) Multiple sclerosis and related disorders, Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 122. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 15–58
Lai X, Chen X, Wang M, Qin C, Zhang Y (2016) Existence, uniqueness, and stability of bubble solutions of a chemotaxis model. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser A 36(2):805–832
Lassmann H (2005) Multiple sclerosis pathology: evolution of pathogenetic concepts. Brain Pathol 15(3):217–222
Lassmann H (2011) Review: the architecture of inflammatory demyelinating lesions: implications for studies on pathogenesis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(7):698–710
Lassmann H, Niedobitek G, Aloisi F, Middeldorp J (2011) Epstein-Barr virus in the multiple sclerosis brain: a controversial issue-report on a focused workshop held in the Centre for Brain Research of the Medical University of Vienna, Austria. Brain 134(9):2772–2786
Lassmann H, Van Horssen J (2011) The molecular basis of neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. FEBS Lett 585(23):3715–3723
Lee S, Liu W, Dickson D, Brosnan C, Berman J (1993) Cytokine production by human fetal microglia and astrocytes: differential induction by lipopolysaccharide and il-1\(\beta \). J Immunol 150(7):2659–2667
Luca M, Chavez-Ross A, Edelstein-Keshet L, Mogilner A (2003) Chemotactic signaling, microglia, and Alzheimer’s disease senile plaques: is there a connection? Bull Math Biol 65(4):693–730
Lucchinetti C, Brück W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H (1999) A quantitative analysis of oligodendrocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions. A study of 113 cases. Brain 122(12):2279–2295
Lucchinetti C, Brück W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H (2000) Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann Neurol 47(6):707–717
Ma M, Ou C, Wang ZA (2012) Stationary solutions of a volume-filling chemotaxis model with logistic growth and their stability. SIAM J Appl Math 72(3):740–766
Madzvamuse A, Ndakwo H, Barreira R (2014) Cross-diffusion-driven instability for reaction-diffusion systems: analysis and simulations. J Math Biol 70(4):709–743
Marik C, Felts P, Bauer J, Lassmann H, Smith K (2007) Lesion genesis in a subset of patients with multiple sclerosis: a role for innate immunity? Brain 130(11):2800–2815
Matkowsky B (1970) Nonlinear dynamic stability. A formal theory. SIAM J Appl Math 18(4):872–883
Ma M, Wang ZA (2015) Global bifurcation and stability of steady states for a reaction-diffusion-chemotaxis model with volume-filling effect. Nonlinearity 28(8):2639
Meier D, Guttmann C (2006) MRI time series modeling of MS lesion development. NeuroImage 32(2):531–537
Moghe P, Nelson R, Tranquillo R (1995) Cytokine-stimulated chemotaxis of human neutrophils in a 3-D conjoined fibrin gel assay. J Immunol Methods 180(2):193–211
Mulone G, Straughan B (2009) Nonlinear stability for diffusion models in biology. SIAM J Appl Math 69(6):1739–1758
Murray JD (2007) Mathematical biology, vol II, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Nagaraja S, Wallqvist A, Reifman J, Mitrophanov A (2014) Computational approach to characterize causative factors and molecular indicators of chronic wound inflammation. J Immunol 192(4):1824–1834
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Neuroforum 11(3):95–96
Painter K, Hillen T (2011) Spatio-temporal chaos in a chemotaxis model. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 240(4–5):363–375
Peferoen L, Vogel D, Ummenthum K, Breur M, Heijnen P, Gerritsen W, Peferoen-Baert R, Van Der Valk P, Dijkstra C, Amor S (2015) Activation status of human microglia is dependent on lesion formation stage and remyelination in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74(1):48–63
Penner K, Ermentrout B, Swigon D (2012) Pattern formation in a model of acute inflammation. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 11(2):629–660
Pennisi M, Rajput AM, Toldo L, Pappalardo F (2013) Agent based modeling of treg-teff cross regulation in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. BMC Bioinform 14(16):S9
Ponomarev E, Shriver L, Maresz K, Dittel B (2005) Microglial cell activation and proliferation precedes the onset of CNS autoimmunity. J Neurosci Res 81(3):374–389
Popescu B, Pirko I, Lucchinetti C (2013) Pathology of multiple sclerosis: where do we stand? CONTINUUM Lifelong Learn Neurol 19(4):901–921
Quinlan R, Straughan B (2005) Decay bounds in a model for aggregation of microglia: application to Alzheimer’s disease senile plaques. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 461(2061):2887–2897
Reynolds A, Rubin J, Clermont G, Day J, Vodovotz Y, Bard Ermentrout G (2006) A reduced mathematical model of the acute inflammatory response: I. Derivation of model and analysis of anti-inflammation. J Theor Biol 242(1):220–236
Rodríguez N (2013) On the global well-posedness theory for a class of PDE models for criminal activity. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 260:191–200
Rodriguez N, Bertozzi A (2010) Local existence and uniqueness of solutions to a PDE model for criminal behavior. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 20(SUPPL. 1):1425–1457
Ruiz-Baier R, Tian C (2013) Mathematical analysis and numerical simulation of pattern formation under cross-diffusion. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 14(1):601–612
Sahraian M, Radü E (2008) MRI atlas of MS lesions. Springer, Berlin
Segel LA, Levin SA (1976) Application of nonlinear stability theory to the study of the effects of diffusion on predator-prey interactions. AIP Conf Proc 27(1):123–152
Van Der Valk P, Amor S (2009) Preactive lesions in multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol 22(3):207–213
van Horssen J, Singh S, van der Pol S, Kipp M, Lim J, Peferoen L, Gerritsen W, Kooi EJ, Witte M, Geurts J, de Vries H, Peferoen-Baert R, van den Elsen P, van der Valk P, Amor S (2012) Clusters of activated microglia in normal-appearing white matter show signs of innate immune activation. J Neuroinflamm 9:156
van Noort J, van den Elsen P, van Horssen J, Geurts J, van der Valk P, Amor S (2011) Preactive multiple sclerosis lesions offer novel clues for neuroprotective therapeutic strategies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10(1):68–81
Wang Z, Hillen T (2007) Classical solutions and pattern formation for a volume filling chemotaxis model. Chaos 17(3):037108
Wang X, Xu Q (2013) Spiky and transition layer steady states of chemotaxis systems via global bifurcation and Helly’s compactness theorem. J Math Biol 66(6):1241–1266
Wiendl H, Hohlfeld R (2009) Multiple sclerosis therapeutics: unexpected outcomes clouding undisputed successes. Neurology 72(11):1008–1015
Wollkind DJ, Manoranjan V, Zhang L (1994) Weakly nonlinear stability analyses of prototype reaction-diffusion model equations. SIAM Rev 36(2):176–214
Wrzosek D (2004) Global attractor for a chemotaxis model with prevention of overcrowding. Nonlinear Anal Theory Methods Appl 59(8):1293–1310
Wrzosek D (2006) Long-time behaviour of solutions to a chemotaxis model with volume-filling effect. R Soc Edinb Proc A 136(2):431–444
Wuerfel J, Bellmann-Strobl J, Brunecker P, Aktas O, McFarland H, Villringer A, Zipp F (2004) Changes in cerebral perfusion precede plaque formation in multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal perfusion MRI study. Brain 127(1):111–119
Zheng J (2015) Boundedness of solutions to a quasilinear parabolic-elliptic Keller-Segel system with logistic source. J Differ Equ 259(1):120–140
Zheng P, Mu C, Hu X (2015) Boundedness and blow-up for a chemotaxis system with generalized volume-filling effect and logistic source. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser A 35(5):2299–2323
Acknowledgements
The work of the second author (RB) has been supported by INDAM-GNFM through a Progetto giovani grant. The authors gratefully thank two anonymous reviewers for their suggestions and comments which have significantly helped in improving the presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been partially supported by the GNFM-INDAM.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lombardo, M.C., Barresi, R., Bilotta, E. et al. Demyelination patterns in a mathematical model of multiple sclerosis. J. Math. Biol. 75, 373–417 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-016-1087-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-016-1087-0